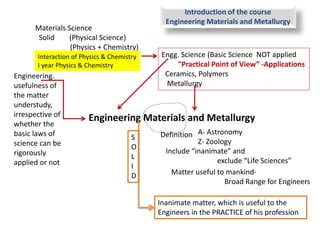
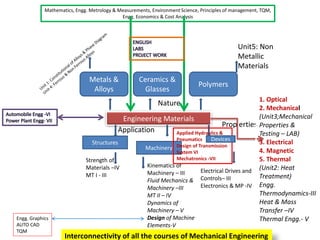
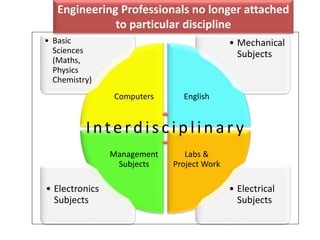
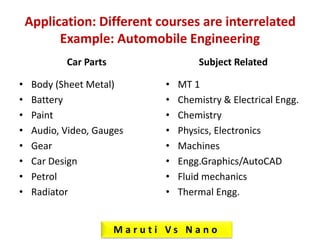
This document provides an overview of the Mechanical Engineering program at Anna University. It discusses the course Engineering Materials and Metallurgy, which covers various engineering materials including metals, alloys, ceramics, polymers, and their structures, properties, and applications. The course also includes units on mechanical properties and testing, heat treatment, and non-metallic materials. The document notes that many courses in the mechanical engineering program are interrelated, such as those involving materials science, strength of materials, machinery, and thermal engineering. It provides the example of how different subjects relate to the engineering of automobiles.