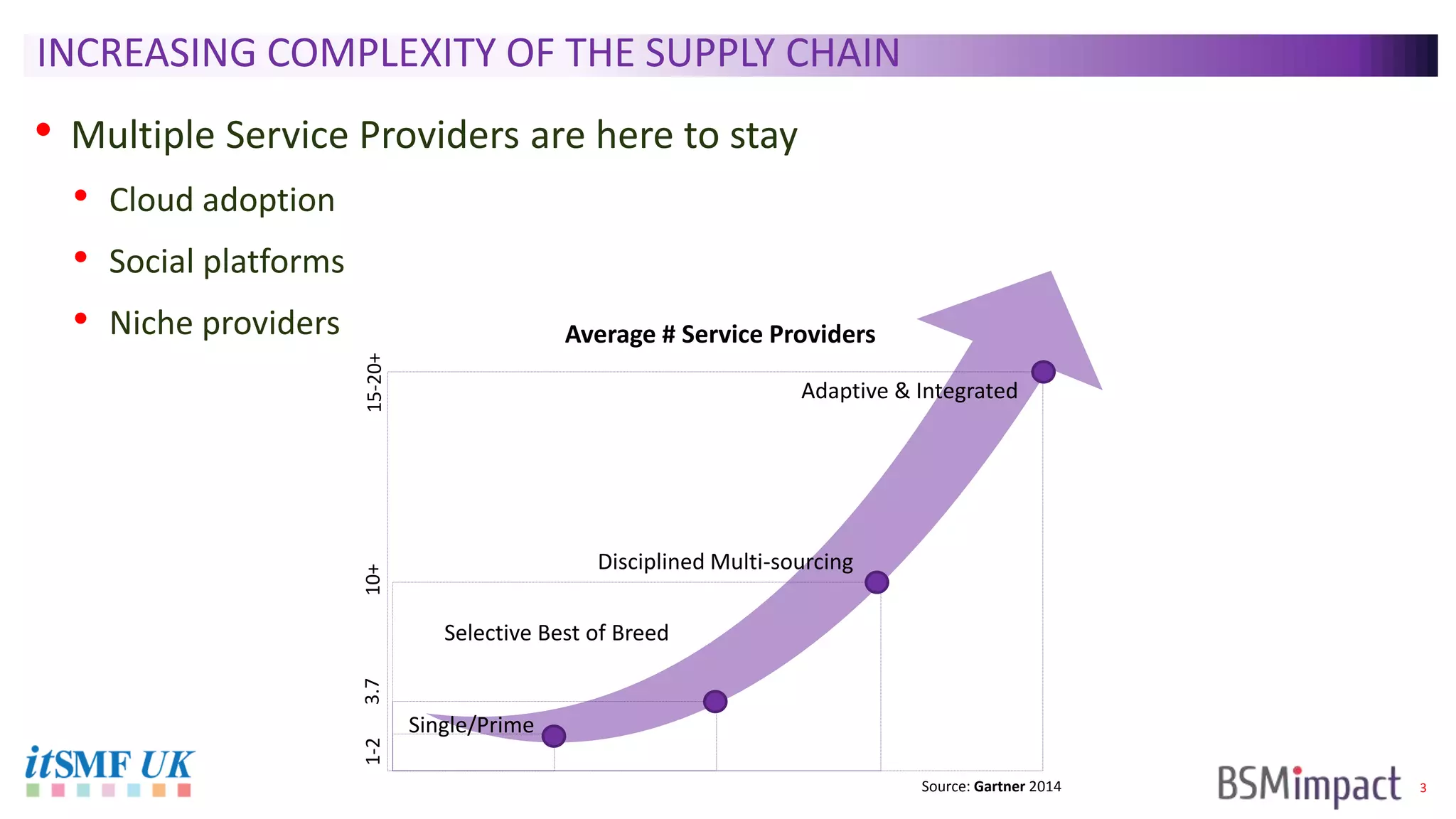
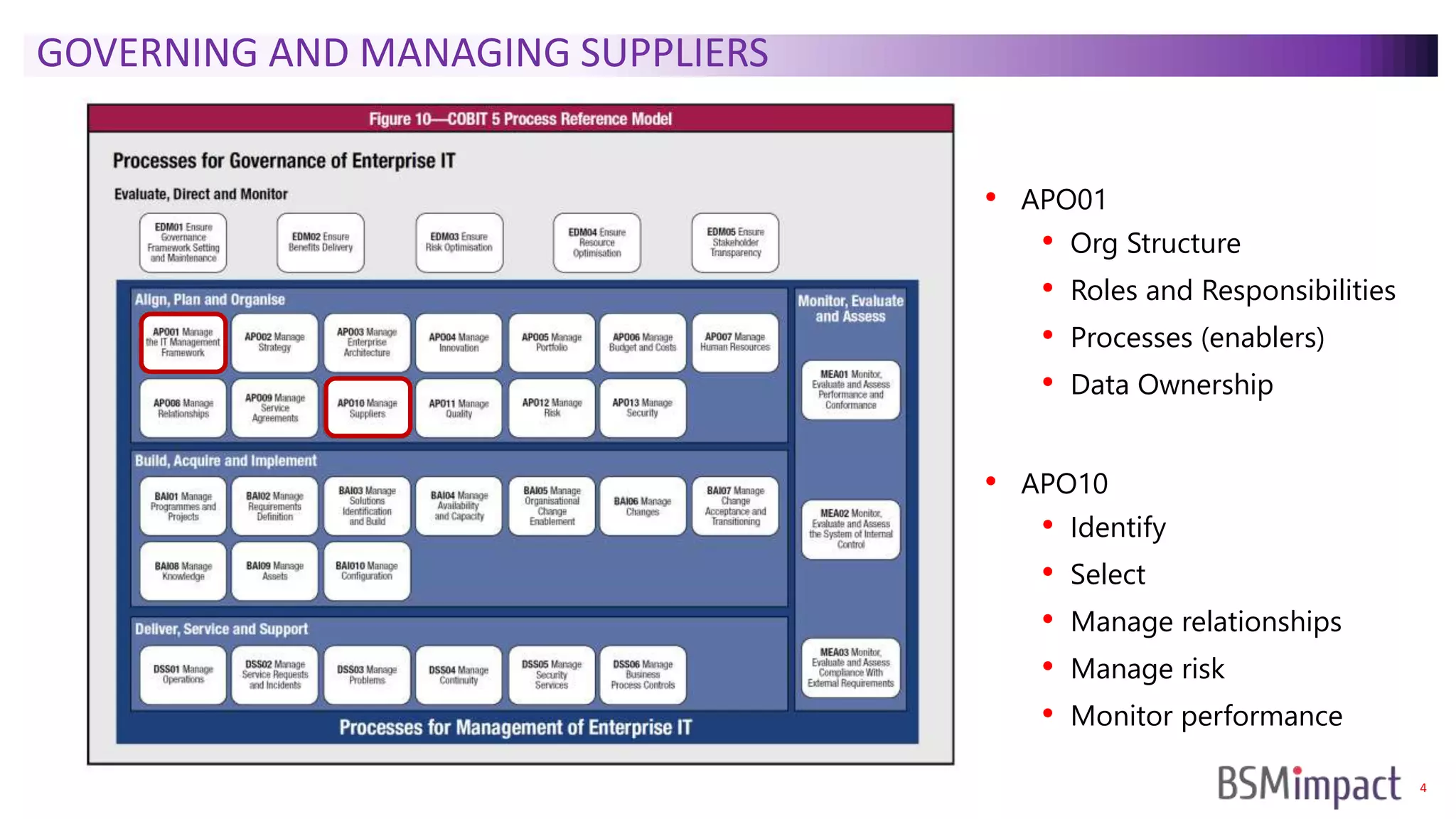
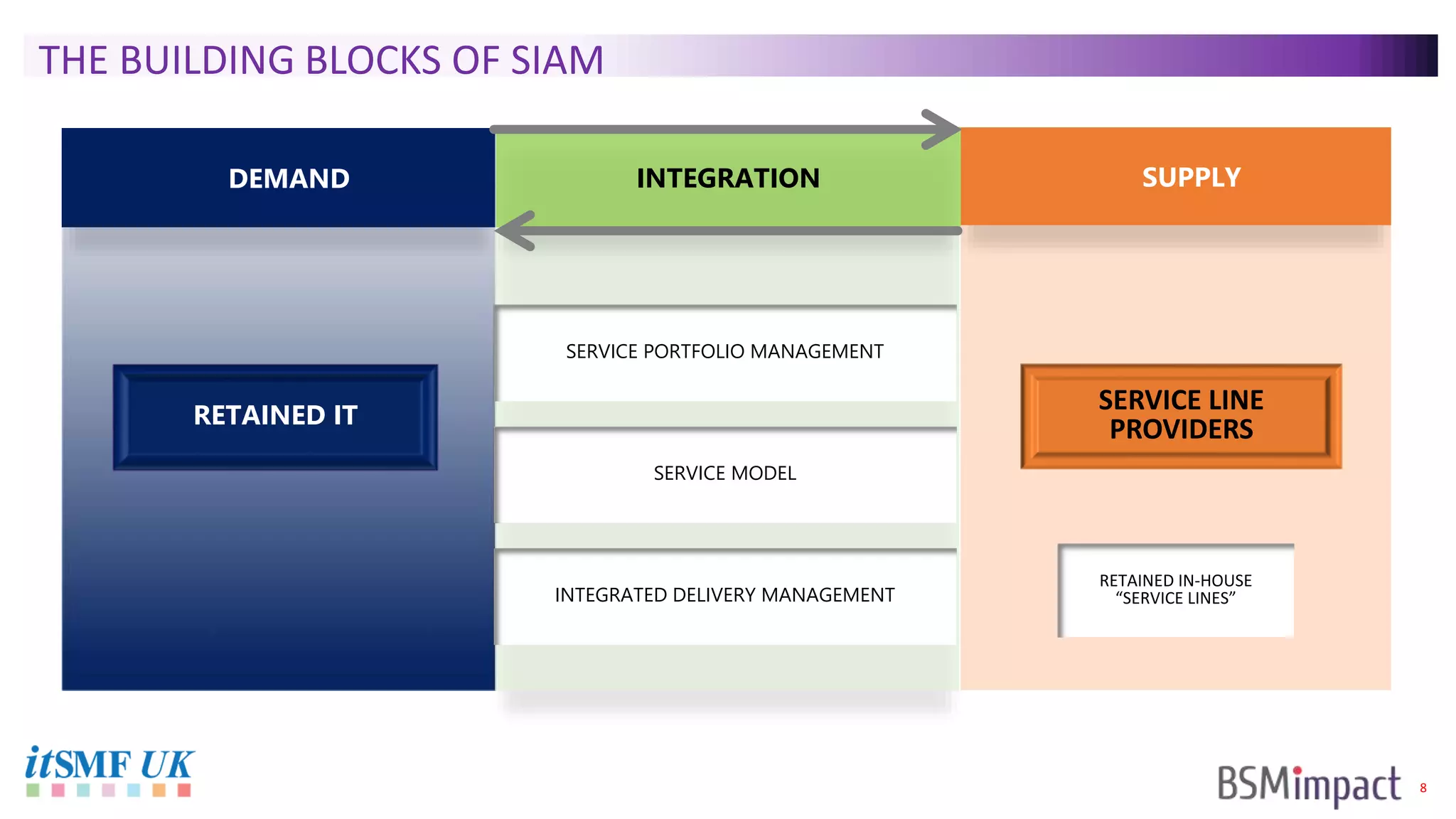
