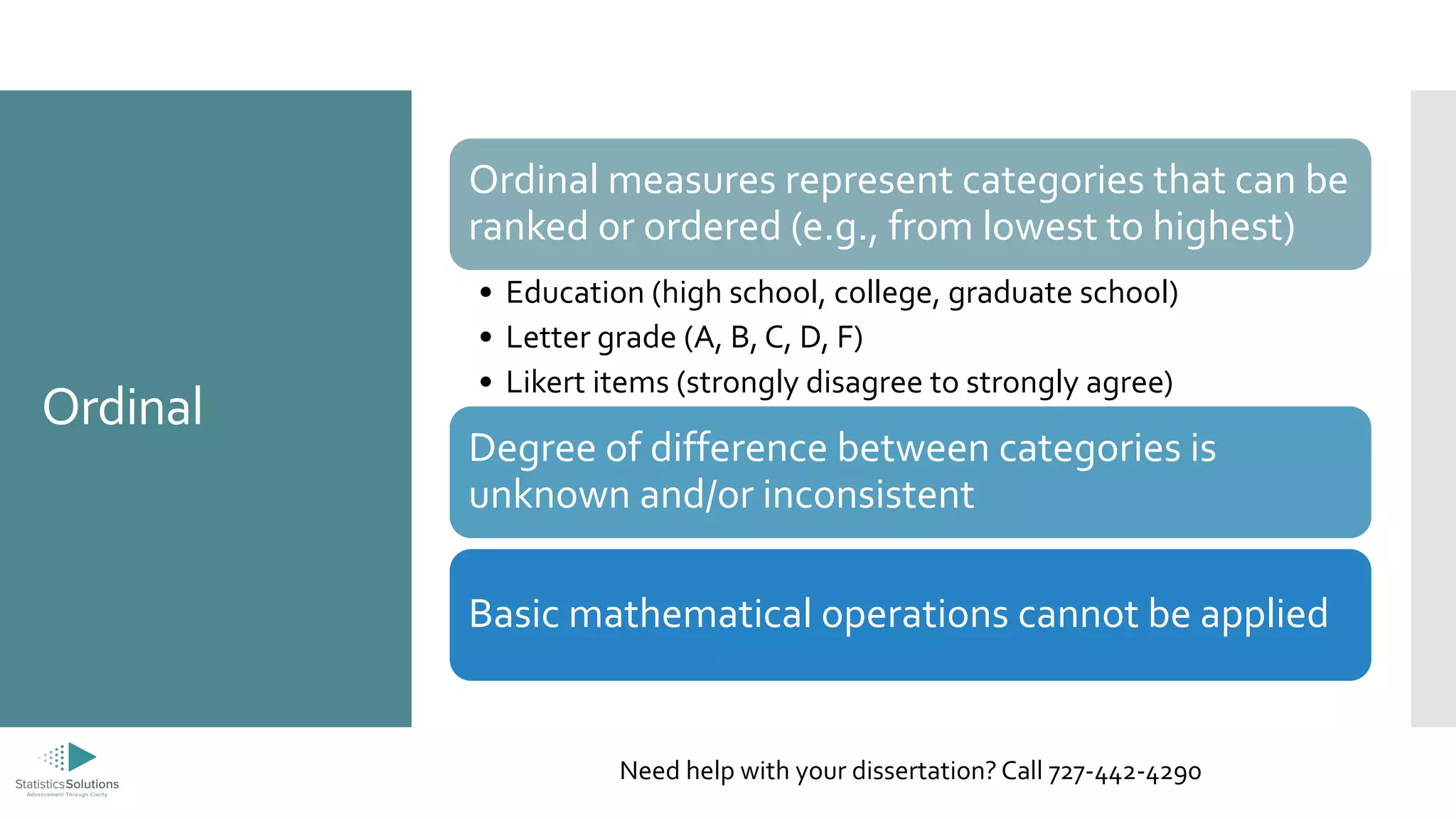
