1) Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations numerically solve Newton's equations of motion to simulate the physical movements of atoms and molecules over time.
2) The Verlet algorithm is commonly used to integrate the equations of motion in MD simulations. It calculates new positions and velocities at each time step based on the forces between particles.
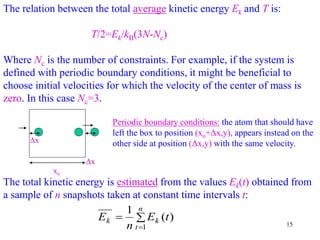
3) MD simulations sample the ensemble of all possible configurations over time. If run long enough, time averages from the simulation converge to ensemble averages, in accordance with the ergodic hypothesis. This allows MD to connect microscopic dynamics to macroscopic thermodynamics.




![7
6
12
4
r
r
r)
(
MD simulations
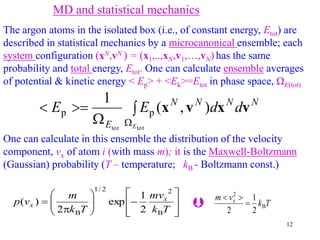
We treat N argon atoms of mass m enclosed in an isolated container.
Each pair interacts via Lennard-Jones potential energy (Etot= const.)
r =σ
ε
r
The force in x1 direction between (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2)
r
x
r
r
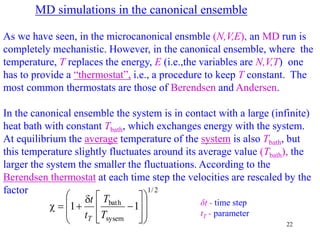
r
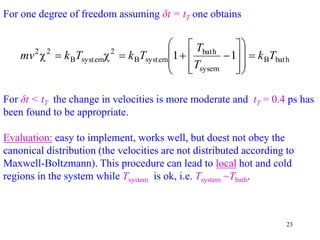
x
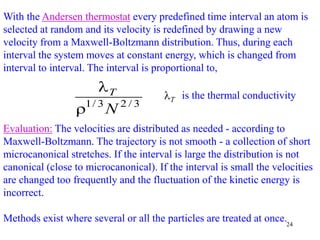
r
x
z
z
y
y
x
x
r
x
r
r
x
Fx
1
7
6
13
12
1
1
2
/
1
2
2
1
2
2
1
2
2
1
1
1
2
24
]
)
(
)
(
)
[(
1
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdcourse-230727033251-4363c0ad/85/MD_course-ppt-7-320.jpg)
![8
Assume that at t=0 atom i is positioned at coordinates xi(0) and has
initial velocity vi(0) (i=1,N); one can solve numerically Newton’s
equations obtaining the positions xi(t) and velocities vi(t) at time t. This
is the essence of MD.
Integration of the equations of motion by a finite differences method
with the popular Verlet algorithm: Taylor expansions to 3rd order for i
Adding these equations gives [up to order (δt)4]
Independent of velocities. a(t) is calculated from F/m; m – mass.
.....
)
(
)
(
6
1
)
(
)
(
2
1
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
....
)
(
)
(
6
1
)
(
)
(
2
1
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
3
2
3
2
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
b
a
v
r
r
b
a
v
r
r
]
)
[(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
2
)
( 4
2
t
O
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
a
r
r
r](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdcourse-230727033251-4363c0ad/85/MD_course-ppt-8-320.jpg)
![9
The velocities (required for the kinetic energy and temperature) are:
)
(
2
/
)]
(
)
(
[
)
( t
t
t
t
t
t
r
r
v
i.e., correct up to (δt)2 . They can also be estimated at half step, t+(1/2)δt,
t
t
t
t
t
t
/
)]
(
)
(
[
)
2
1
( r
r
v
The process is iterative. Starts with initial coordinates and velocities;
then t+δt t and t t- δt etc. Irrespective of initial conditions the
particles get mixed according the laws of statistical mechanics.
Most of computer time is spent on calculation of the forces, f = a/m.
The Verlet algorithm satisfies time reversal r(t + δt) = r(t - δt).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdcourse-230727033251-4363c0ad/85/MD_course-ppt-9-320.jpg)

