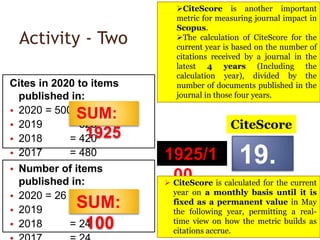
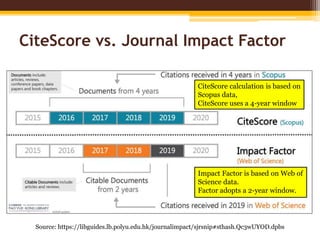
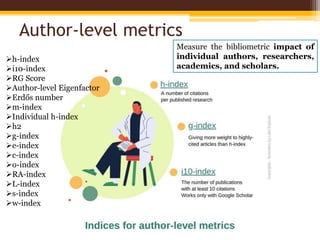
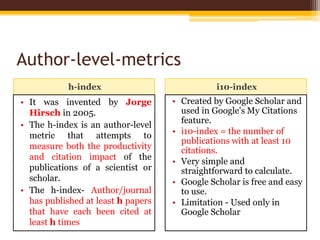
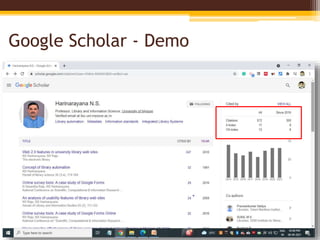
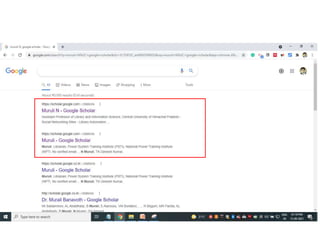
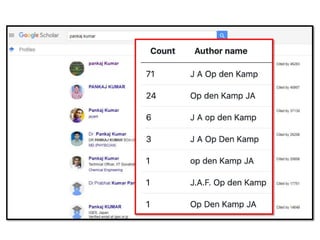
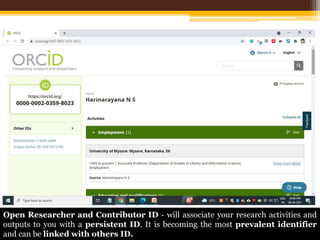
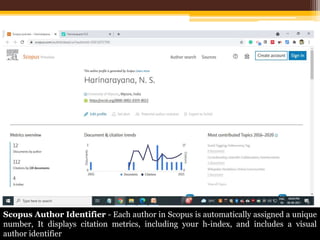
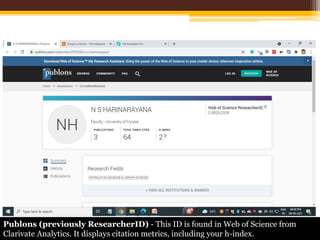
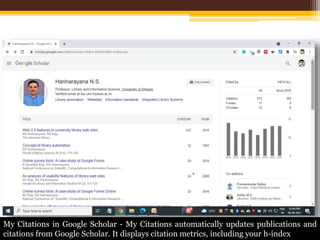
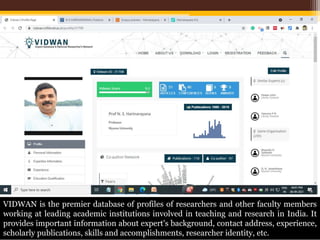
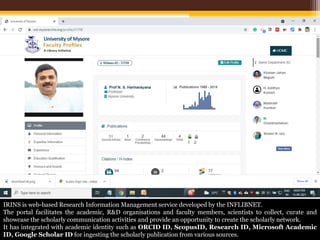
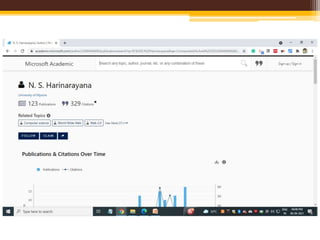
The document discusses measuring scientific productivity through various citation databases, impact factors, and author identification systems. It covers the significance of metrics like h-index, impact factor, and citation databases such as Web of Science and Scopus, emphasizing the need for multiple metrics for comprehensive evaluation. Additionally, it highlights academic social networking sites and unique author identification systems that contribute to scholarly communication.