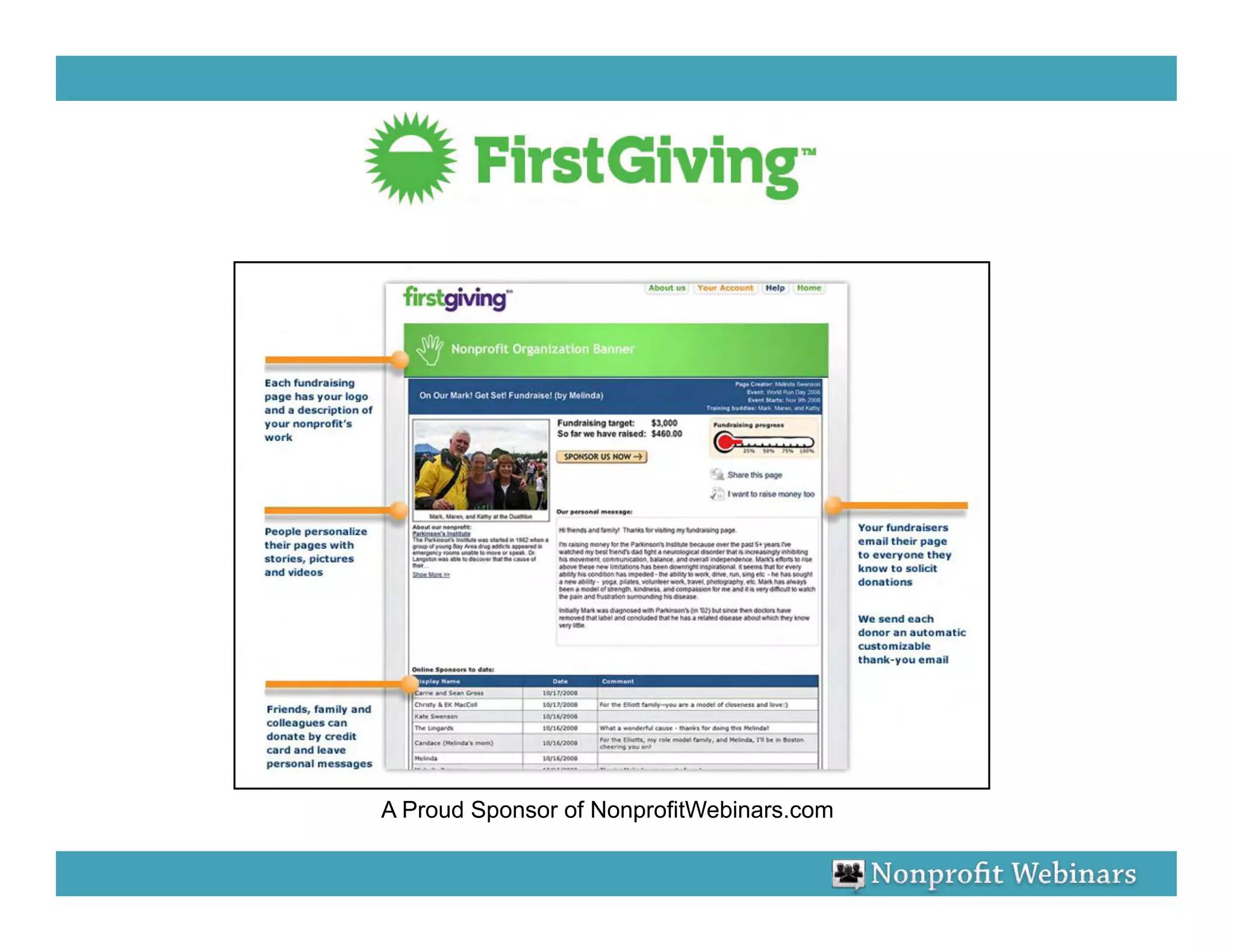
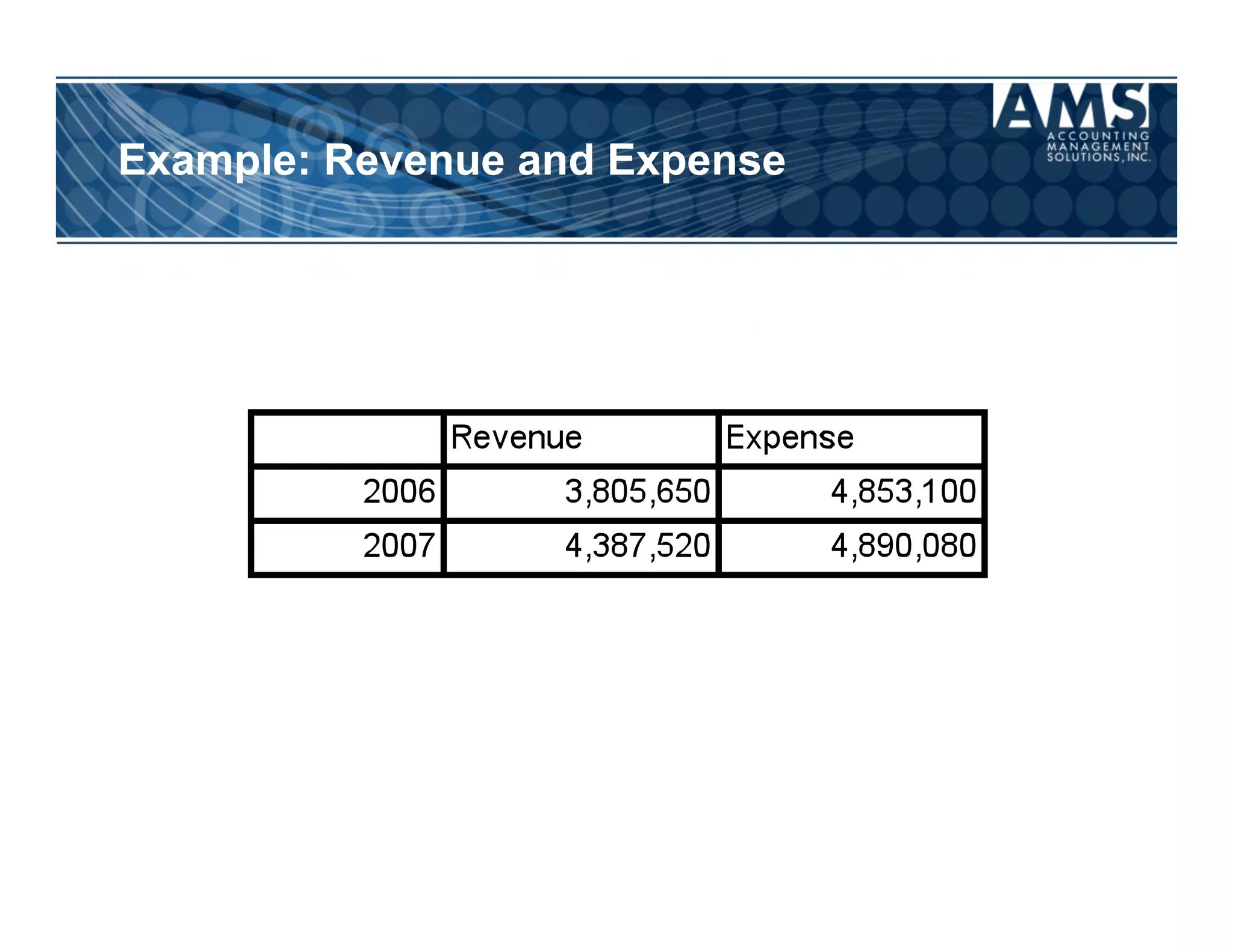
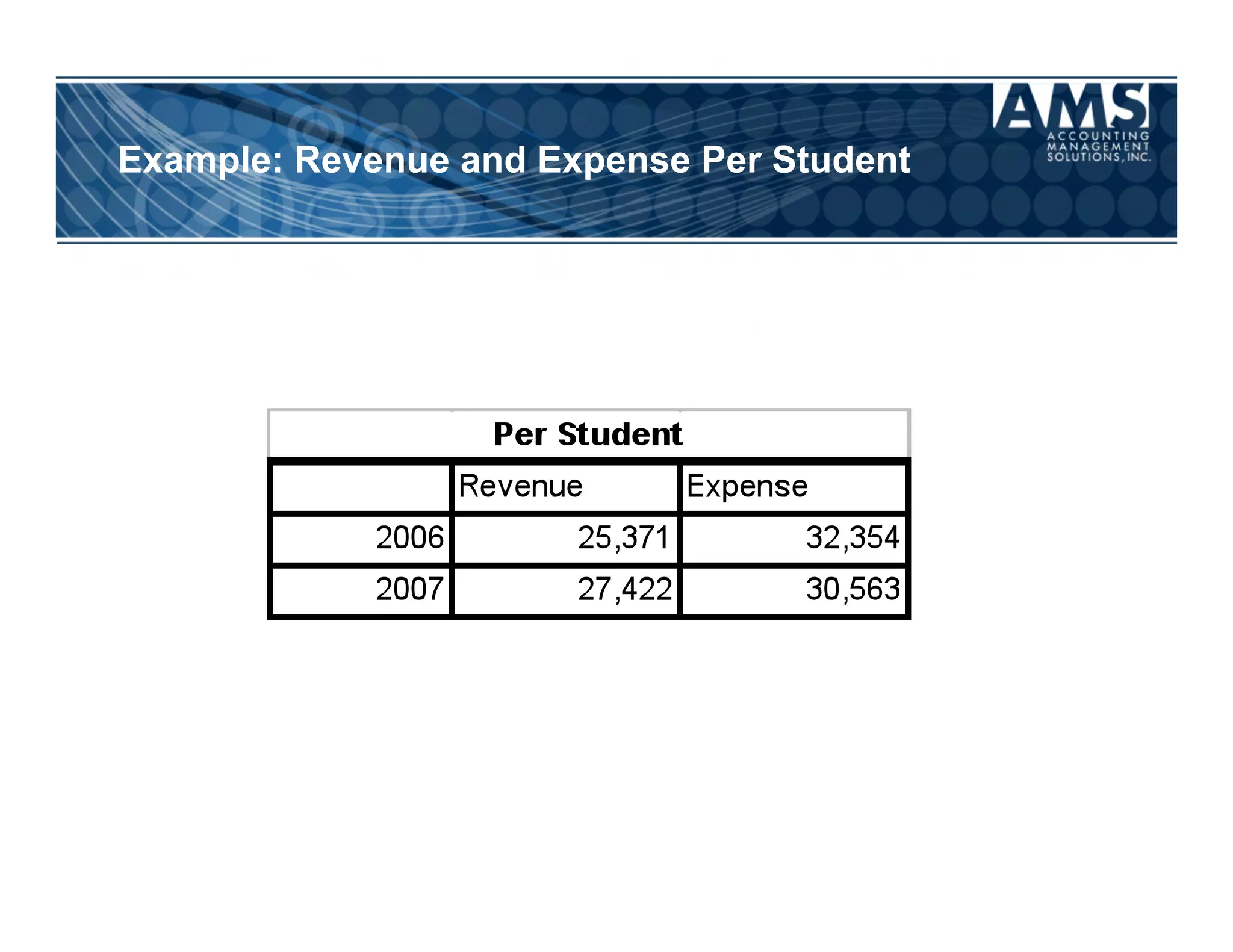
