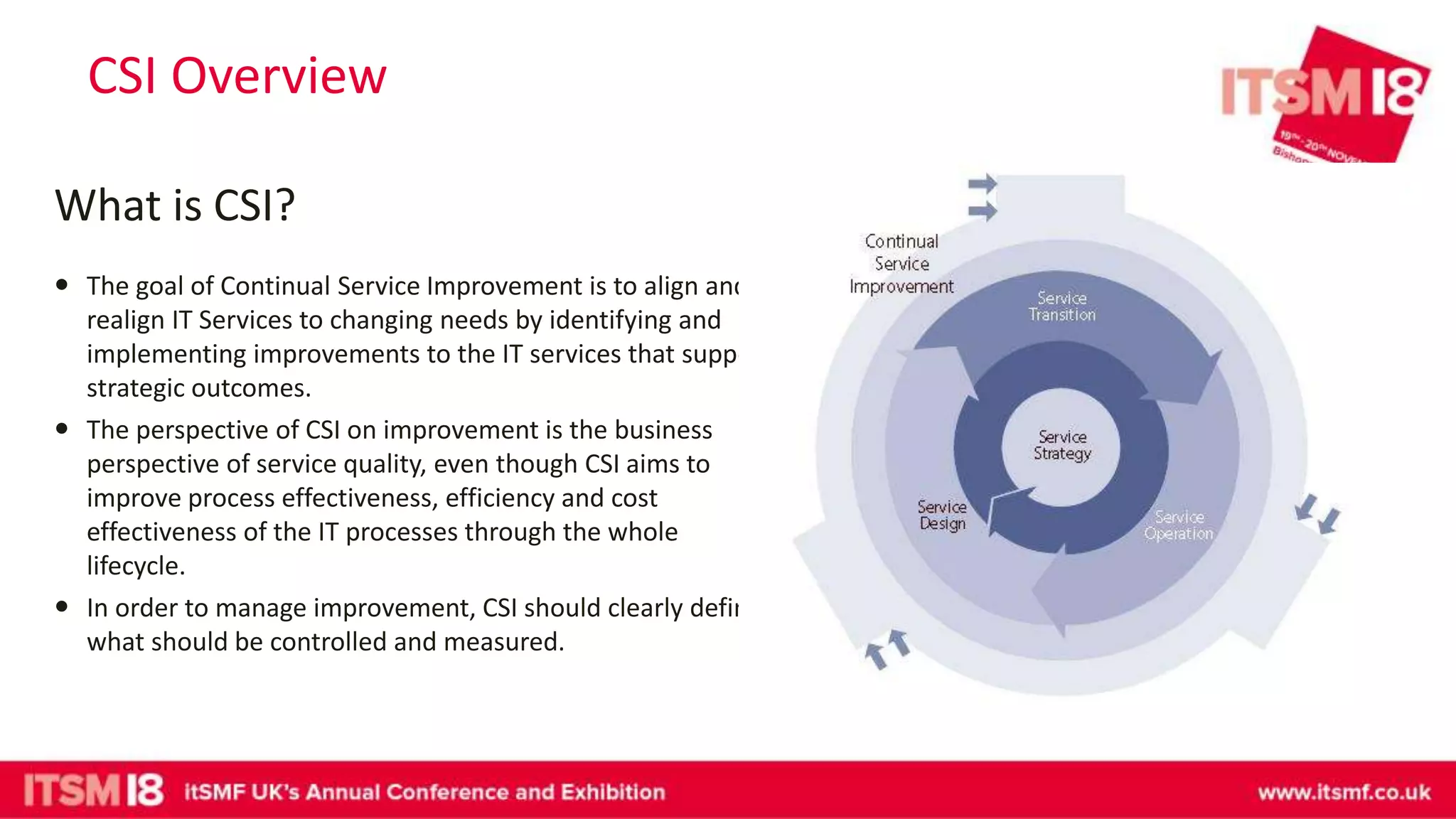
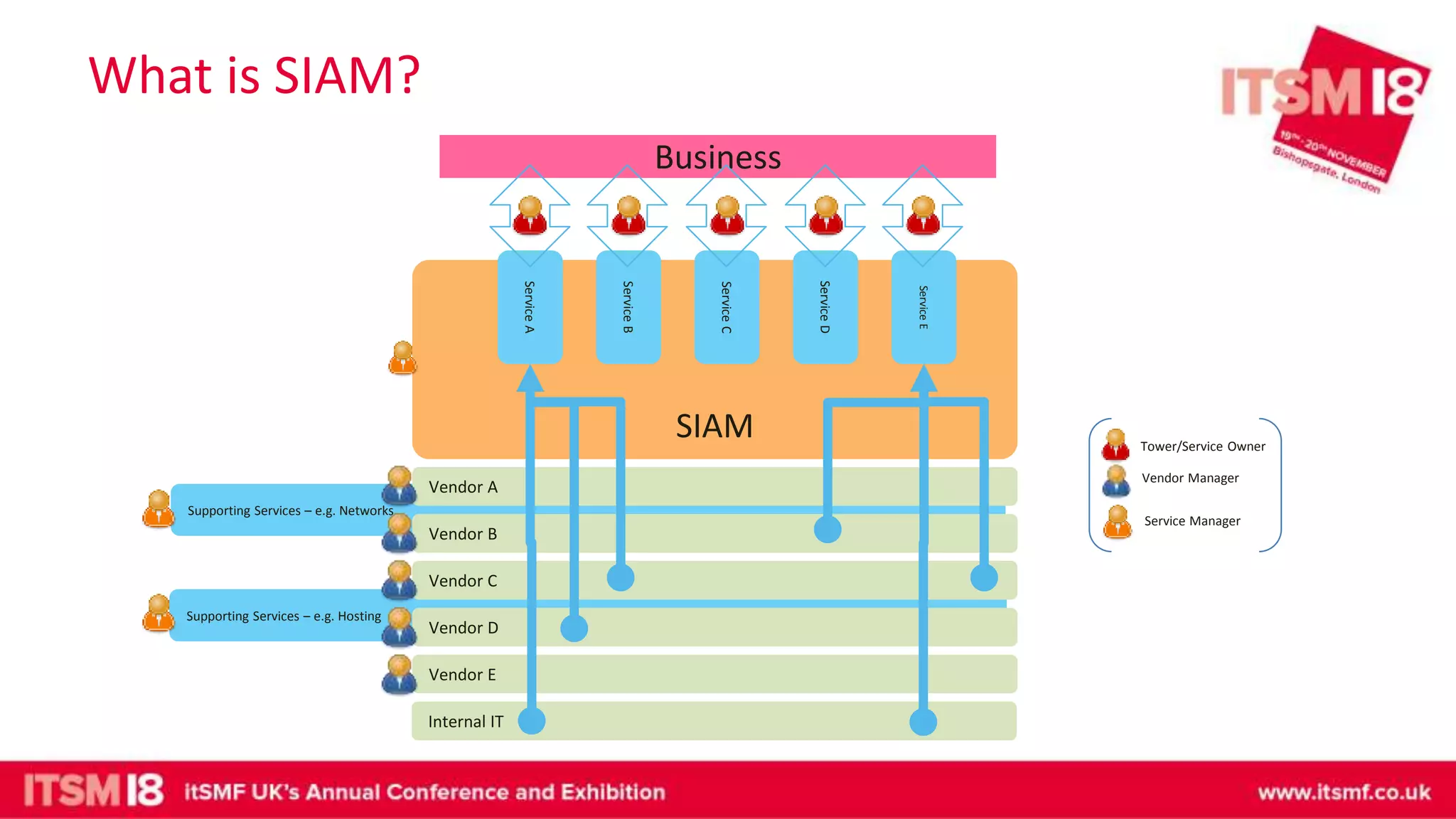
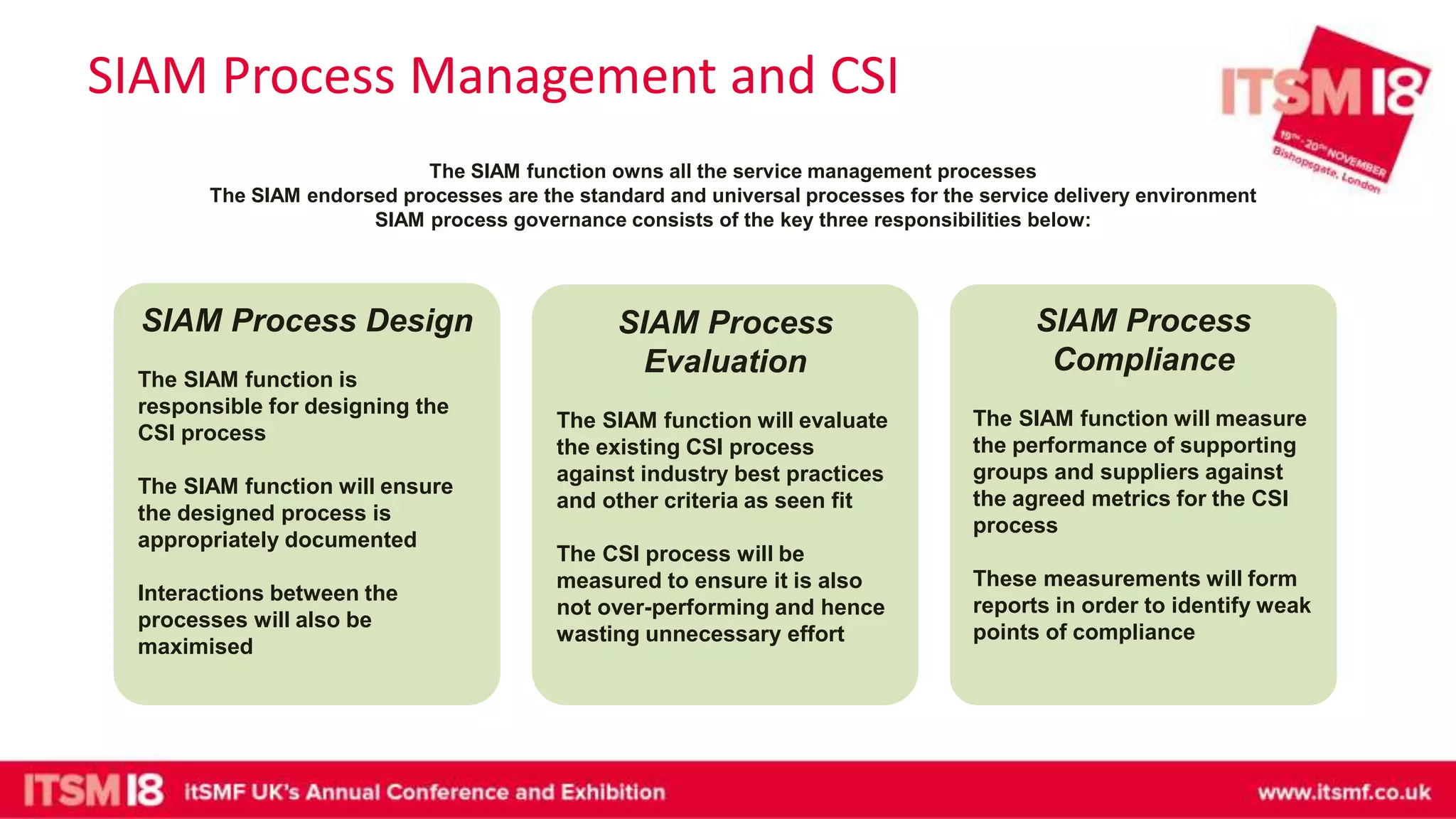
