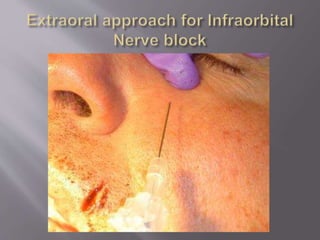
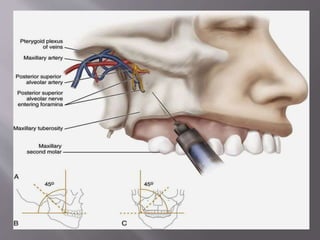
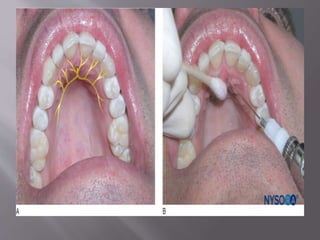
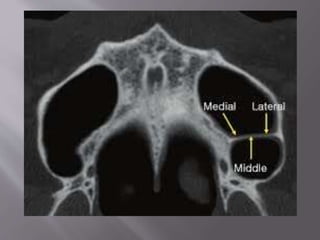
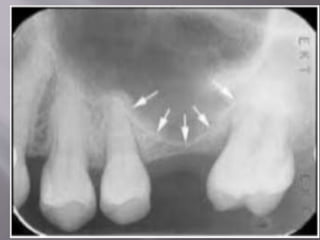
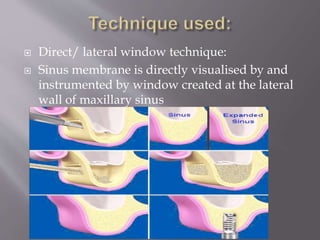
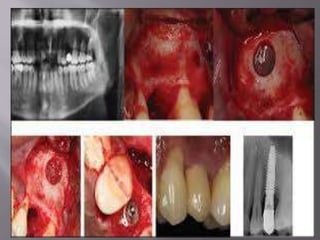
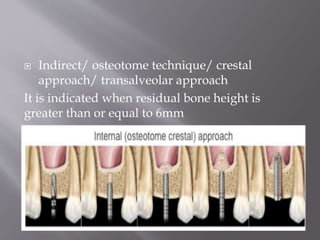
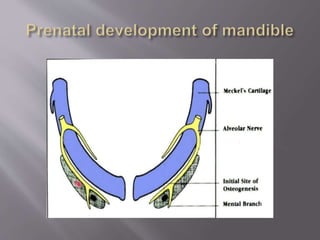
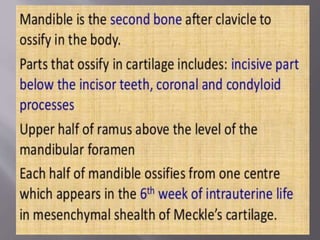
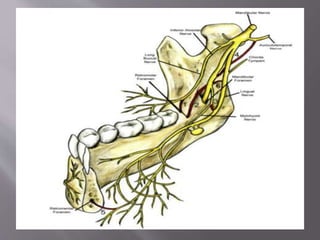
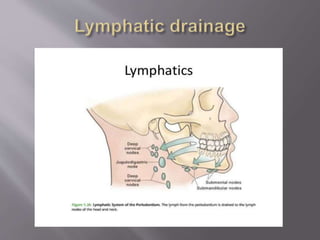
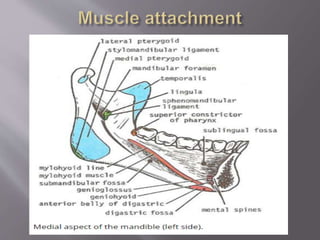
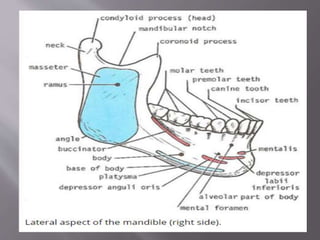
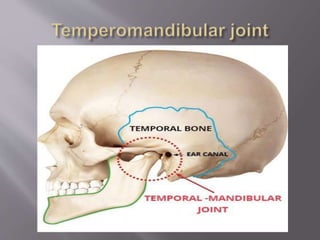
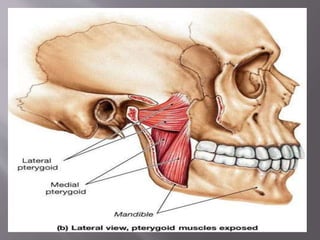
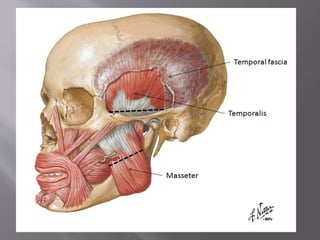
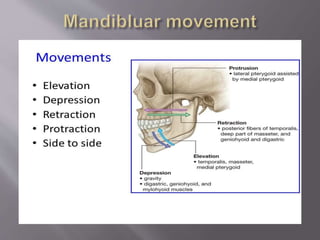
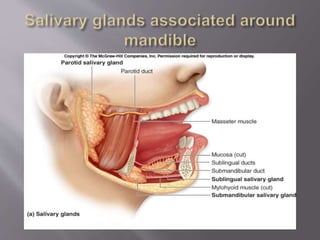
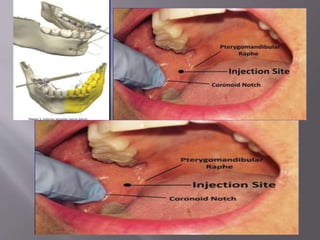
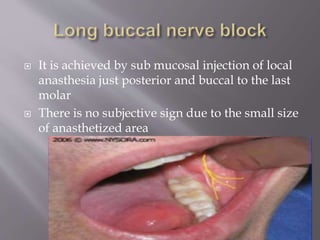
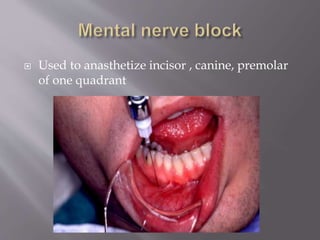
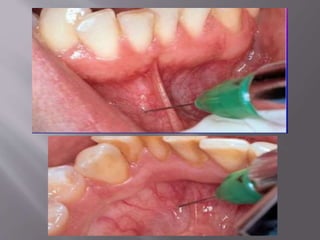