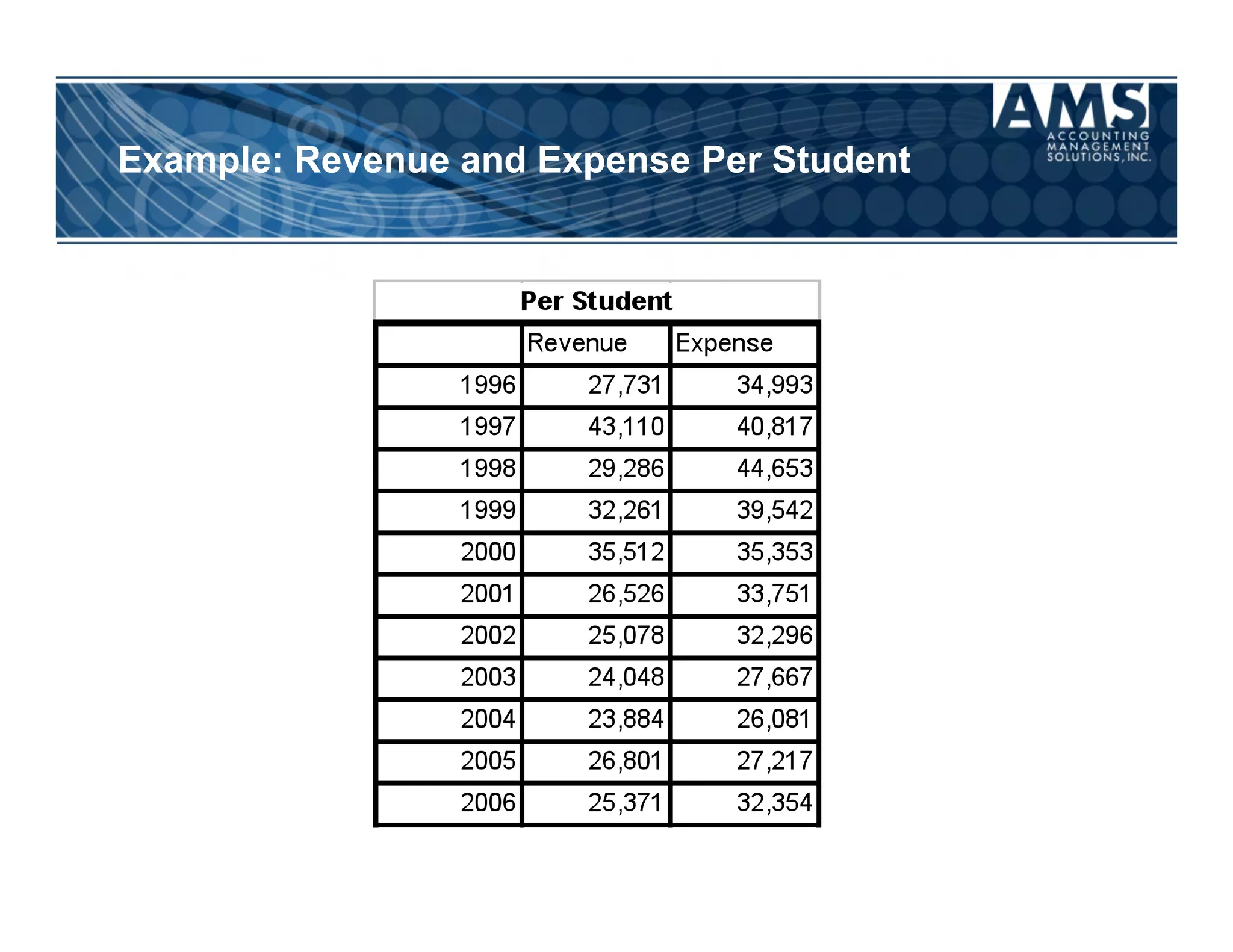
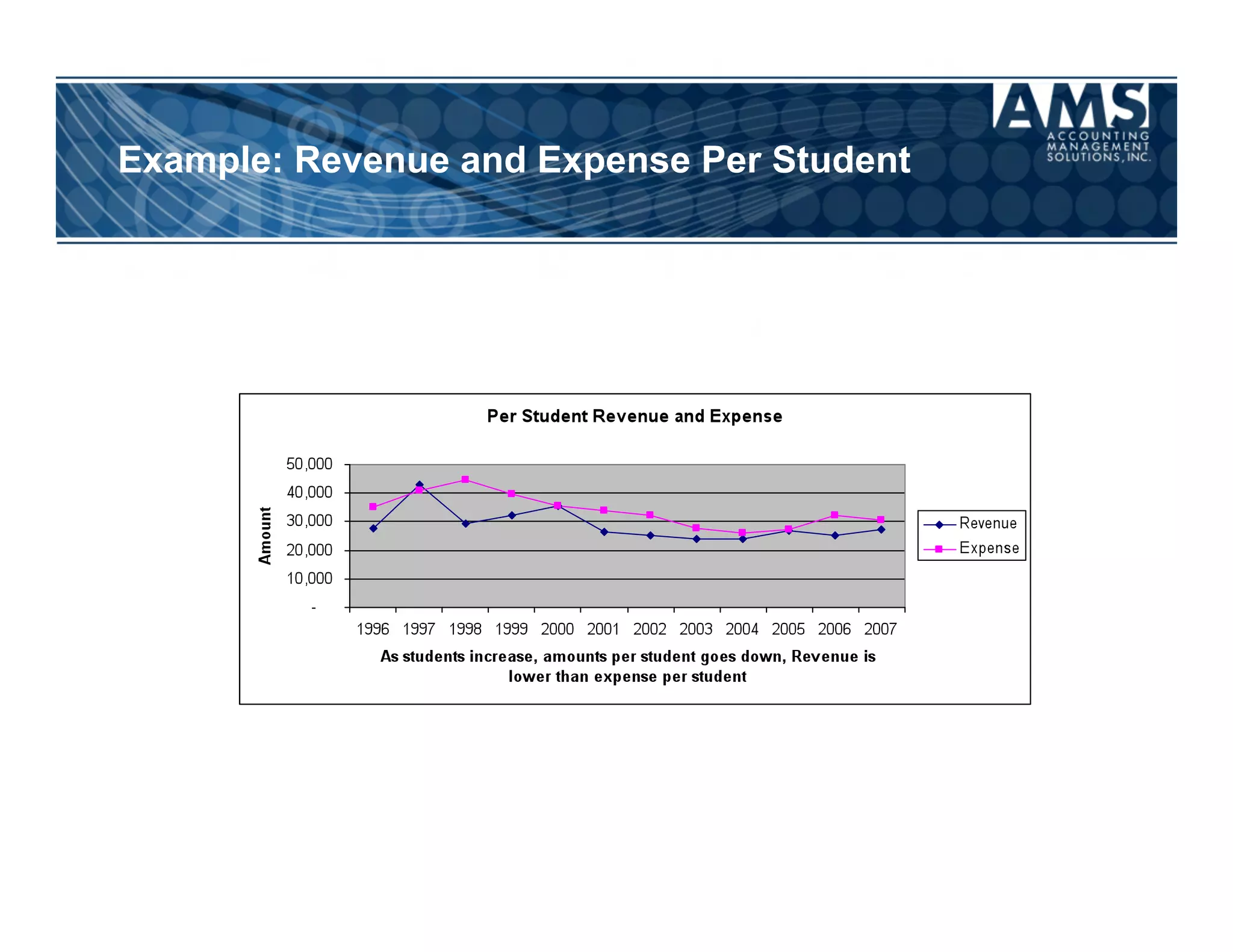
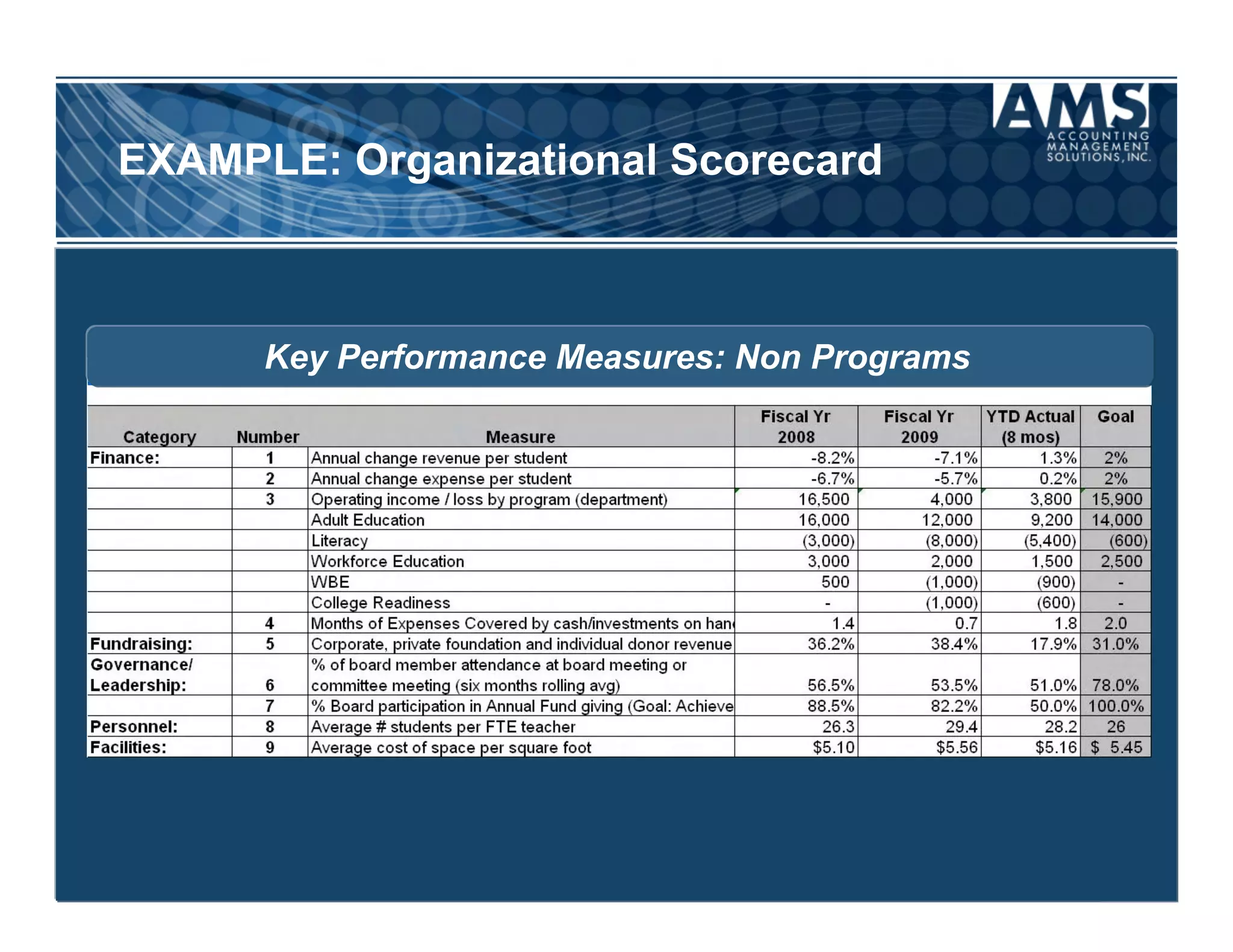