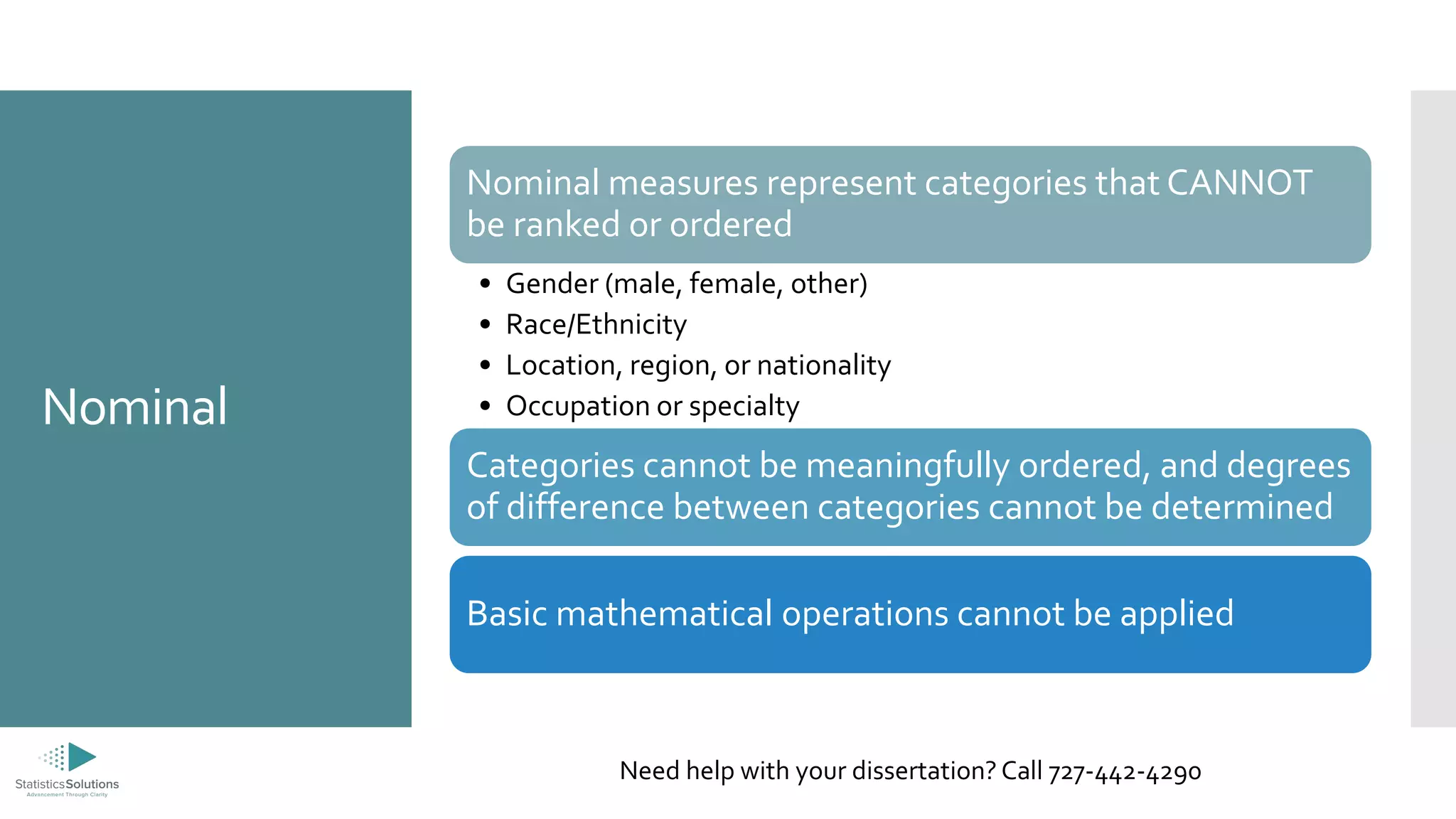