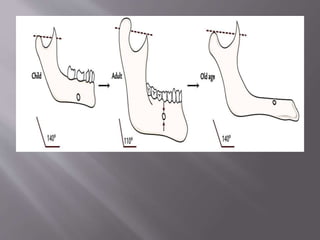
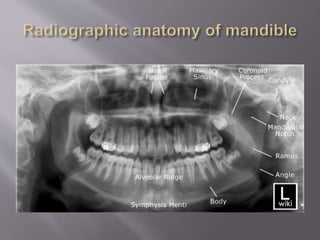
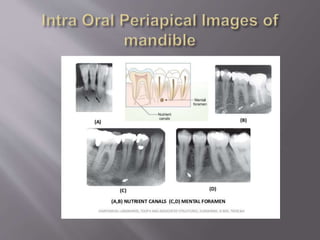
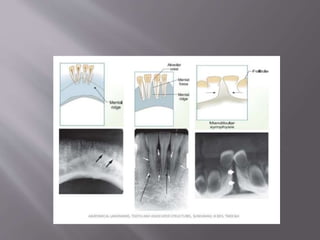
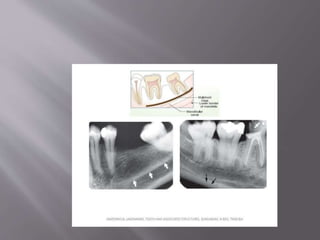
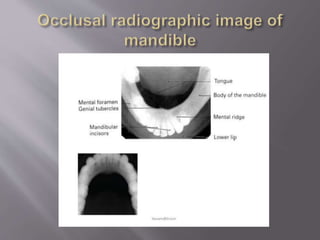
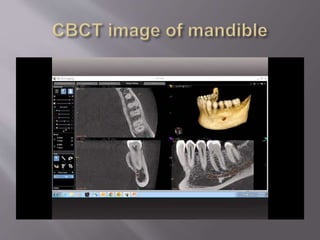
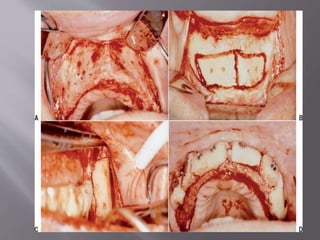
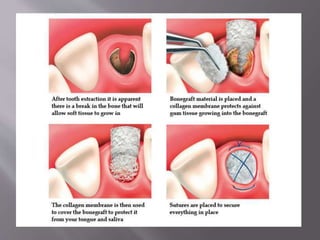
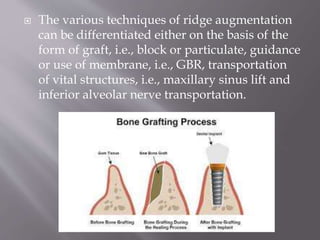
The document discusses the development of the maxilla and mandible. It describes how the maxilla develops from the maxillary processes and fuses in the midline. It also discusses palate development including primary and secondary palate formation. The mandible develops from the first pharyngeal arch. The document outlines the anatomy and blood supply of the maxilla and mandible. It also discusses clinical implications such as maxillary sinus augmentation and inferior alveolar nerve blocks.



