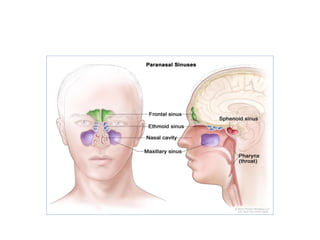
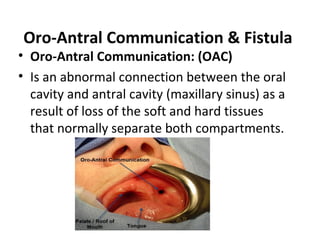
The maxillary sinus is an air-filled space within the maxilla bone that communicates with the nasal cavity. It is one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Maxillary sinusitis is inflammation of the maxillary sinus that can be acute, sub-acute, or chronic. It can occur due to infection or allergies spreading from dental sources like periapical or periodontal lesions, overextended dental materials into the sinus, or iatrogenic sinus perforation during dental surgery. Symptoms of maxillary sinusitis include toothache, facial pain, and tenderness over the sinus that is worsened by lowering the head. An oro-antral communication is an abnormal connection between the oral cavity and