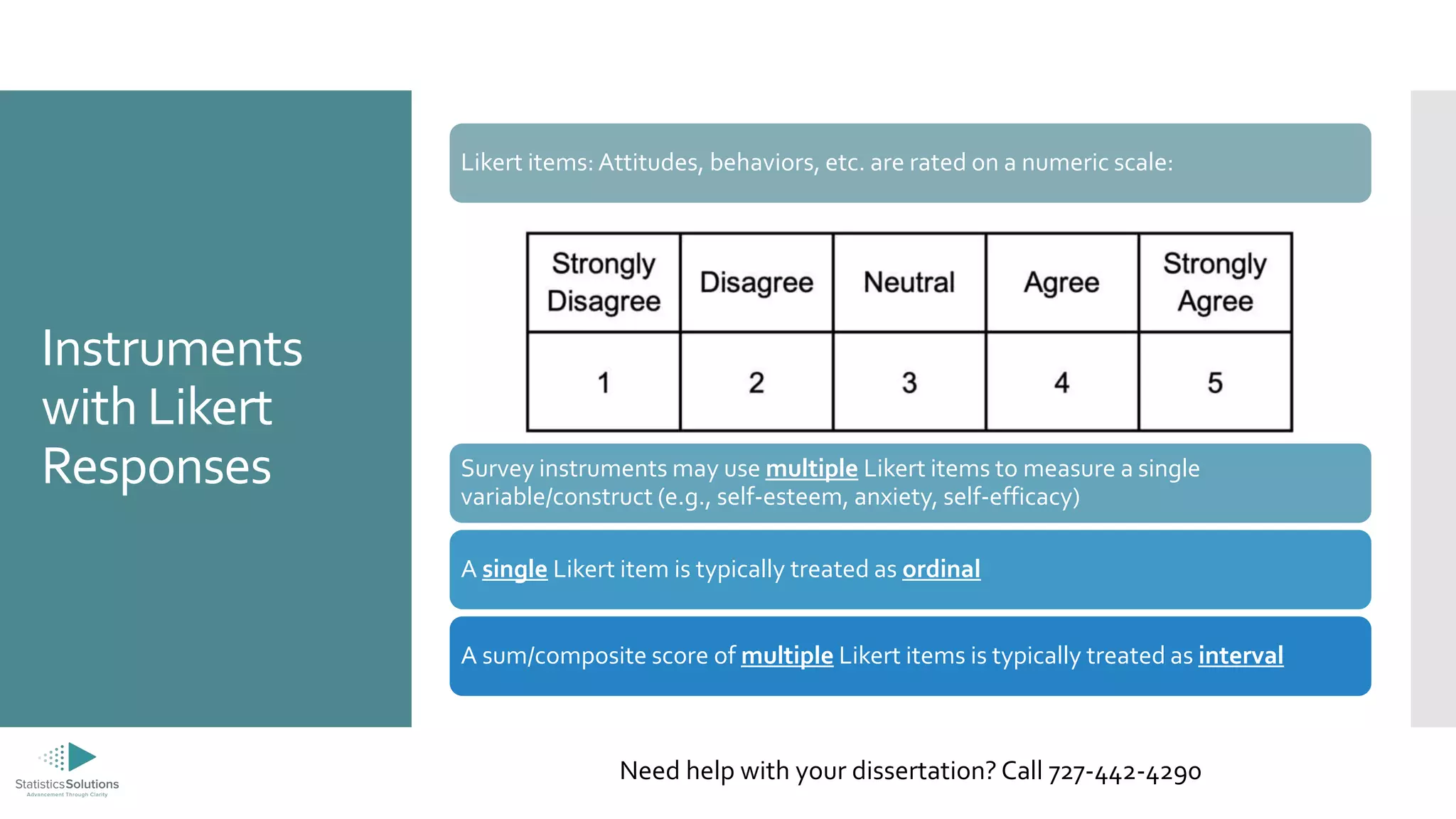
