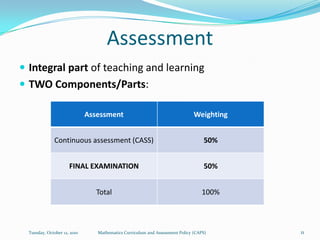
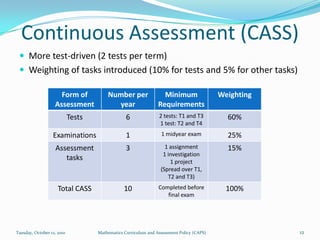
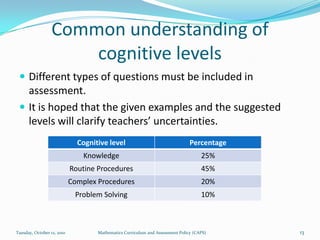
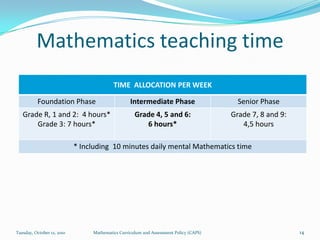
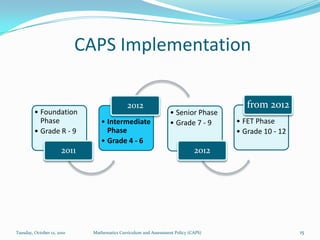
The document outlines the new Curriculum and Assessment Policy Statement (CAPS) for mathematics in the Intermediate Phase (grades 4-6) in South Africa. CAPS aims to simplify and strengthen the existing curriculum by filling gaps, ensuring progression between grades, and providing clear guidelines for teachers. It focuses on developing strong conceptual understanding through content-based learning, mental calculations, and problem solving. Assessment will have two components - continuous and common tasks - with clearer cognitive levels and weightings defined. Feedback from teachers and stakeholders informed changes to streamline the curriculum while maintaining high standards.