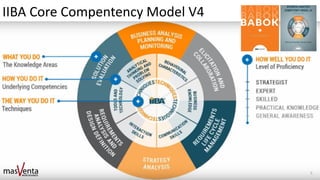
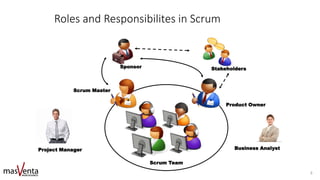
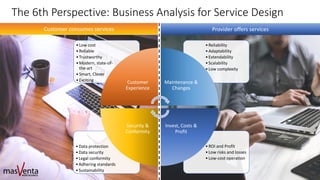
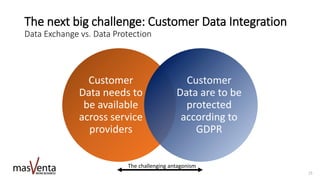
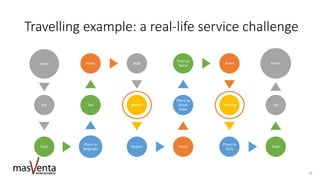
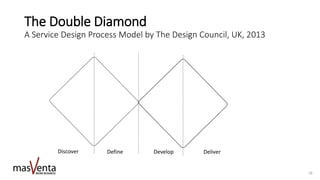
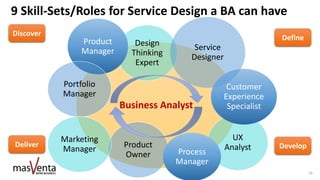
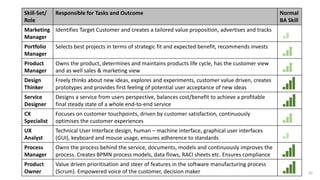
The document emphasizes the importance of sharp business analysis skills over holding a formal title as a business analyst, highlighting that many roles involve business analysis tasks. It discusses the CBAP® certification as a gold standard for business analysts and outlines essential competencies needed in digital business analysis, along with various roles such as product owner and project manager. The text also reflects on the significance of understanding customer experience, embracing agility, and leveraging data in contemporary business environments.

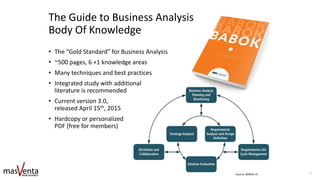
![Definition: Business Analysis is…
“…the practice of
enabling change in
an enterprise
[context] by defining
needs and
recommending
solutions that deliver
value to
stakeholders”
Source: BABOK v3
4
BABOK® v3 - Core Concept Model (BACCM TM).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masventabaskills2019-191013174101/85/masVenta-Business-Analysis-Skills-4-320.jpg)