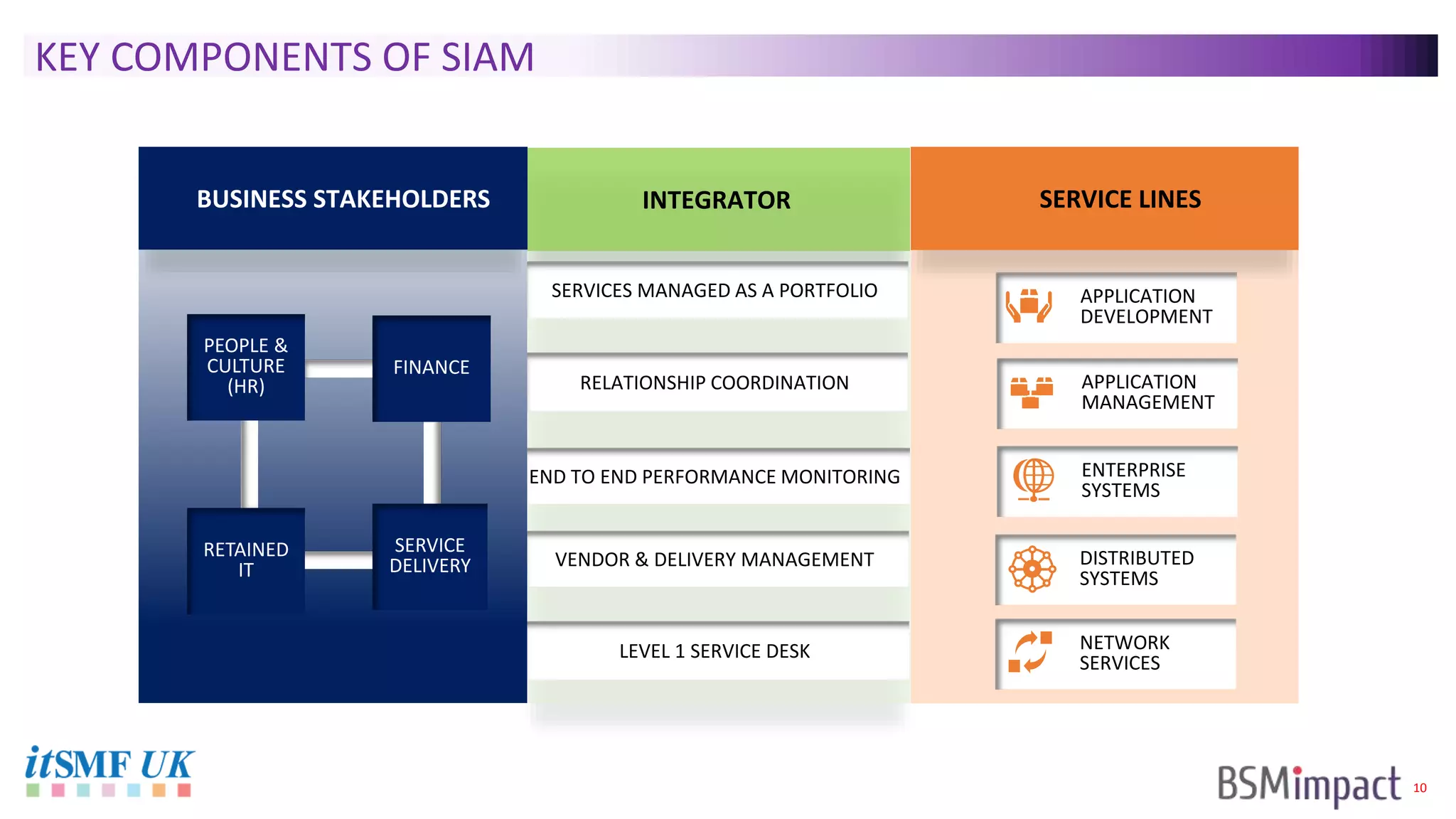
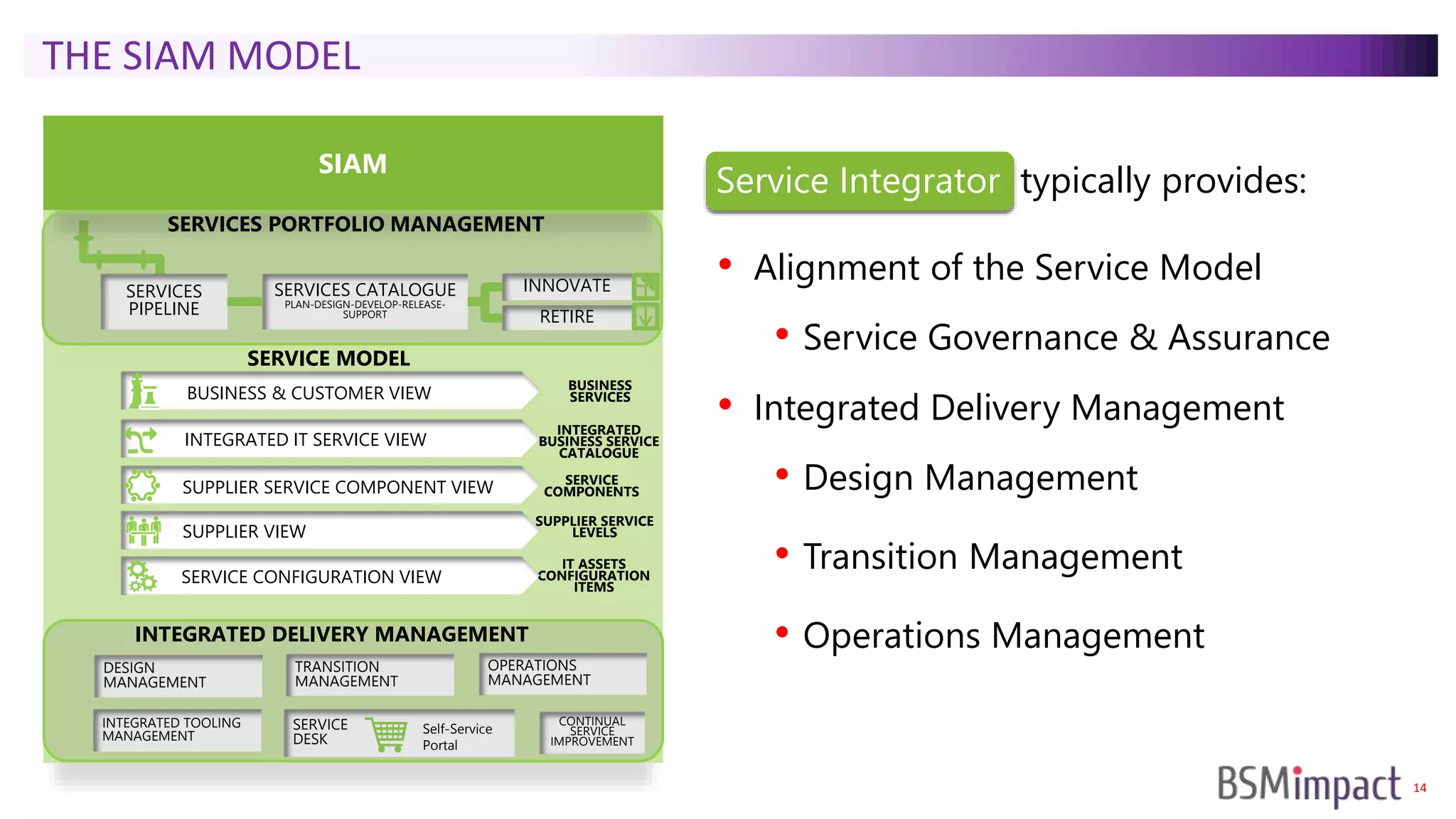
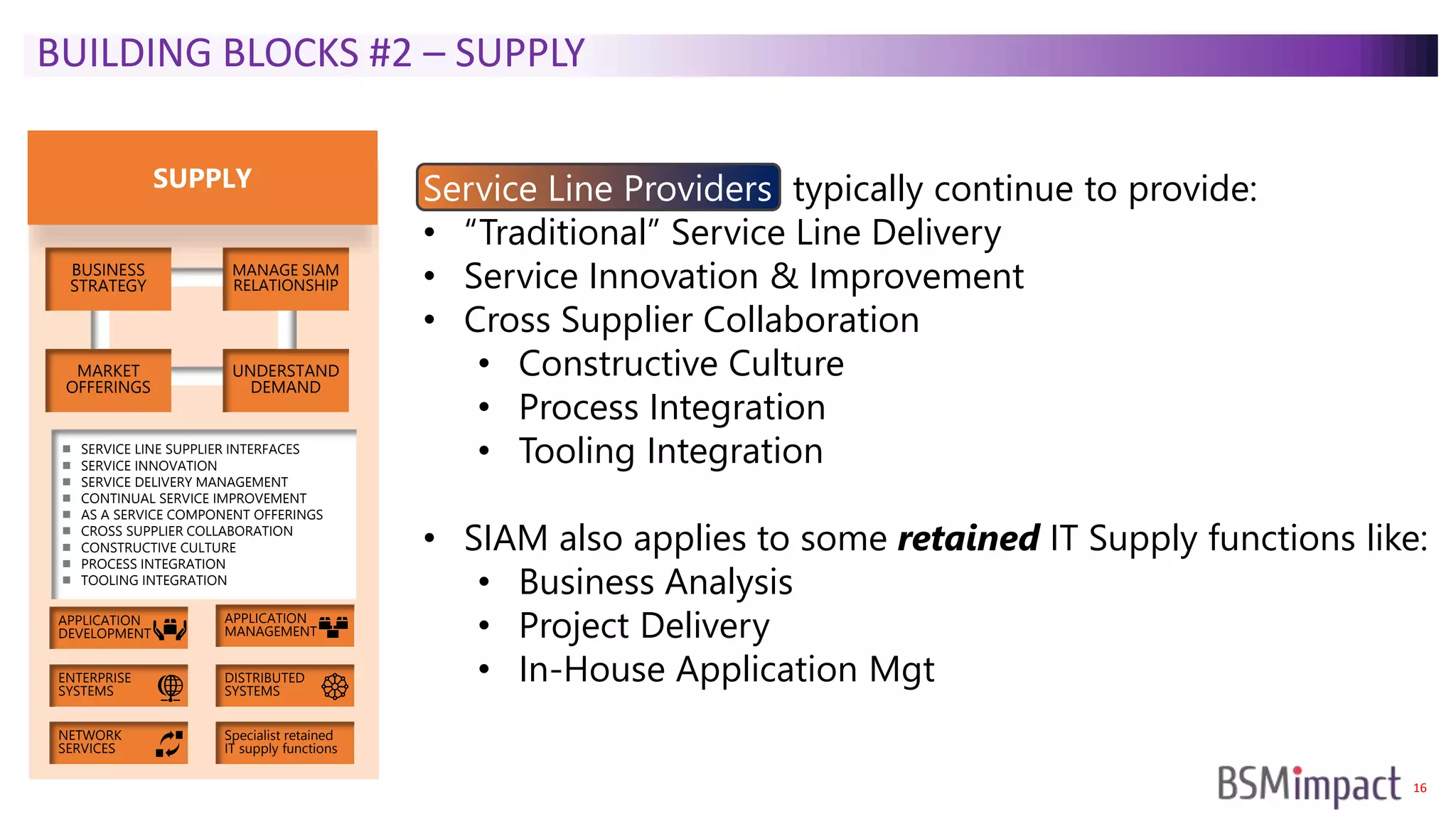
