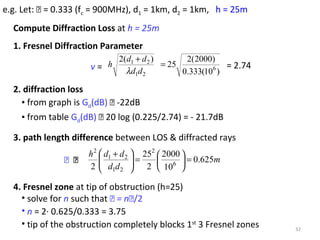
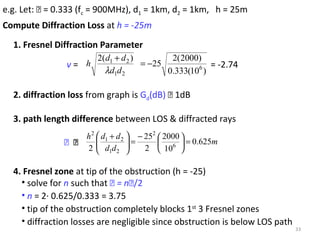
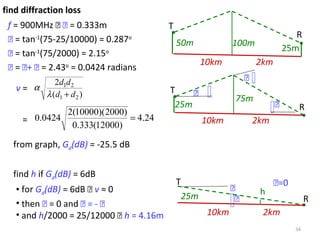
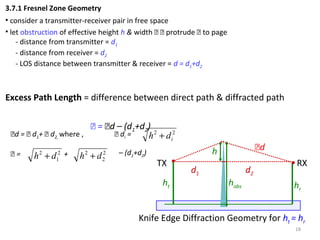
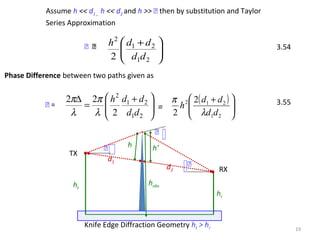
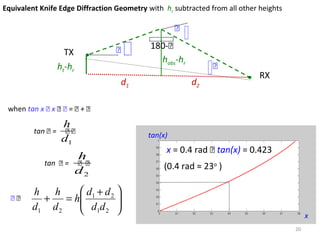
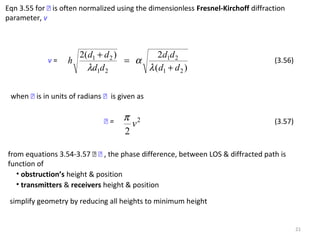
1) The document discusses propagation models for wireless communication systems, including free space propagation and the Fresnel zone model.
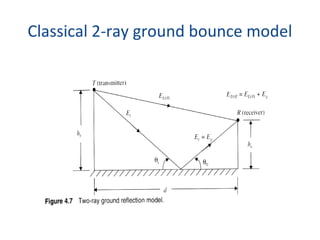
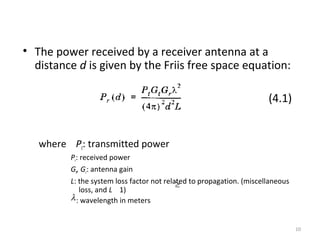
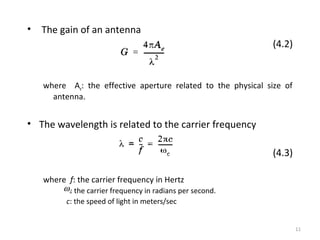
2) Free space propagation assumes a clear line-of-sight path between the transmitter and receiver. Received power is calculated using the Friis transmission equation and depends on transmitted power, antenna gains, wavelength, and distance between antennas.
