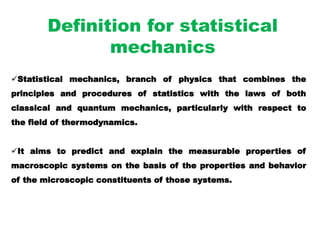
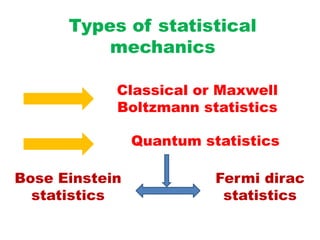
Statistical mechanics combines principles of statistics and mechanics to predict and explain measurable properties of macroscopic systems based on microscopic constituents. It discusses three types of statistics: classical Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics, Bose-Einstein statistics for integer spin particles like photons allowing multiple occupancy, and Fermi-Dirac statistics for half-integer spin fermions like electrons following Pauli's exclusion principle of single occupancy. The document provides examples and characteristics of each statistical approach.



![Classical or Maxwell Boltzmann [MB]
Statistics Characteristics
Identical
Distinguishable
Any spin
Example: Molecules of gas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematicalphysicsandstatisticalmechanics-200819130252/85/Mathematical-physics-and-statistical-mechanics-6-320.jpg)
![Bose Einstein [BE] Statistics
Characteristics
Identical
Indistinguishable
Zero or integral spin
Particles are called bosons
Example: Helium atoms at low
temperature, photons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematicalphysicsandstatisticalmechanics-200819130252/85/Mathematical-physics-and-statistical-mechanics-8-320.jpg)

![Fermi dirac [FD] Statistics
Characteristics
Identical
Indistinguishable
Half integral spin [eg:1/2, 3/2 etc]
Particles are called fermions
Example: electrons,protons,neutrons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematicalphysicsandstatisticalmechanics-200819130252/85/Mathematical-physics-and-statistical-mechanics-10-320.jpg)


