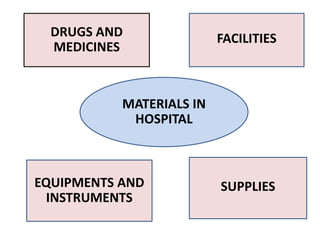
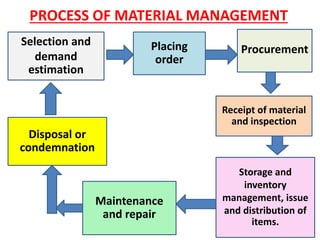
The document discusses material management in healthcare. It defines material management as the planning, organizing, and control of materials from initial purchase through final use. Material management aims to ensure a continuous supply of materials needed for patient care at the right price through processes like demand estimation, procurement, storage, and maintenance. It integrates functions like purchasing, inventory control, and disposal to efficiently manage over 40% of healthcare funds spent on materials.