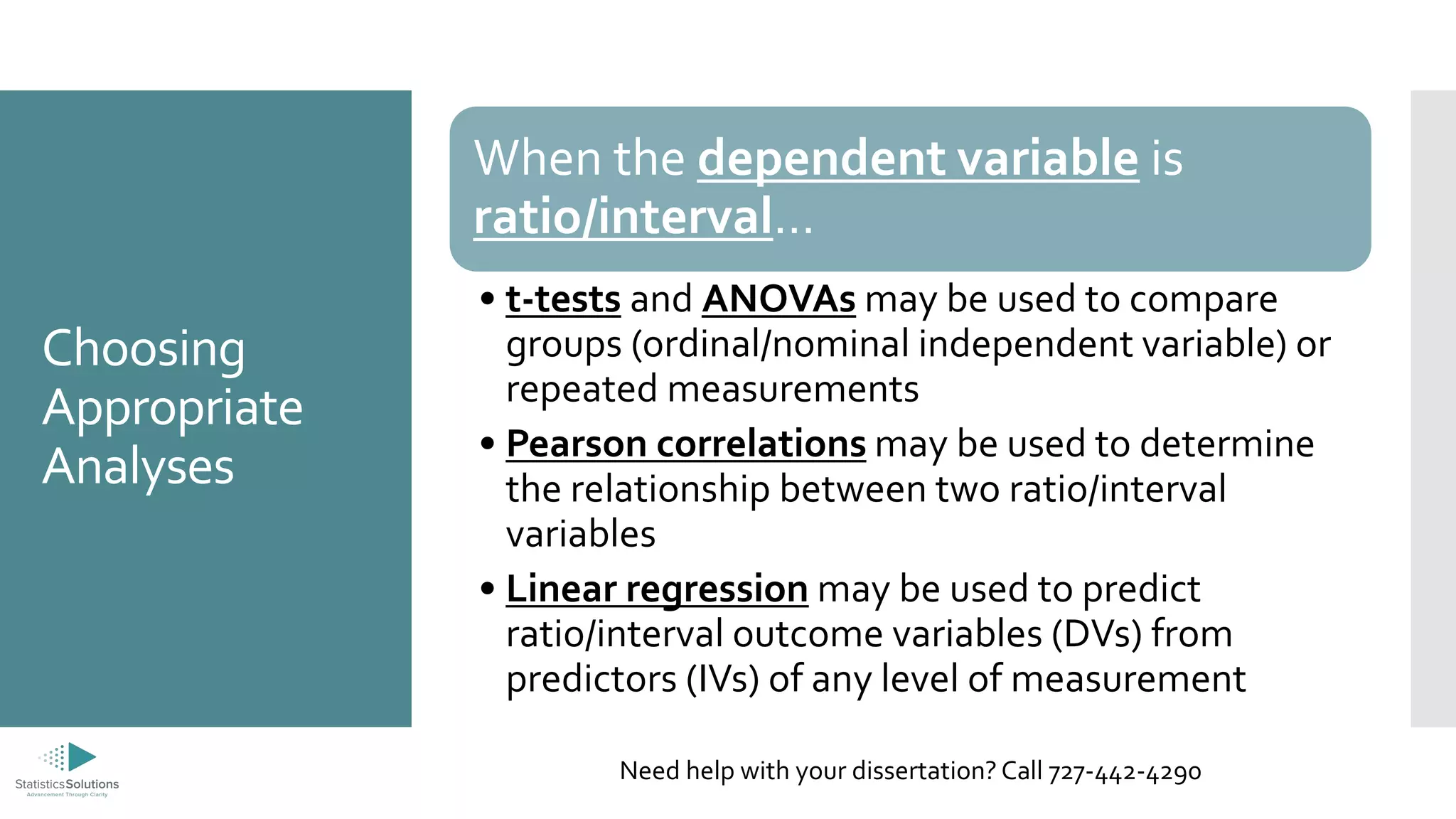