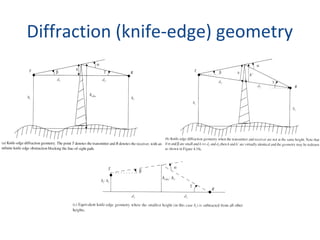
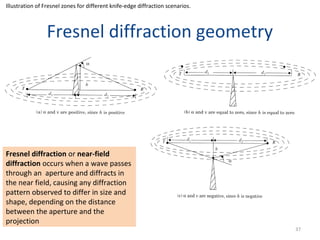
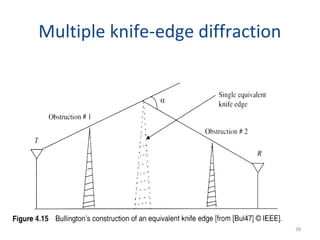
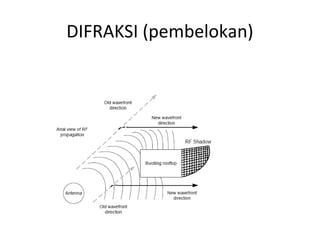
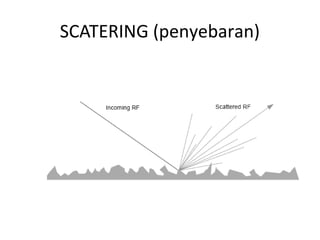
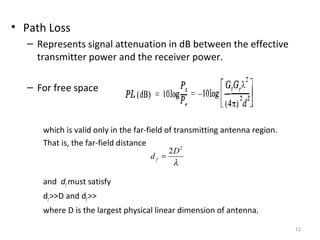
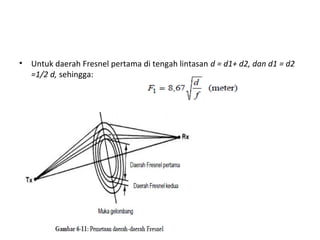
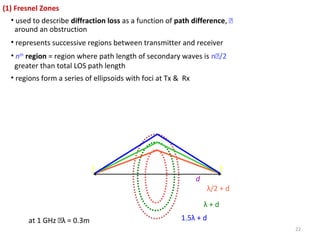
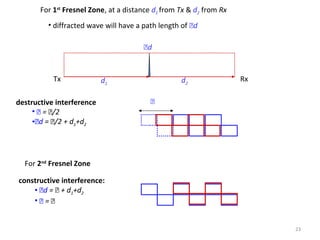
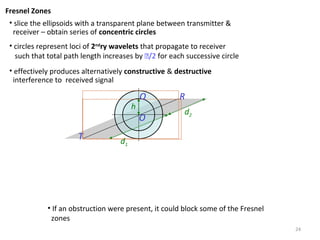
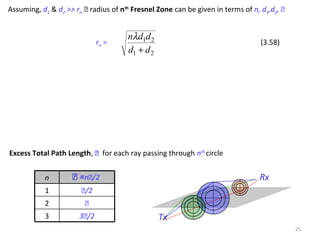
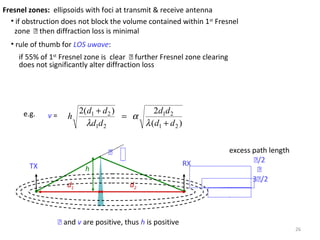
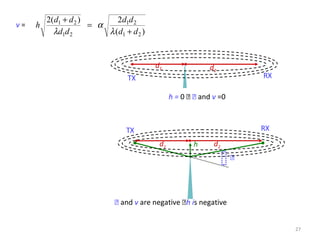
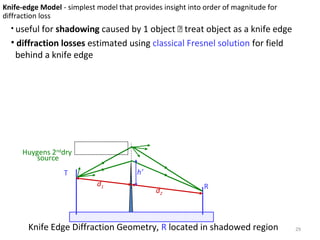
3) The Fresnel zone model describes diffraction of radio waves around obstructions. It represents successive regions between transmitter and receiver where the secondary path length increases in increments of half the wavelength. Blocking of the first Fresnel zone can significantly increase diffraction loss.








![31
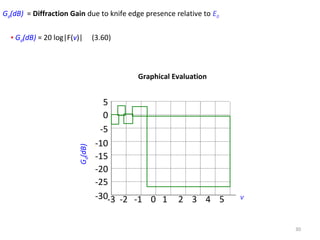
Table for Gd(dB)
[0,1]20 log(0.5 e- 0.95v
)
[-1,0]20 log(0.5-0.62v)
> 2.420 log(0.225/v)
[1, 2.4]20 log(0.4-(0.1184-(0.38-0.1v)2
)1/2
)
-10
vGd(dB)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/materikul6fesnel-140526003454-phpapp02/85/Materi-kul6-fesnel-31-320.jpg)