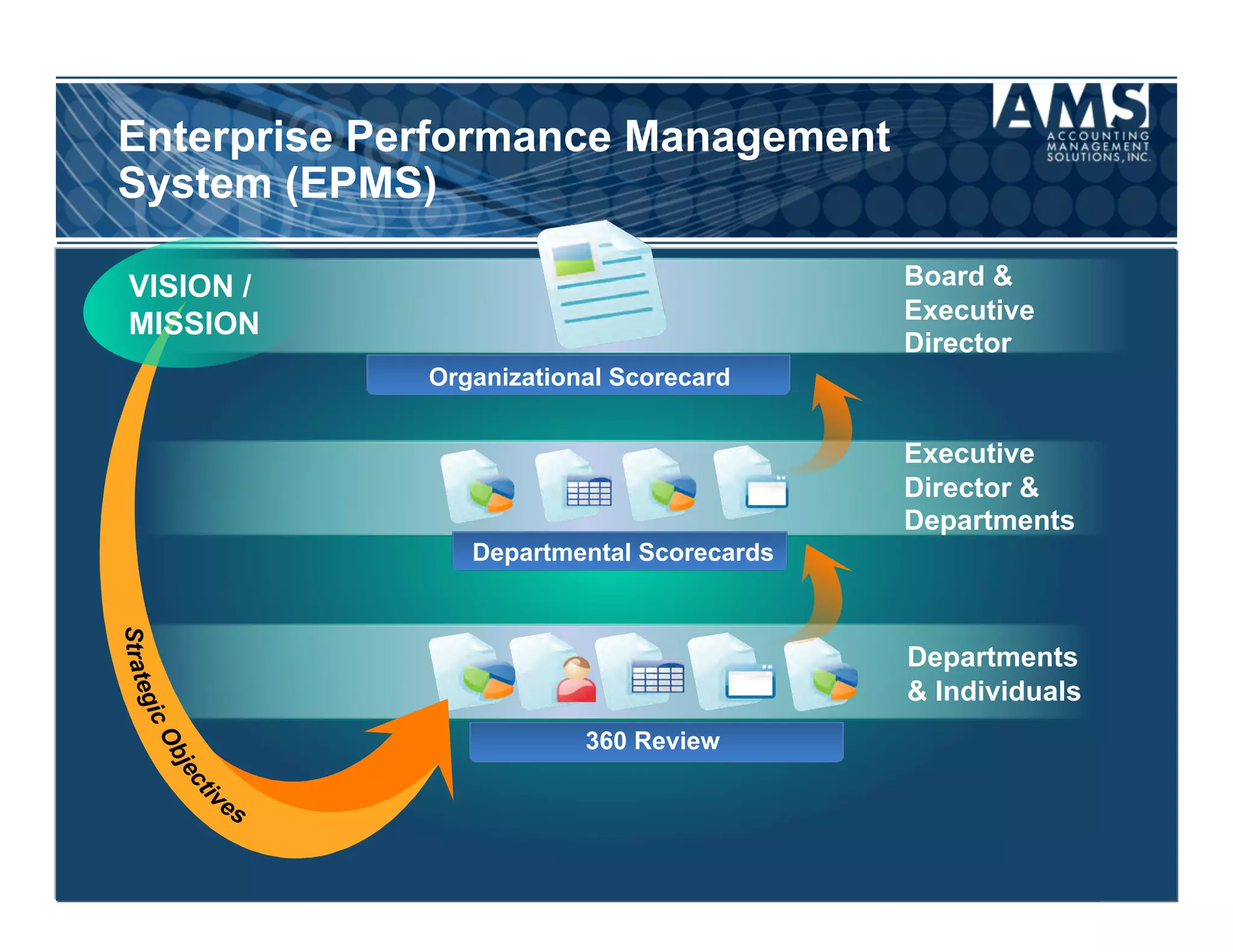
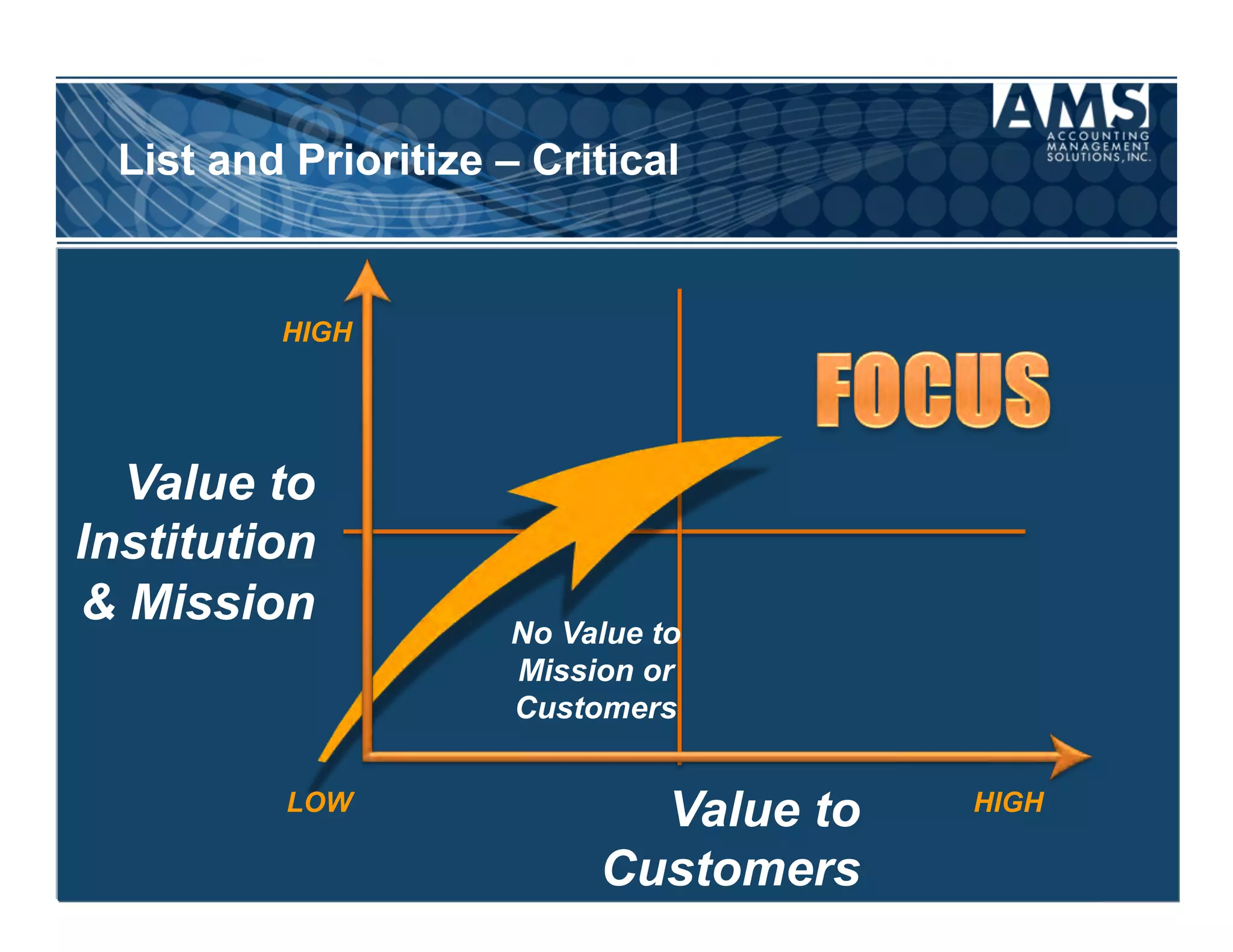
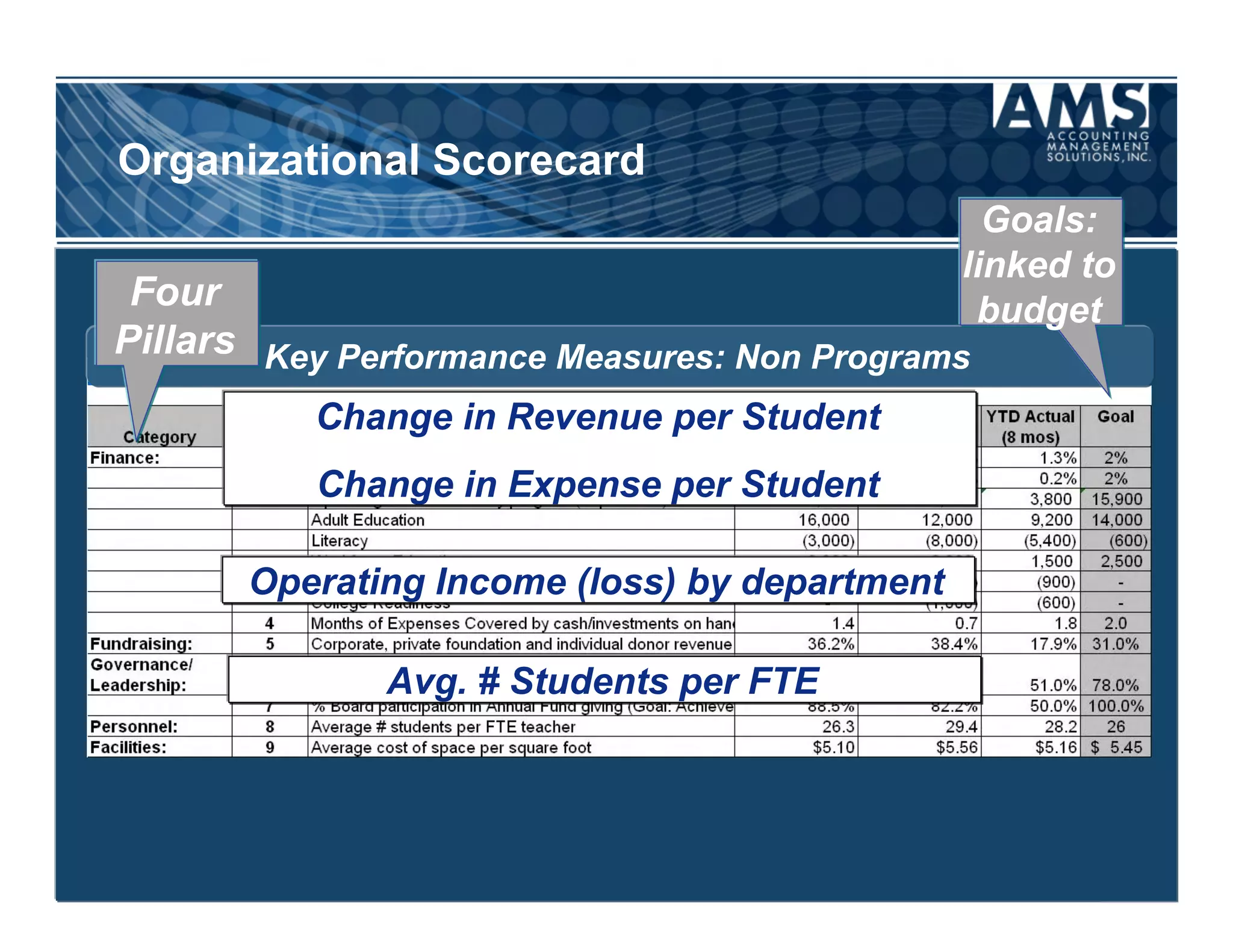