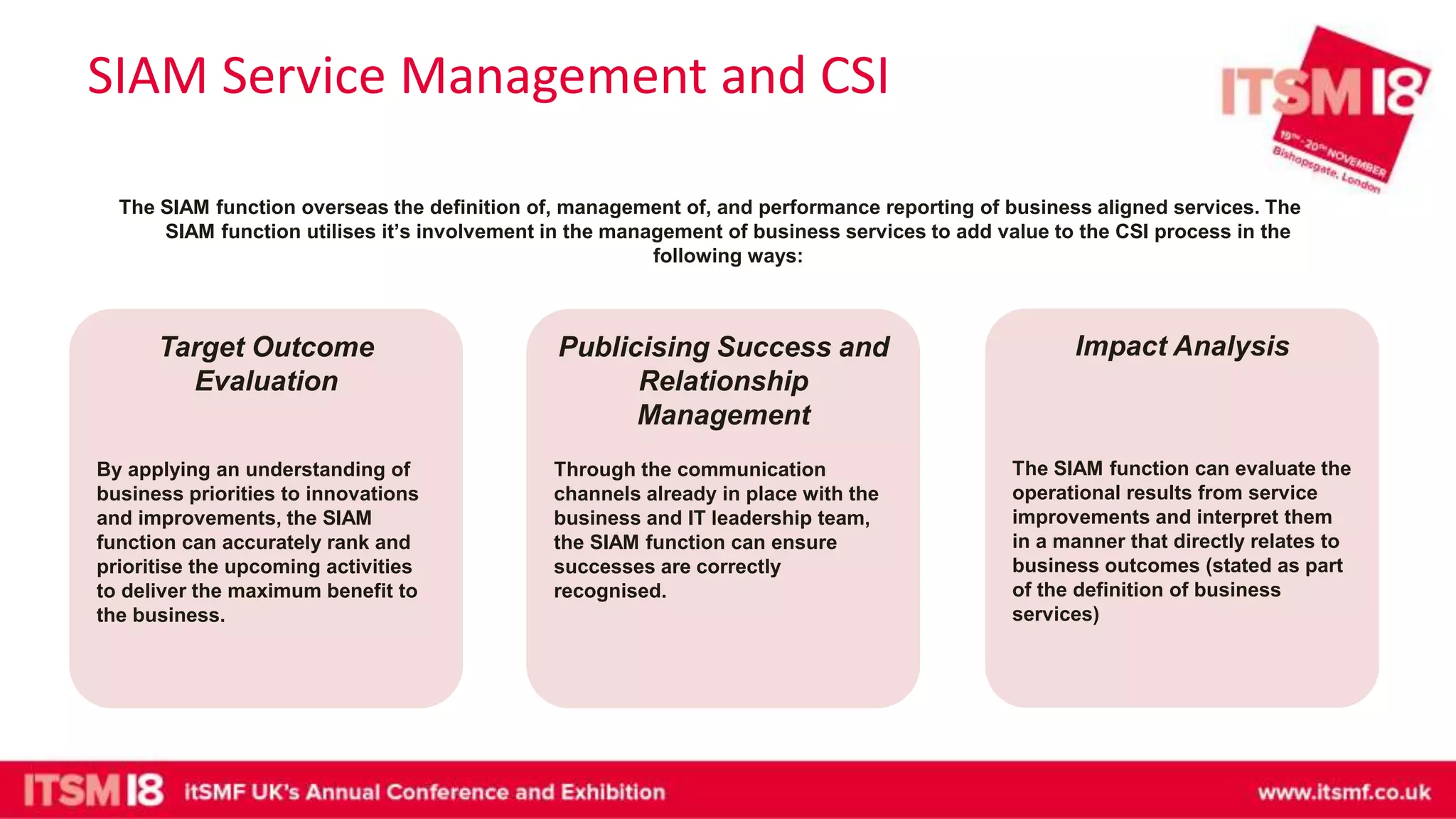
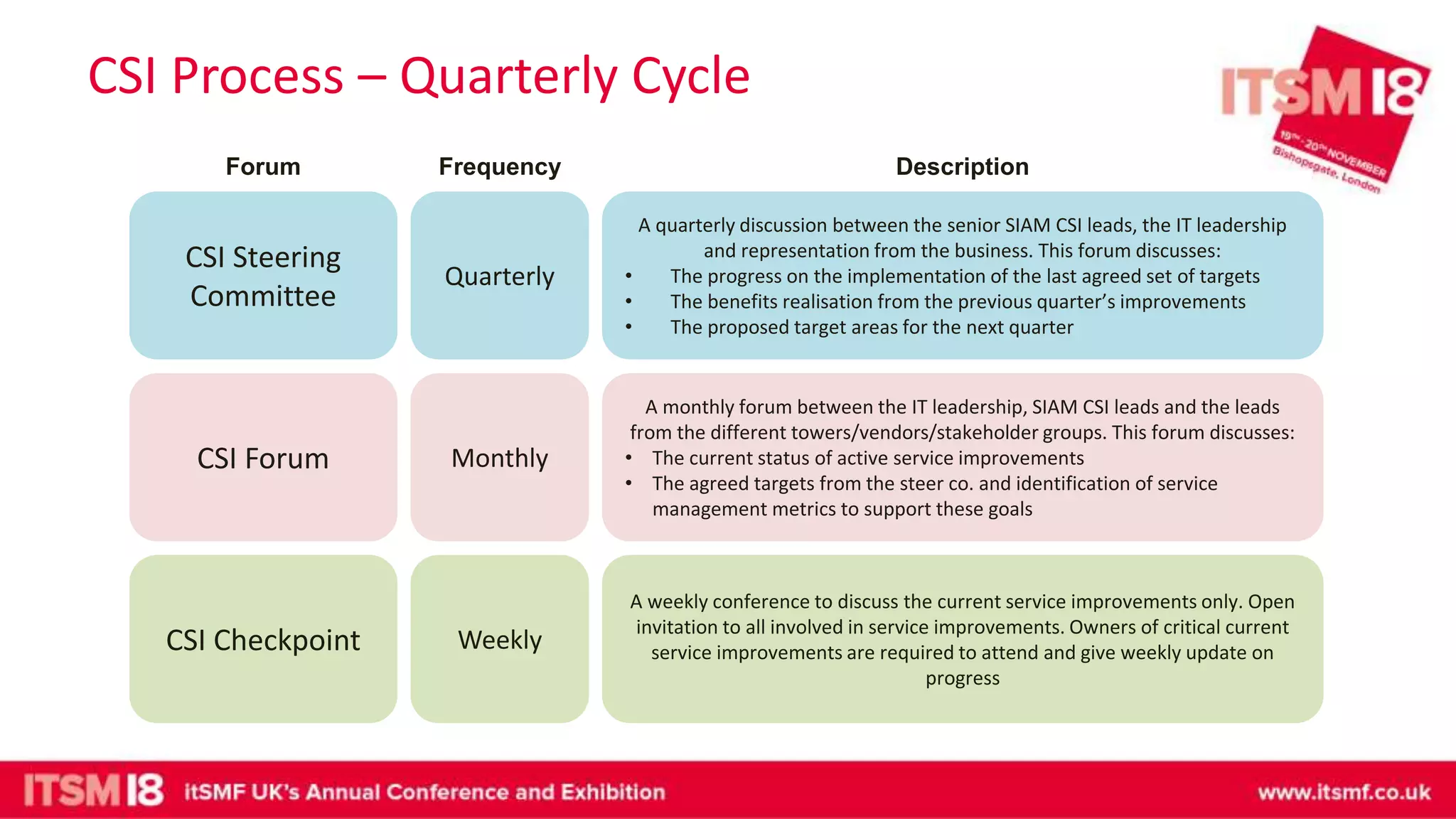
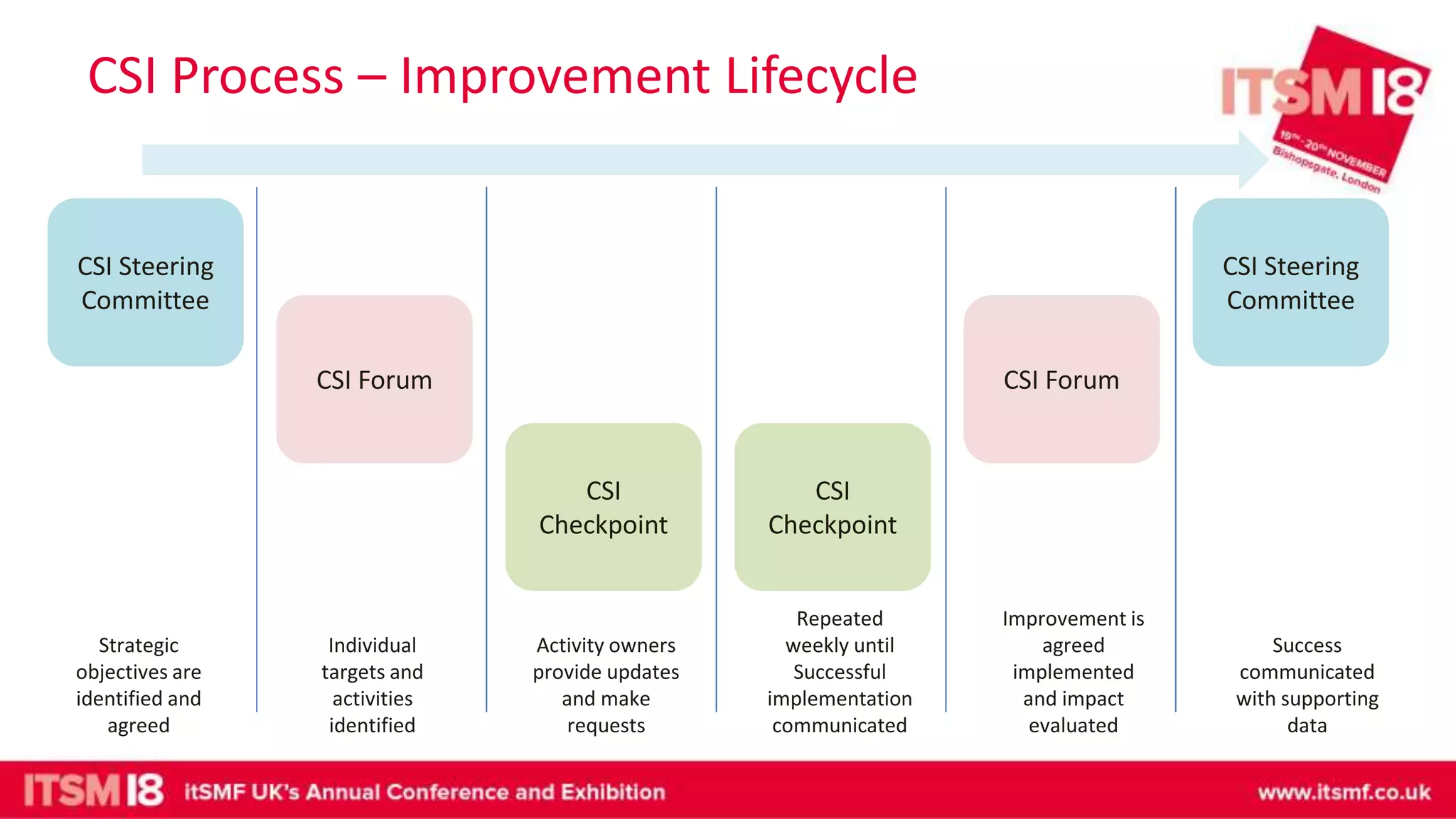
The document discusses continual service improvement (CSI) in the context of a Service Integration and Management (SIAM) environment, emphasizing the need to align IT services with business goals. It outlines the challenges of traditional service improvement approaches, advocating for a more integrated and cooperative method among vendors to enhance service delivery. Key functions of SIAM, such as process management, vendor management, and service management, are highlighted as crucial for effectively implementing and measuring CSI initiatives.