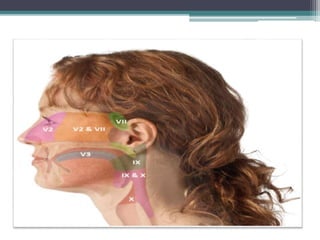
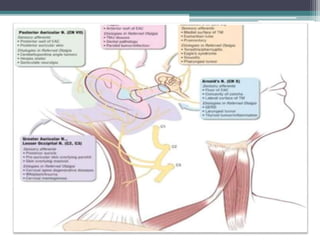
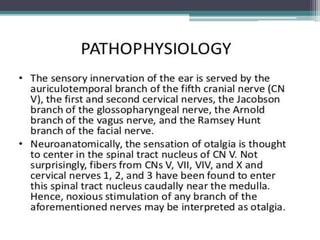
Otalgia, or ear ache, can be caused by diseases of the ear itself (primary otalgia) or by non-ear related conditions that cause referred pain to the ear (secondary otalgia). The most common causes of primary otalgia are infections like acute otitis media, while dental issues, throat infections, and cervical spine problems frequently cause secondary otalgia by irritating the trigeminal, facial, or vagus nerves. It is important to determine whether the source of the ear pain is local to the ear or referred from another site before treating in order to address the underlying cause.










![• Irritation of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve
V) is the most common cause of referred ear
pain.[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0talgiaearache-180905150234/85/0talgia-ear-ache-16-320.jpg)