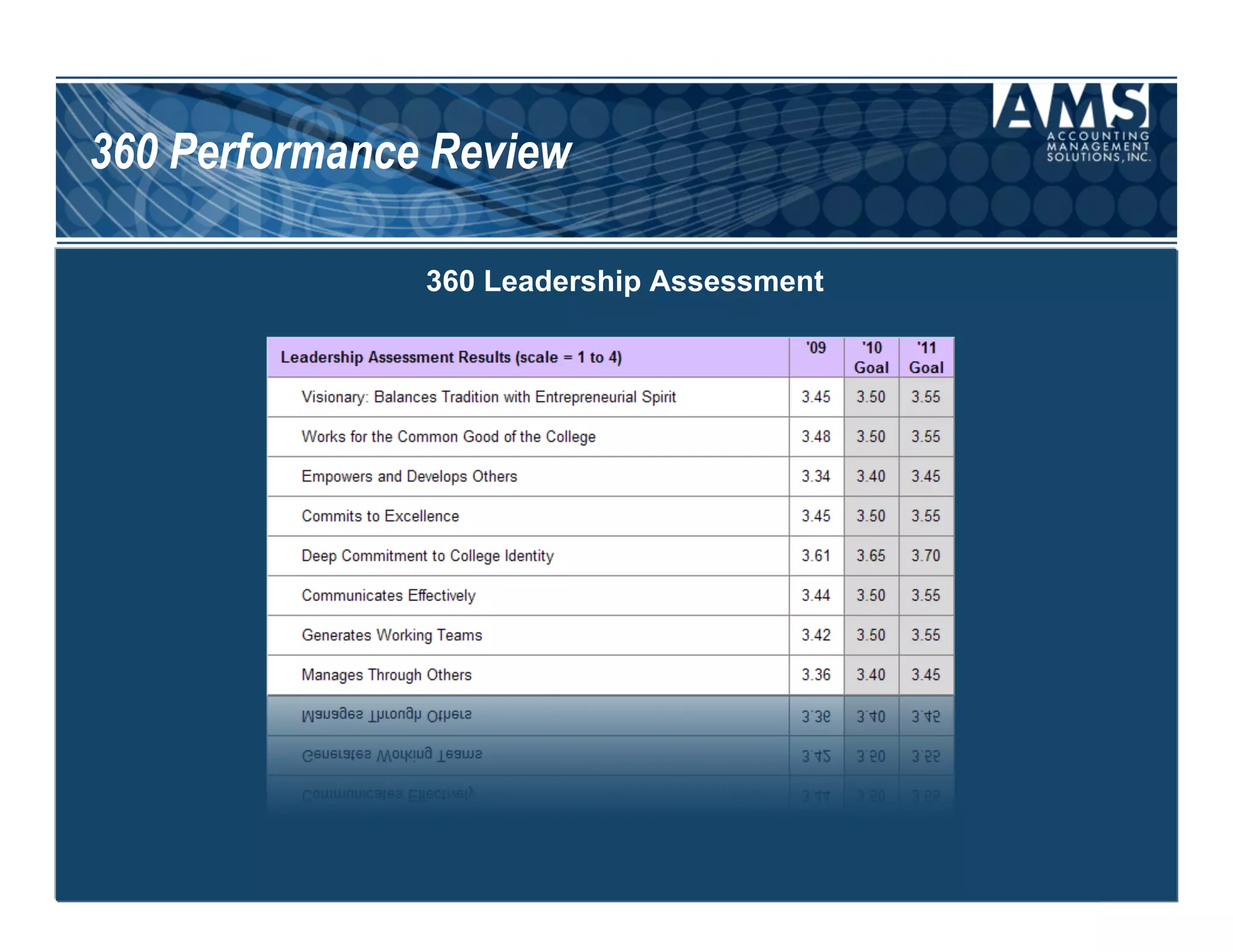
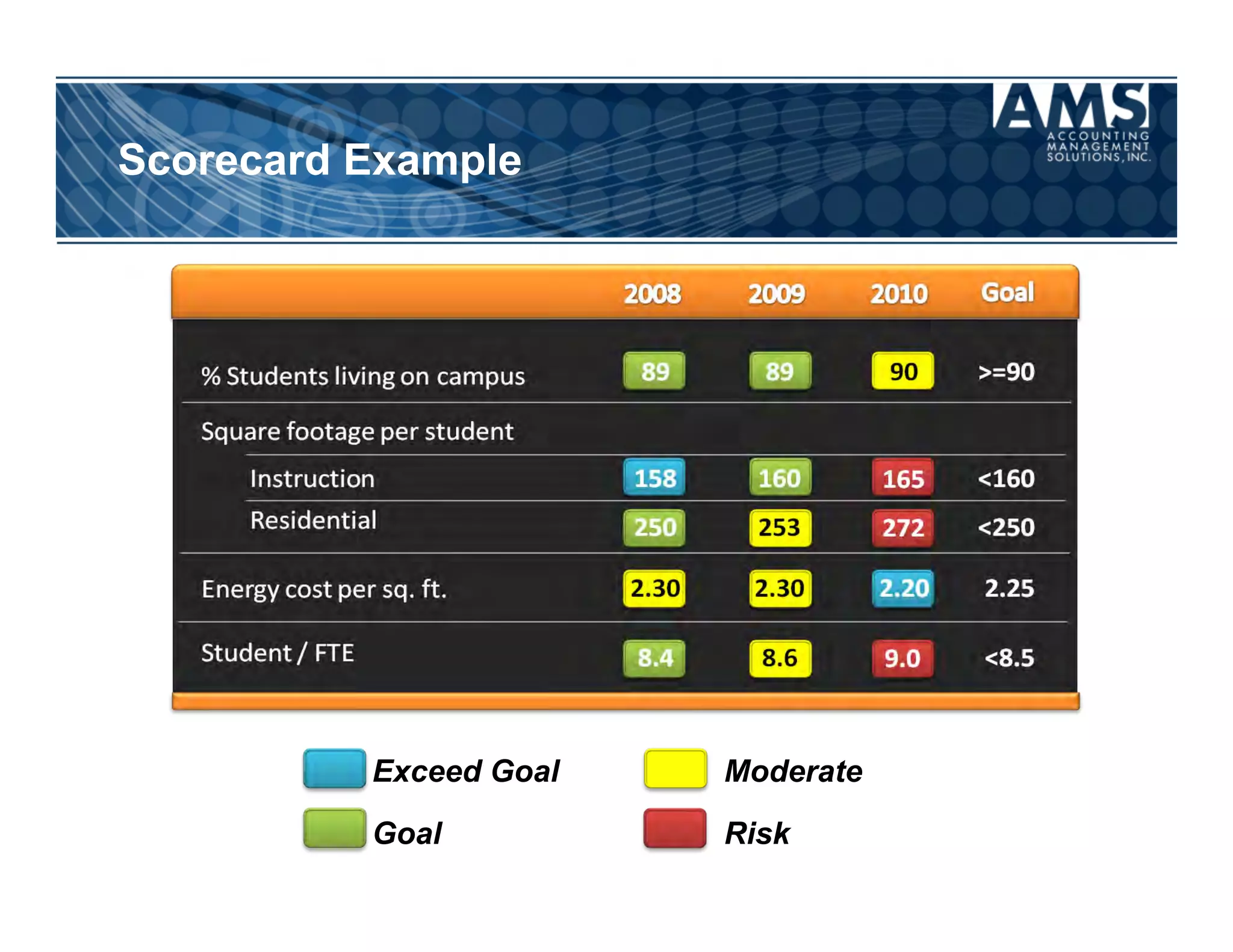
The document discusses the importance of scorecards in linking financial performance to organizational mission, highlighting how scorecards can effectively measure and present both financial and non-financial data. It outlines the characteristics of effective financial reporting, the benefits of scorecards, and key performance indicators (KPIs) needed for strategic goal alignment. The document emphasizes the need for clear communication, cross-functional teamwork, and ongoing evaluation to enhance organizational performance.