MATLAB allows for the creation and manipulation of character strings. Strings can be defined using single quotes and treated as character arrays. Strings can be combined vertically using concatenation or char, and horizontally using concatenation, strcat, or by converting to a cell array of strings using cellstr. MATLAB contains many string functions for tasks like formatting, comparison, searching/replacing, and more.

![Youcancombine strings vertically ineither of the following ways:
Using the MATLAB concatenationoperator [] and separating eachrow witha semicolon(;). Please note
that inthis method eachrow must containthe same number of characters. For strings withdifferent
lengths, youshould pad withspace characters as needed.
Using the char function. If the strings are different length, char pads the shorter strings withtrailing
blanks so that eachrow has the same number of characters.
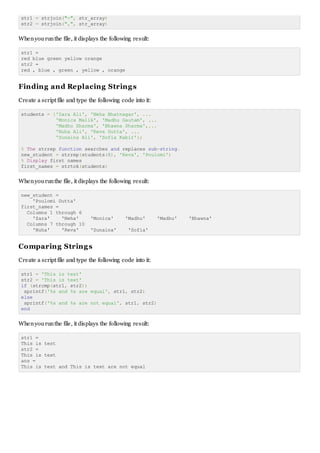
Example
Create a script file and type the following code into it:
doc_profile = ['Zara Ali '; ...
'Sr. Surgeon '; ...
'R N Tagore Cardiology Research Center']
doc_profile = char('Zara Ali', 'Sr. Surgeon', ...
'RN Tagore Cardiology Research Center')
Whenyourunthe file, it displays the following result:
doc_profile =
Zara Ali
Sr. Surgeon
R N Tagore Cardiology Research Center
doc_profile =
Zara Ali
Sr. Surgeon
RN Tagore Cardiology Research Center
Youcancombine strings horizontally ineither of the following ways:
Using the MATLAB concatenationoperator, [] and separating the input strings witha comma or a space.
This method preserves any trailing spaces inthe input arrays.
Using the string concatenationfunction, strcat. This method removes trailing spaces inthe inputs
Example
Create a script file and type the following code into it:
name = 'Zara Ali ';
position = 'Sr. Surgeon ';
worksAt = 'R N Tagore Cardiology Research Center';
profile = [name ', ' position ', ' worksAt]
profile = strcat(name, ', ', position, ', ', worksAt)
Whenyourunthe file, it displays the following result:
profile =
Zara Ali , Sr. Surgeon , R N Tagore
Cardiology Research Center
profile =
Zara Ali,Sr. Surgeon,R N Tagore Cardiology Research Center
Combining Strings into a Cell Array
Fromour previous discussion, it is clear that combining strings withdifferent lengths could be a painas allstrings
inthe array has to be of the same length. We have used blank spaces at the end of strings to equalize their length.
However, a more efficient way to combine the strings is to convert the resulting array into a cellarray.
MATLAB cellarray canhold different sizes and types of data inanarray. Cellarrays provide a more flexible way
to store strings of varying length.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabstrings-150713154435-lva1-app6891/85/Matlab-strings-2-320.jpg)