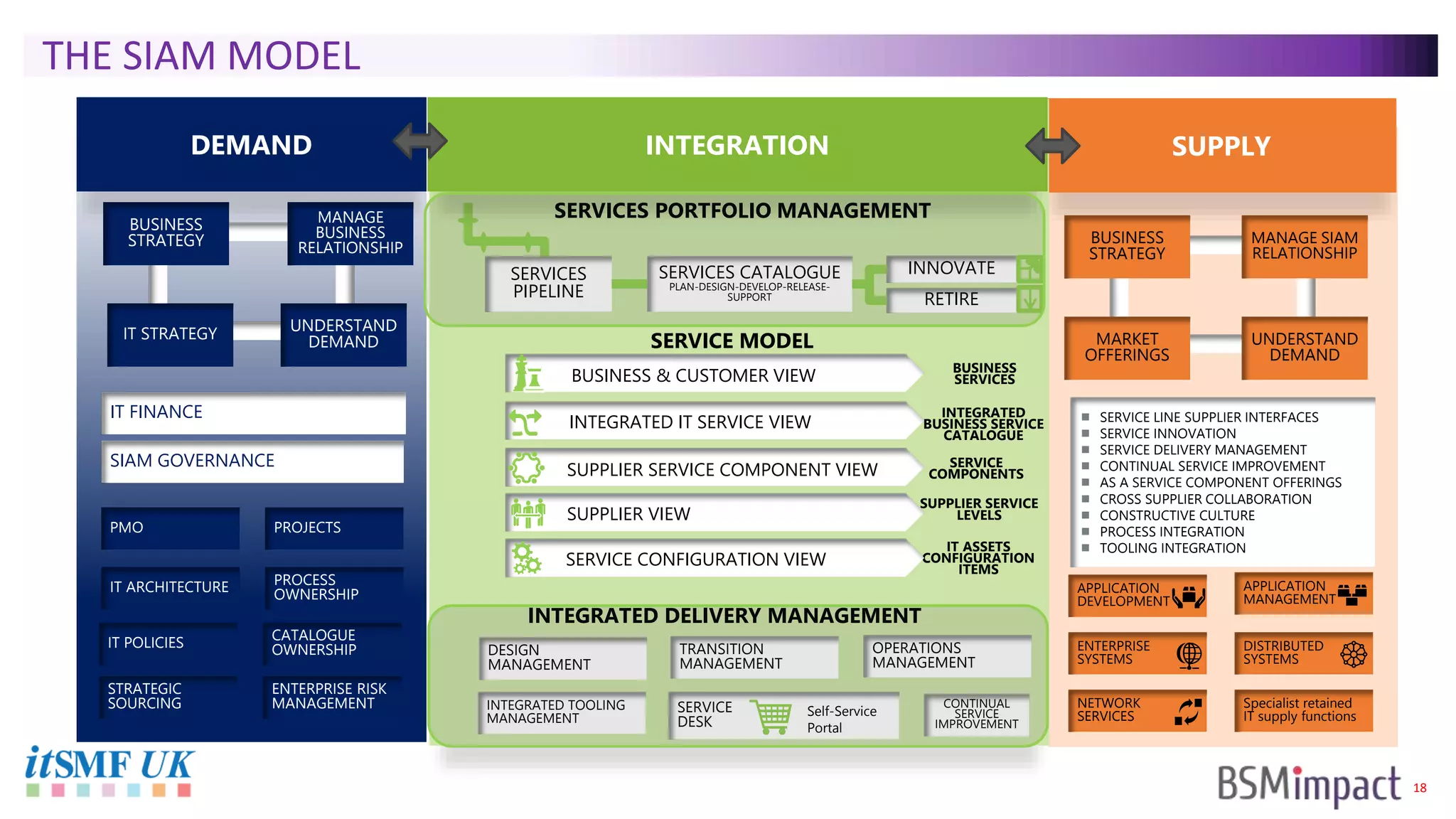
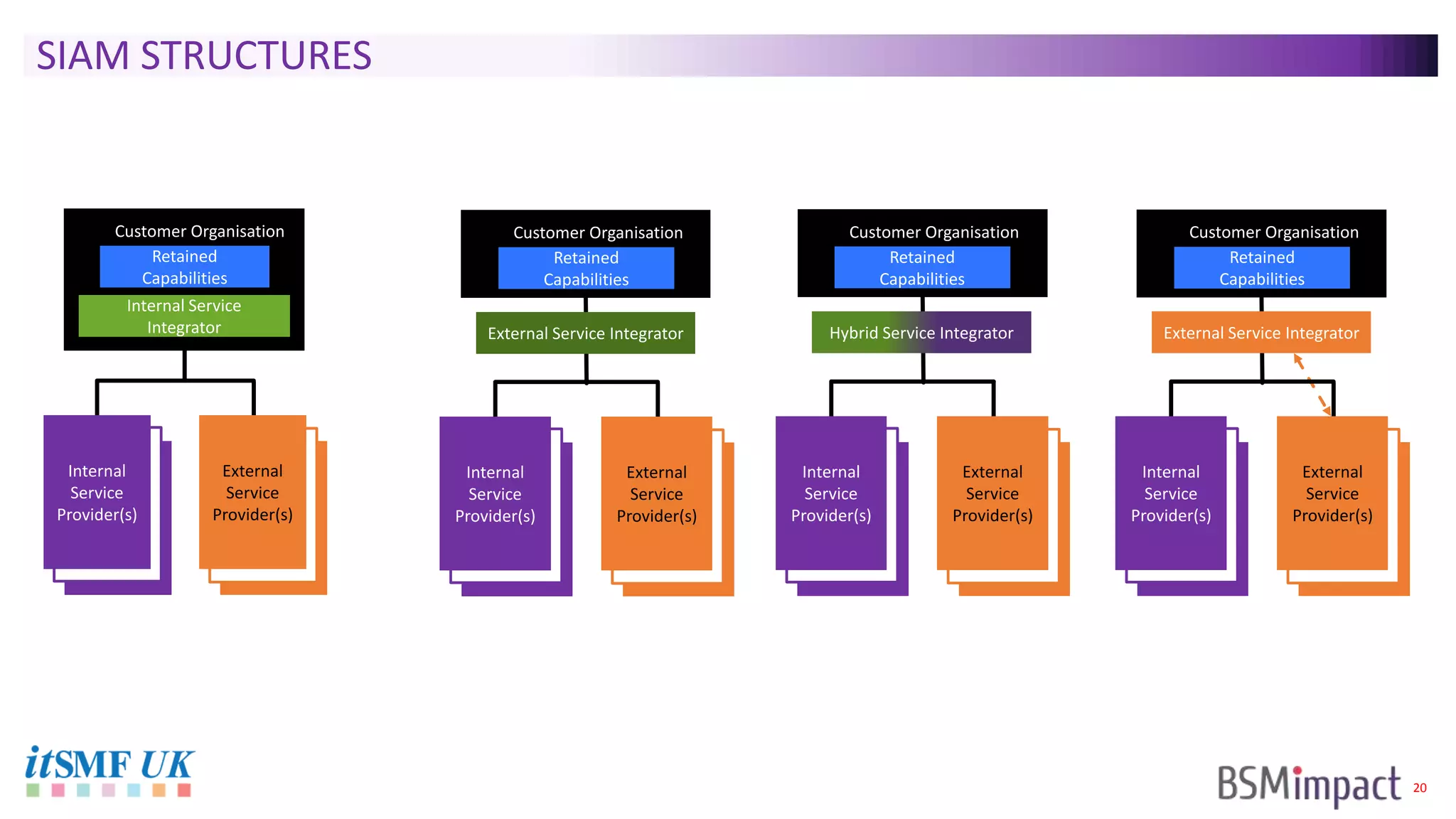
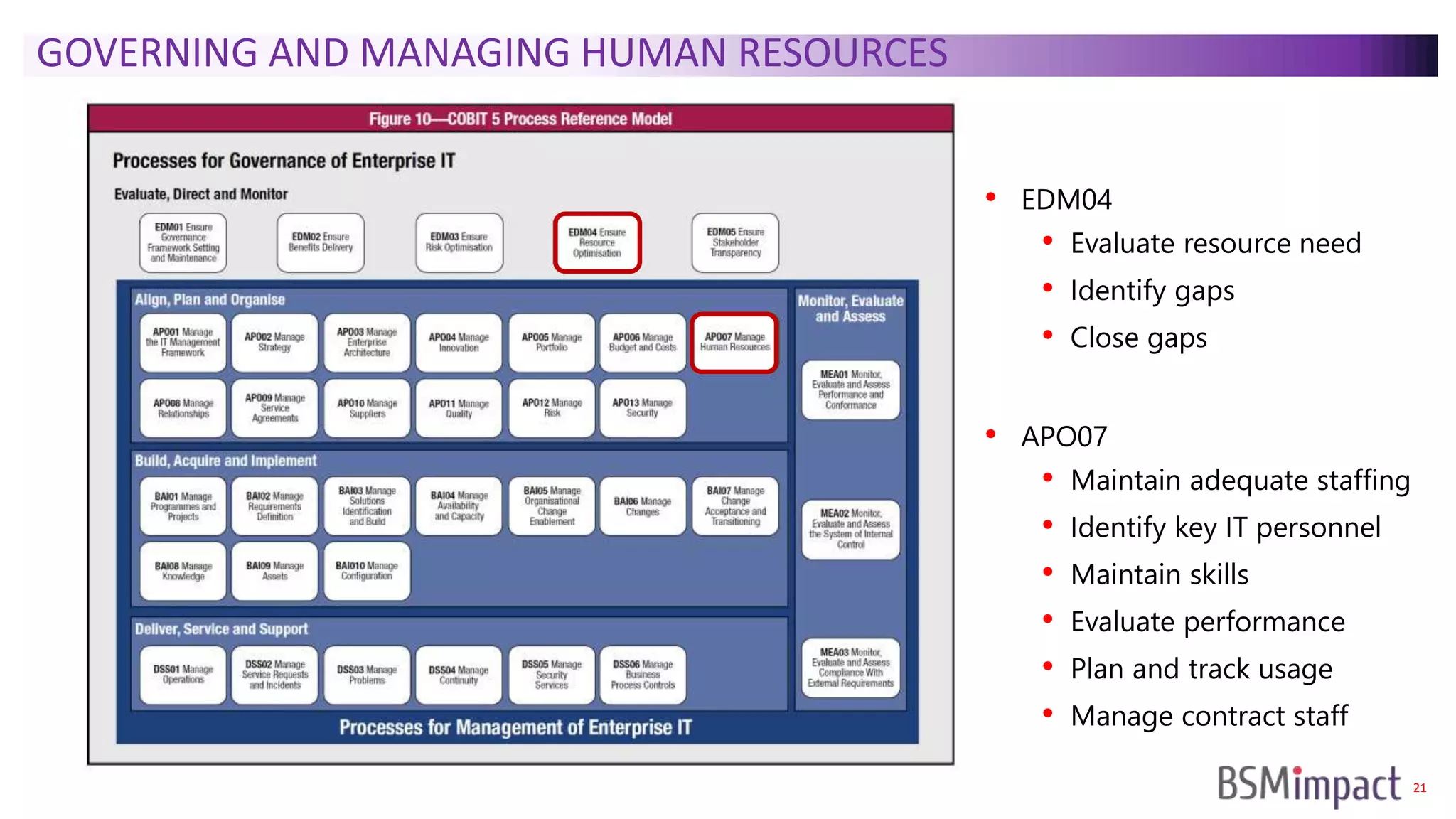
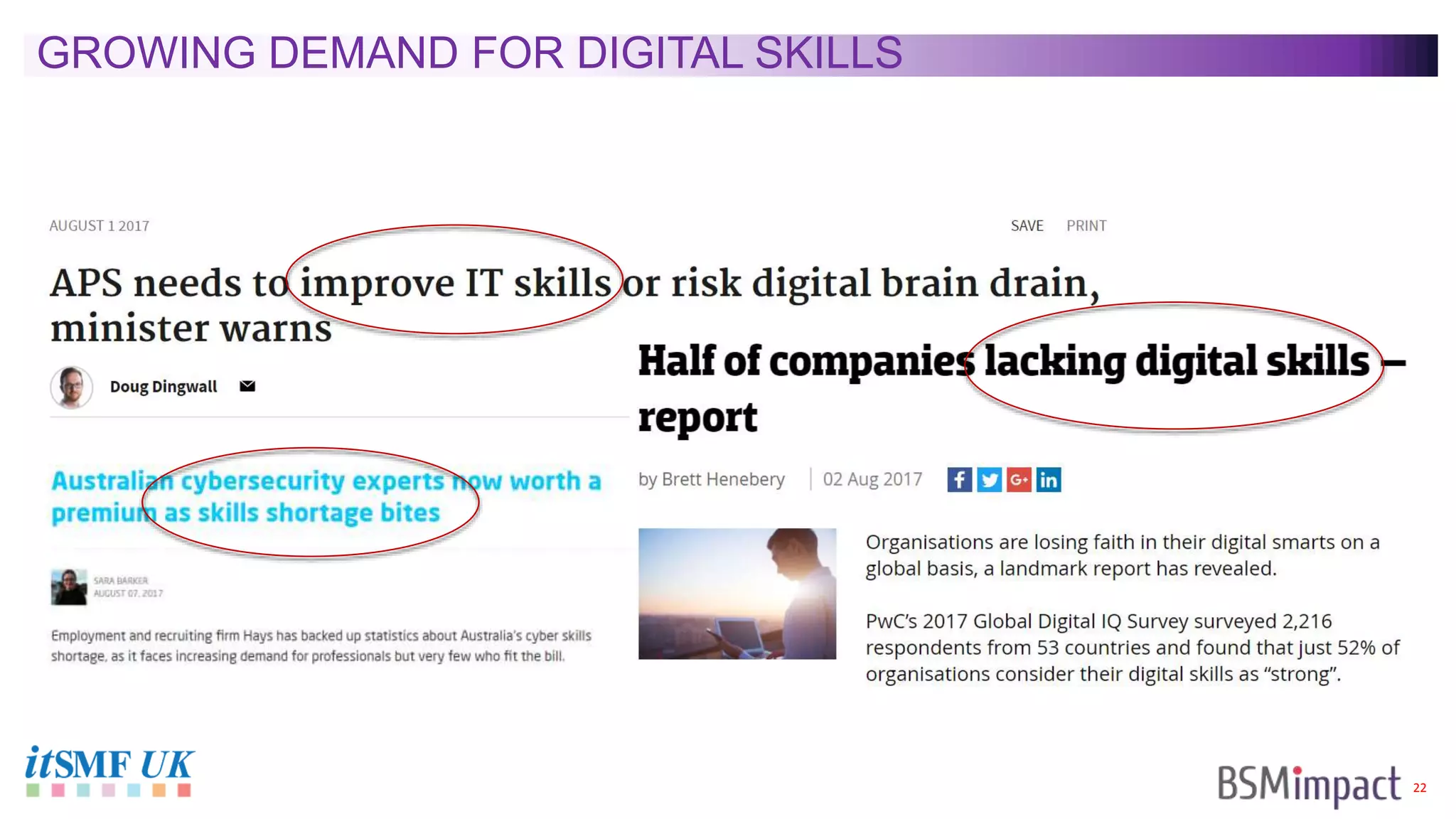
