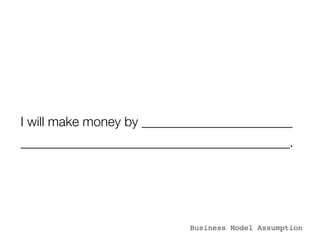
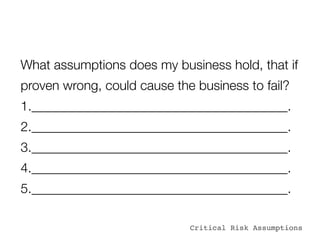
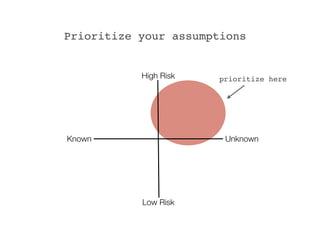
The document discusses how to validate business ideas through experiments and MVPs (minimal viable products) before fully developing them. It emphasizes reducing waste by testing assumptions with customers early. Some examples of experiments mentioned include manual delivery, acting as the software through "concierge" support, pre-sales with letters of intent, landing pages with calls to action, videos, and paper prototypes. It notes that an MVP is not a finished product but an iterative process of learning through customer feedback to find product-market fit. Key aspects of running experiments outlined are having a hypothesis to test, brainstorming different tests, breaking tests into small units, setting goals, reviewing results, and deciding next steps.