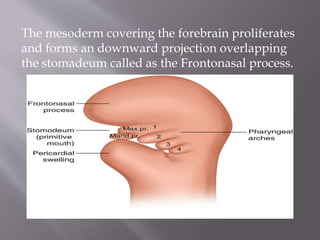
![1]A prominent
bulge appears on
the ventral surface
of the embryo
corresponnding to
the developing
brain at 4th
week of intrauterine
life.
2] Stomadeum corresponds to the primitive
mouth
3]Buccopharyngeal membrane helps to form floor
of stomadeum](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maxillamandible-190819114739/85/Maxilla-and-Mandible-5-320.jpg)
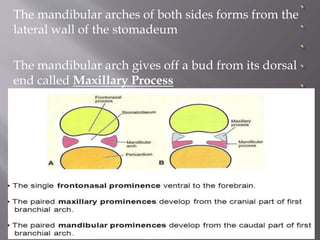
![4] 5 brachial arches
forms at the region
Of head and neck
By 4th week of
Intrauterine life.
5] they are initially
5 in number but the
4th arch disaapears
After formation
6] the first brachial arch plays a role in
development of nasomaxillary region](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maxillamandible-190819114739/85/Maxilla-and-Mandible-6-320.jpg)
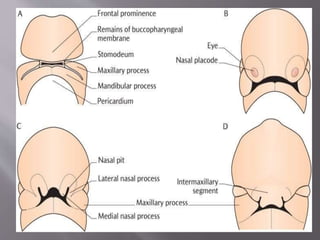
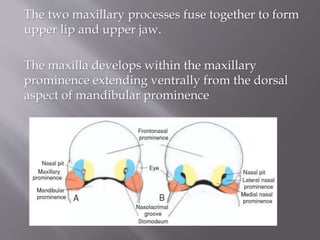
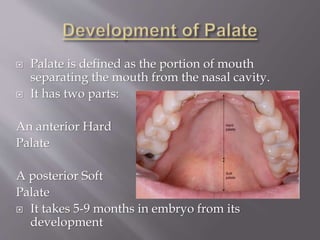
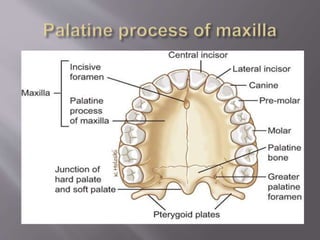
![ Secondary palate formation starts from 6th
week of embryogenic stage and completes by
12th week.
From each maxillary process, a plate like shelf
grows medially. This is called Palatal process.
Secondary palate formation takes place by the
fusion of the following:
1] The two palatine process.