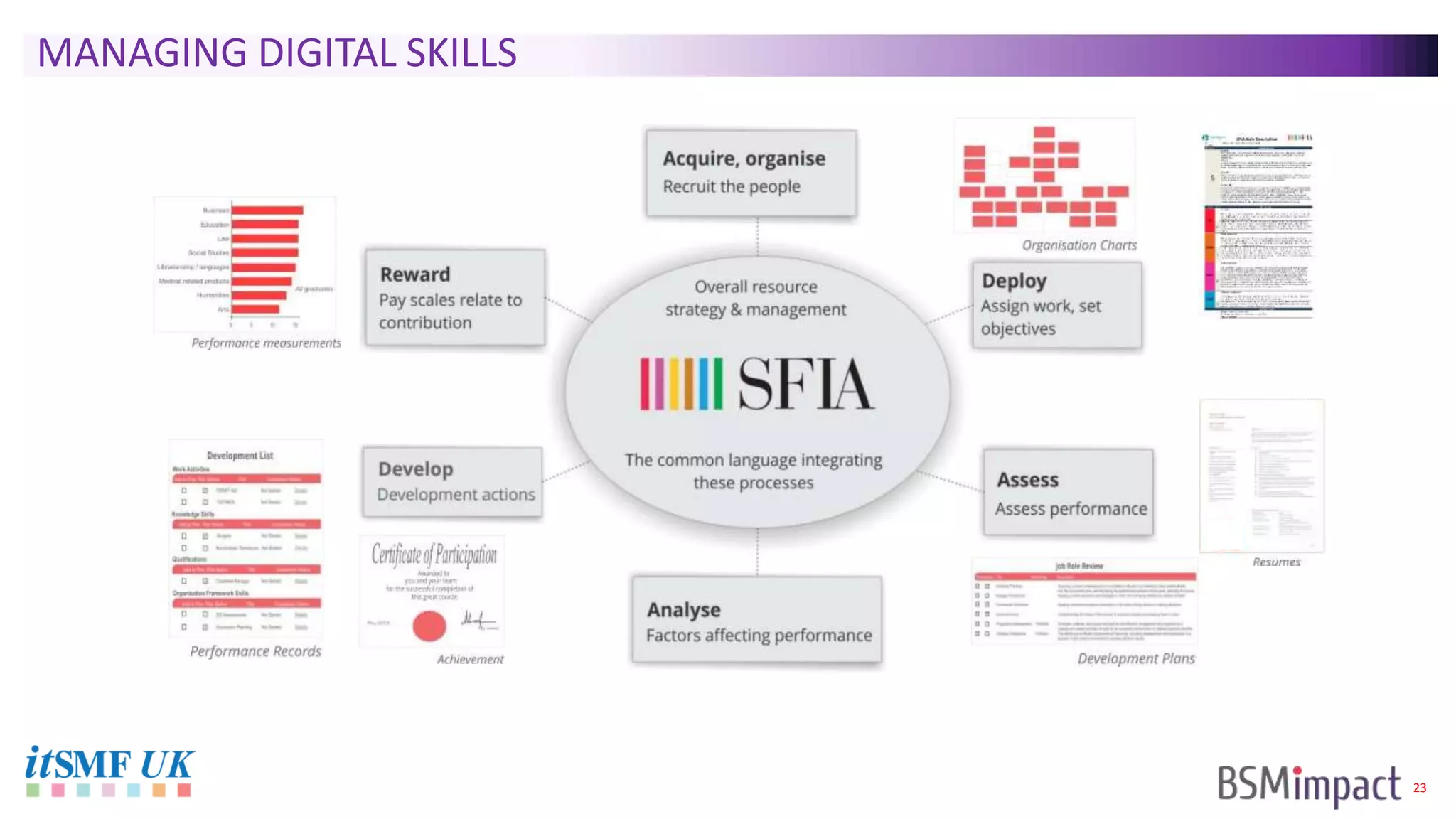
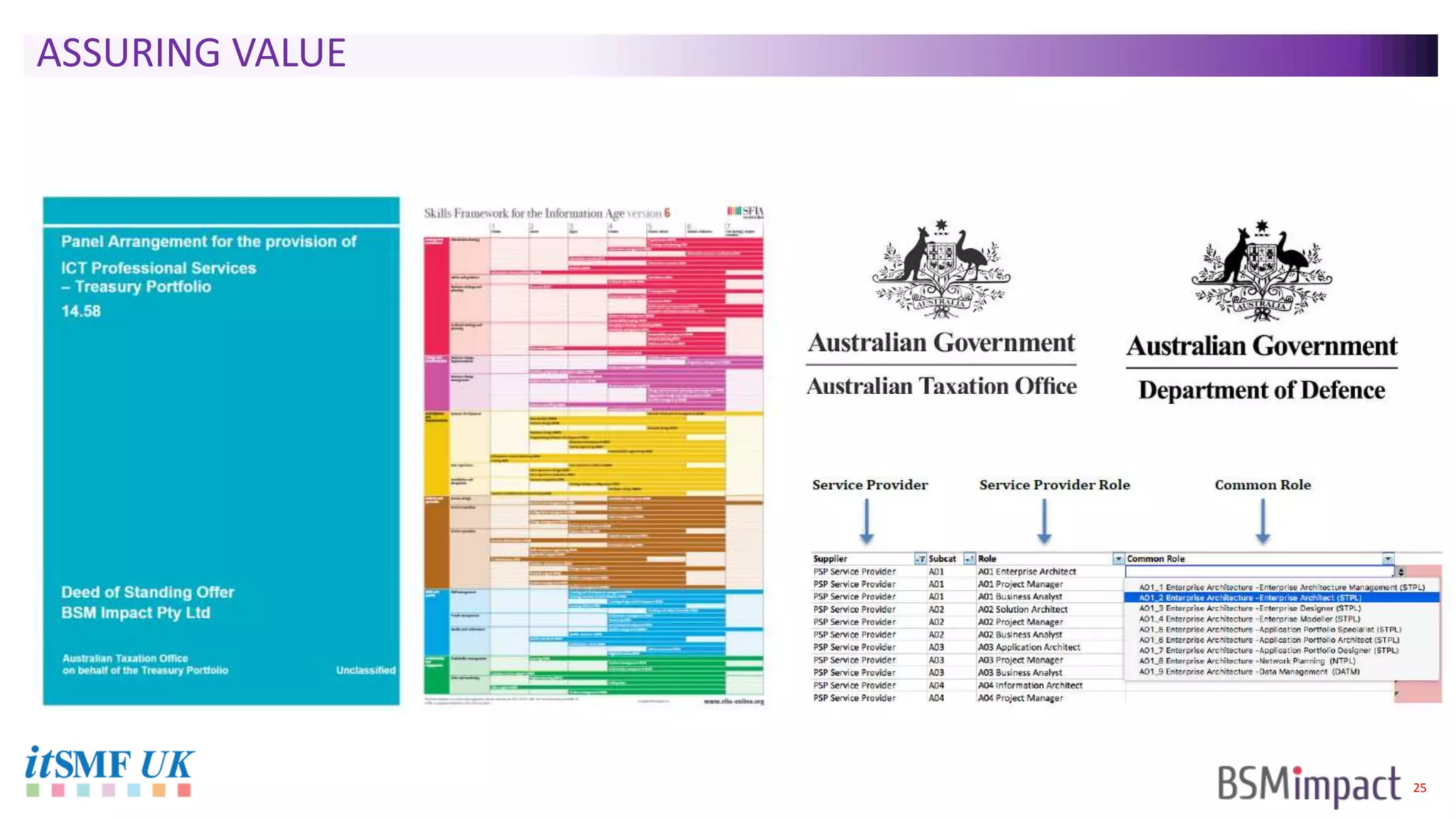
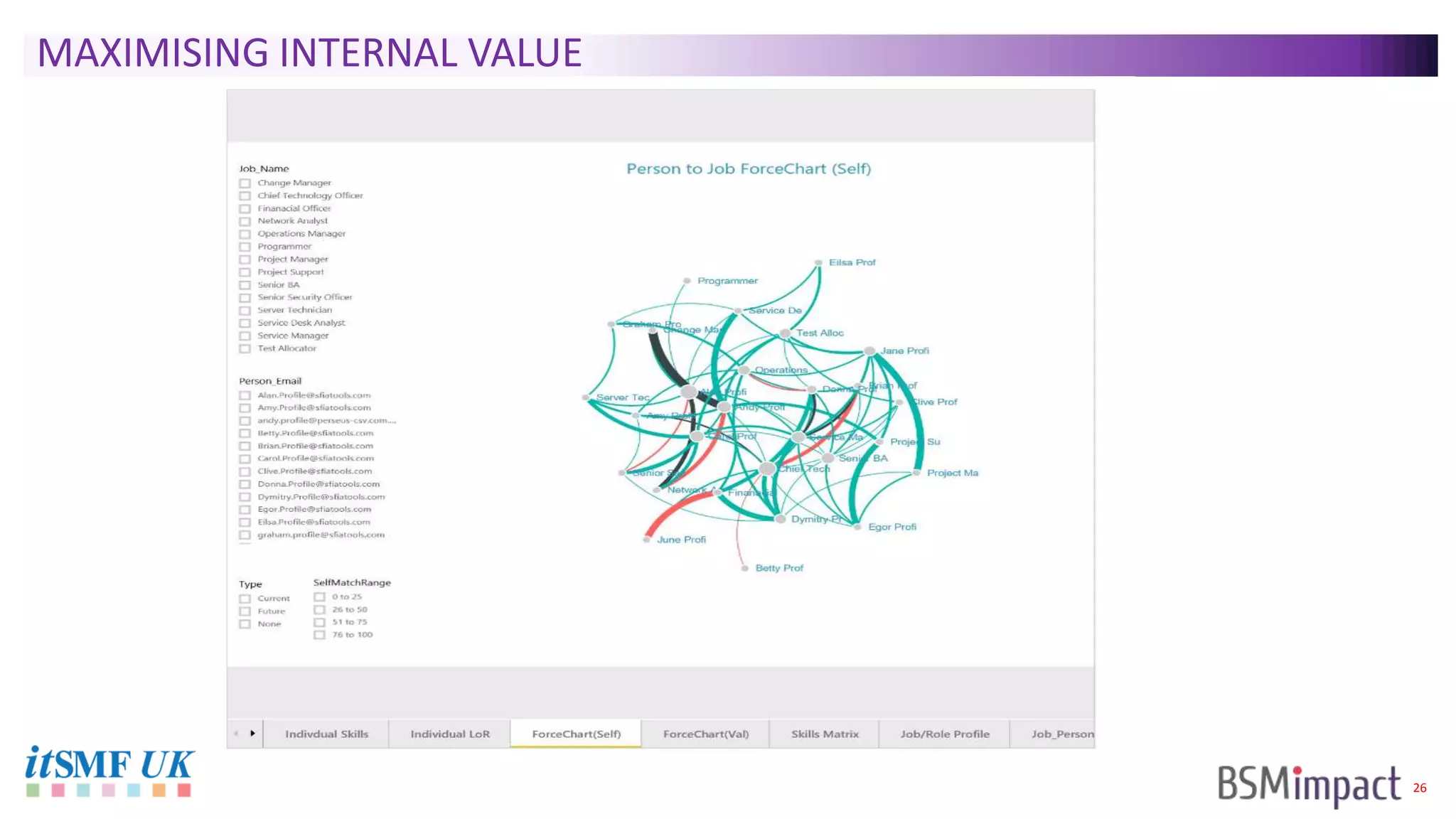
