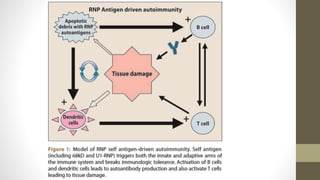
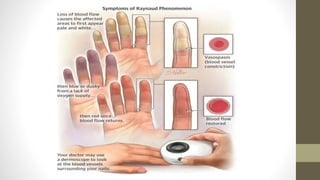
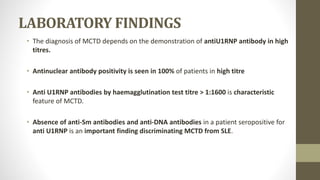
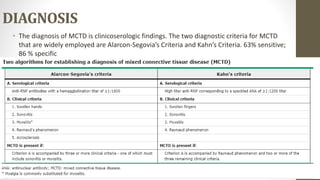
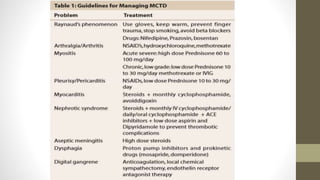
Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) is characterized by features of systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. It is defined by very high levels of anti-U1RNP antibodies. Clinical features include Raynaud's phenomenon, joint and muscle involvement, lung and heart disease, gastrointestinal issues, and kidney disease. Diagnosis requires clinical and serological criteria including high titers of anti-U1RNP antibodies. Treatment depends on organ system involvement but may include analgesics, steroids, immunosuppressants, and calcium channel blockers. Prognosis is variable depending on degree of organ involvement.