2] Primitive palate formed from the frontonasal
process
Each palatine process fuses with the posterior
margin of the primitive palate
The two palatine process fuse with each other in
the midline . Fusion begins ant. And proceed
backward](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maxillamandible-190819114739/85/Maxilla-and-Mandible-13-320.jpg)
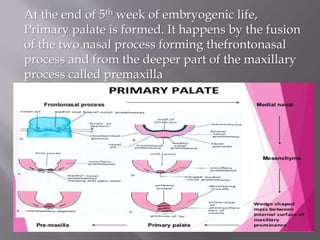
![ Cleft palate
Etiology of cleft palate:
1] delay in shelf elevation
2] disturbance in mech. of shelf elevation
3]failure of shelves to contact due to lack of
growth
4] failure to displace tongue during closure
5] failure to fuse after contact as epithelium
doesn’t break down
6] rupture after fusion
7]defective merging](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maxillamandible-190819114739/85/Maxilla-and-Mandible-14-320.jpg)




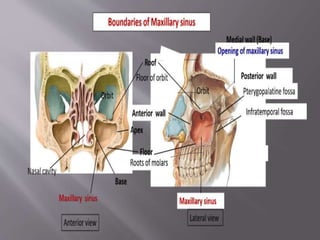
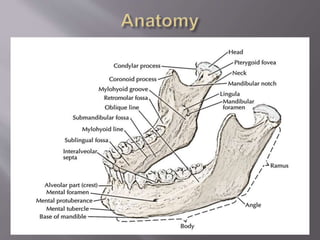
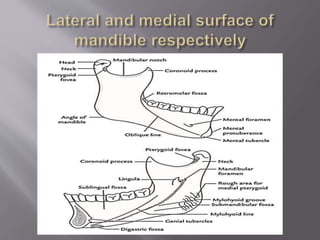
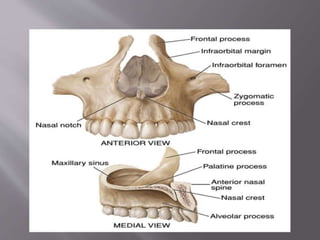
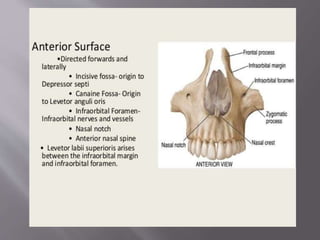
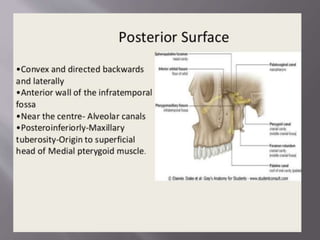
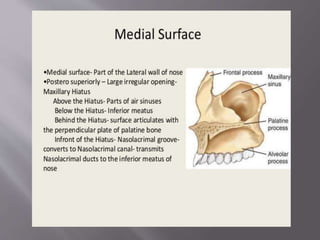
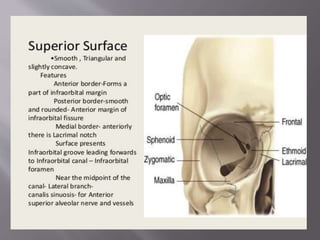
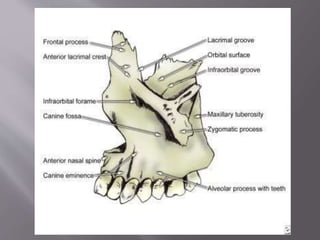
![ It mainly has two parts:
Body:
1] Anterior or facial surface
2] Posterior or infratemporal surface
3] Nasal or medial surface
4] Orbital or superior surface
Processes:
1] Zygomatic
2] Frontal
3] Alveolar
4] Palatine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maxillamandible-190819114739/85/Maxilla-and-Mandible-25-320.jpg)
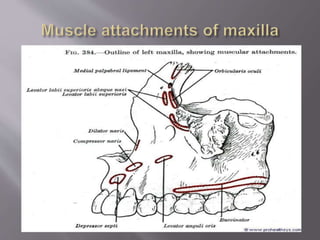
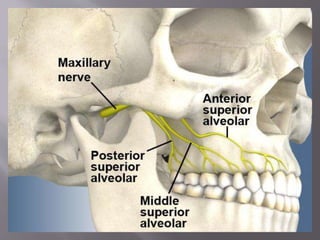
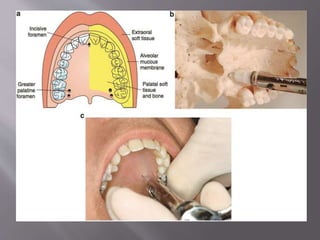
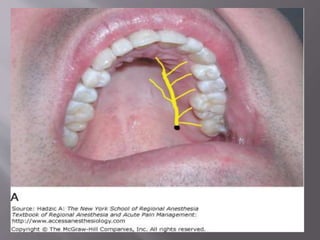
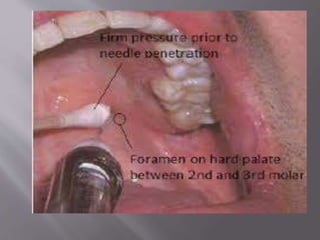
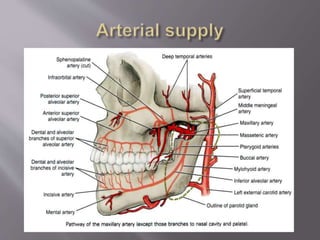
![A] Nasopalatine artery B] Descending palatine artery
C]Greater palatine artery D] Lesser palatine artery
E]Maxillary artery F]Ascending pharyngeal artery
G] Ascending palatine artery H] Facial artery
I] External carotid artery](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maxillamandible-190819114739/85/Maxilla-and-Mandible-33-320.jpg)