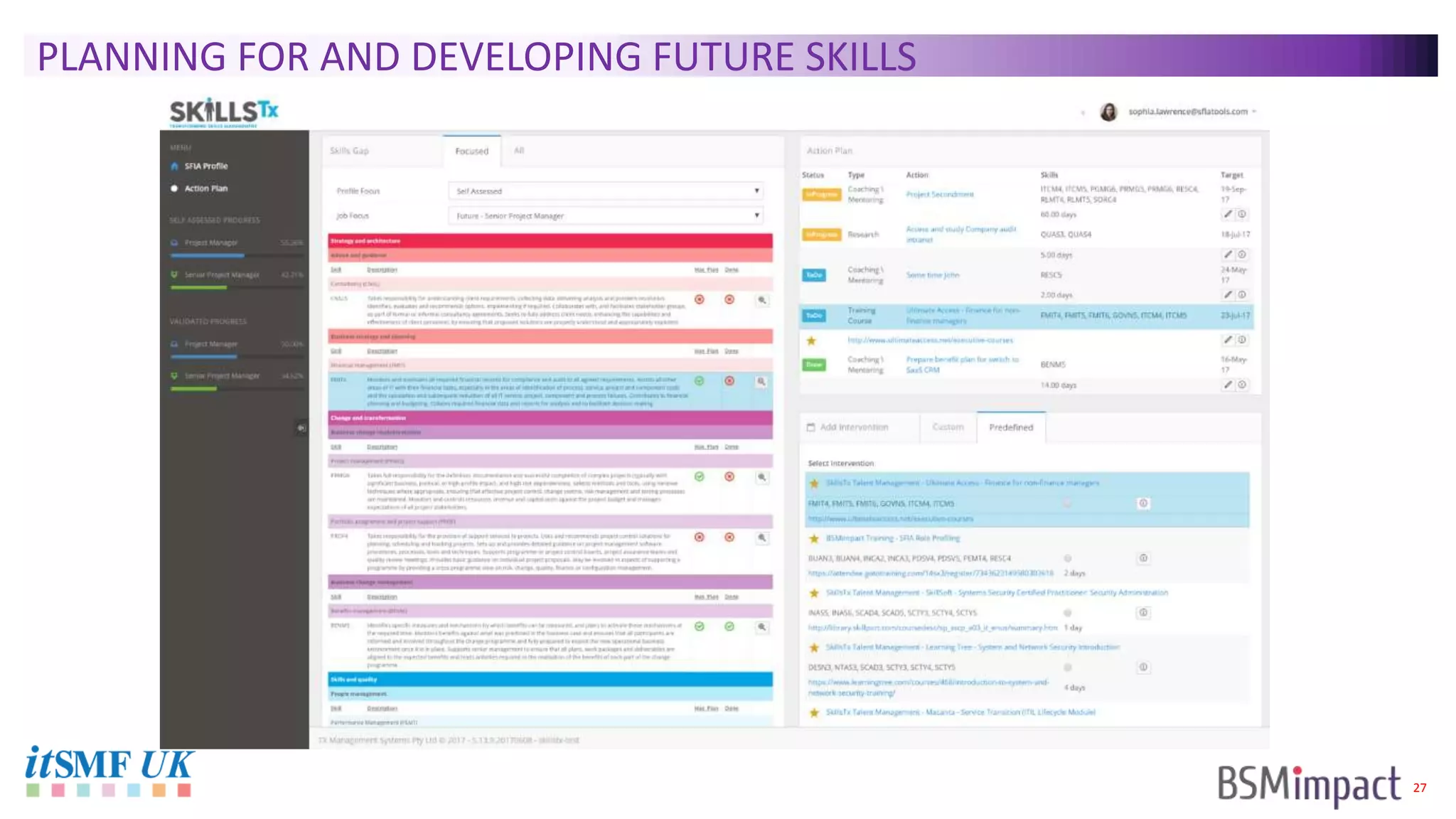
The document discusses Service Integration and Management (SIAM) and digital skills management. It describes SIAM as a framework for managing a complex, multi-supplier IT environment through integrated governance, management, delivery, and assurance processes. It also addresses the growing demand for digital skills and how organizations can baseline current capabilities, design an operating model, and create a transition plan to develop needed skills over 12 weeks or less.