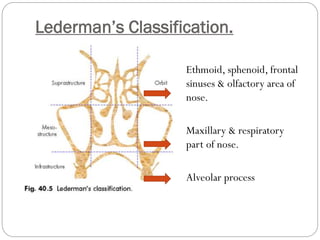
The maxillary sinus is the largest and most commonly involved sinus in malignancies. Maxillary sinus carcinoma arises from the sinus lining and spreads locally through bone destruction and invasion of surrounding structures. Distant metastases occasionally occur in the lungs. Diagnosis involves radiography, CT scan, and biopsy. Treatment depends on tumor stage and may involve surgery, radiation therapy, or chemoradiation. Prognosis diminishes with increased stage, with a 5-year survival rate of 40-50% even with advances in multimodal therapy.