![11
Many other algorithms have been developed. Some are equivalent to
Verlet’s method - leap-frog (Hockney, 1970) and velocity Verlet (Swope,
Andersen, Berens& Wilson, 1982), where v is more accurate
)]
(
)
(
[
2
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
2
1
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
( 2
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
a
a
v
v
a
v
r
r
Here, first r(t+ δt) is calculated from v(t) and a(t). v(t+ δt ) is calculated
in two stages, first at mid-step, i.e., v(t+ δt/2)
)
(
2
)
(
)
(
)
2
1
( t
t
t
t
t a
v
v
Finally, a(t+ δt) is calculated and the corresponding force, which lead to
v(t+ δt)
)
(
2
)
(
)
2
1
(
)
( t
t
t
t
t
t
t
a
v
v](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdcourse-230727033251-4363c0ad/85/MD_course-ppt-11-320.jpg)



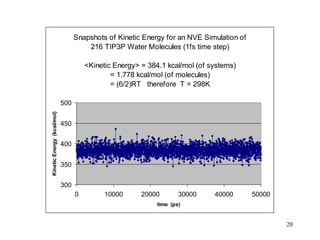
![19
Fluctuations in Total Energy for an NVE Simulation of
216 TIP3P Water Molecules (1fs time step)
[the run was initiated at E = -1730.32 kcal/mol]
-1730.5
-1730.45
-1730.4
-1730.35
-1730.3
-1730.25
-1730.2
0 10000 20000 30000 40000 50000
time (ps)
Total
Energy
(kcal/mol)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdcourse-230727033251-4363c0ad/85/MD_course-ppt-19-320.jpg)
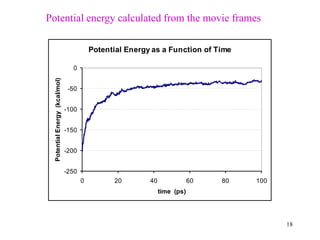
![21
Snapshots of Potential Energy for an NVE Simulation of
216 TIP3P Water Molecules (1fs time step)
<Potential Energy> = -2114.4 kcal/mol (of systems)
= -9.789 kcal/mol (of molecules) [exp. = -9.92 kcal/mol]
-2180
-2160
-2140
-2120
-2100
-2080
-2060
0 10000 20000 30000 40000 50000
time (ps)
Potential
Energy
(kcal/mol)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdcourse-230727033251-4363c0ad/85/MD_course-ppt-21-320.jpg)
![25
Dynamics
MD not only provides statistical mechanics averages, but also allows
calculating dynamical properties. One can calculate from an MD
trajectory time correlation functions that lead to dynamic parameters
such as diffusion coefficients. For example, the autocorrelation function
of the velocity
)
(
)
0
( t
i
i v
v
can be estimated from an MD trajectory, where the velocities are
measured n times in time intervals t
In practice, the measurements start at time (m+1)t and go back m time
intervals. Contribution from all particles are considered and averaged.
N
i
i
i
n
m
k
i
i t
m
k
kt
N
m
n
mt
1
1
]
)
[(
]
[
)
1
(
1
)
(
)
0
( v
v
v
v](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdcourse-230727033251-4363c0ad/85/MD_course-ppt-25-320.jpg)

![27
Biological macromolecules - proteins
The typical potential energy function (force field) is:
EFF = bonds Kr(r - req)2 + angles K( - eq)2
+ dihedrals Vn /2 [1 + cos(n - )]
+ i<j [Aij /Rij
12 – Bij /Rij
6 + qiqj /Rij]
where Kr , K , req, eq, , n, Vn, Aij, Bij, and qi are parameters
optimized by applying this function to a large amount of experimental
data and results obtained from quantum mechanical ab initio
calculations.
Rij is the distance between atoms i and j and is a dielectric constant.
A protein in vacuum – no solvent effects - the screening of the Coulomb
potentials by water can partially be obtained by increasing .
Rij
r](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mdcourse-230727033251-4363c0ad/85/MD_course-ppt-27-320.jpg)