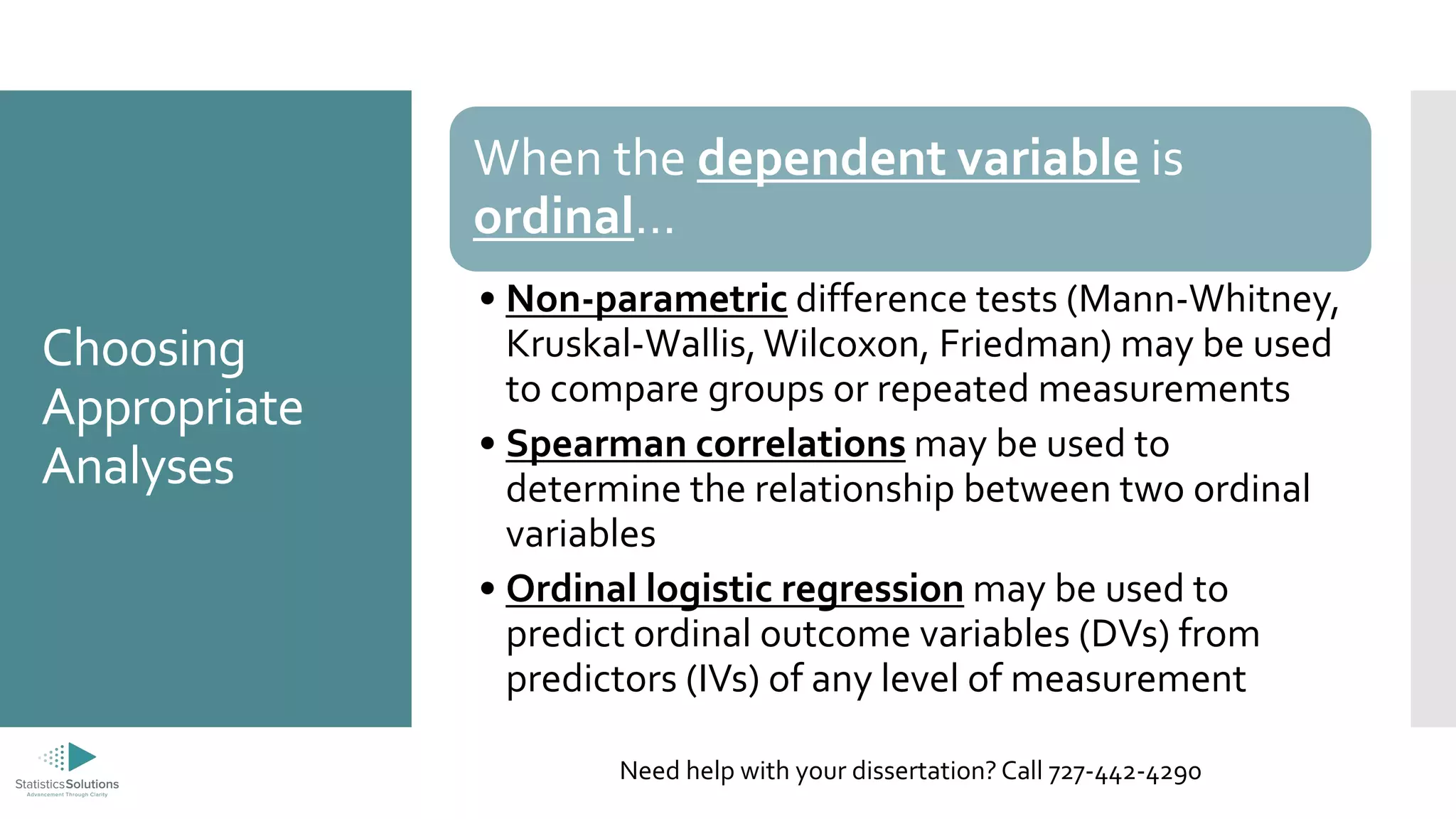
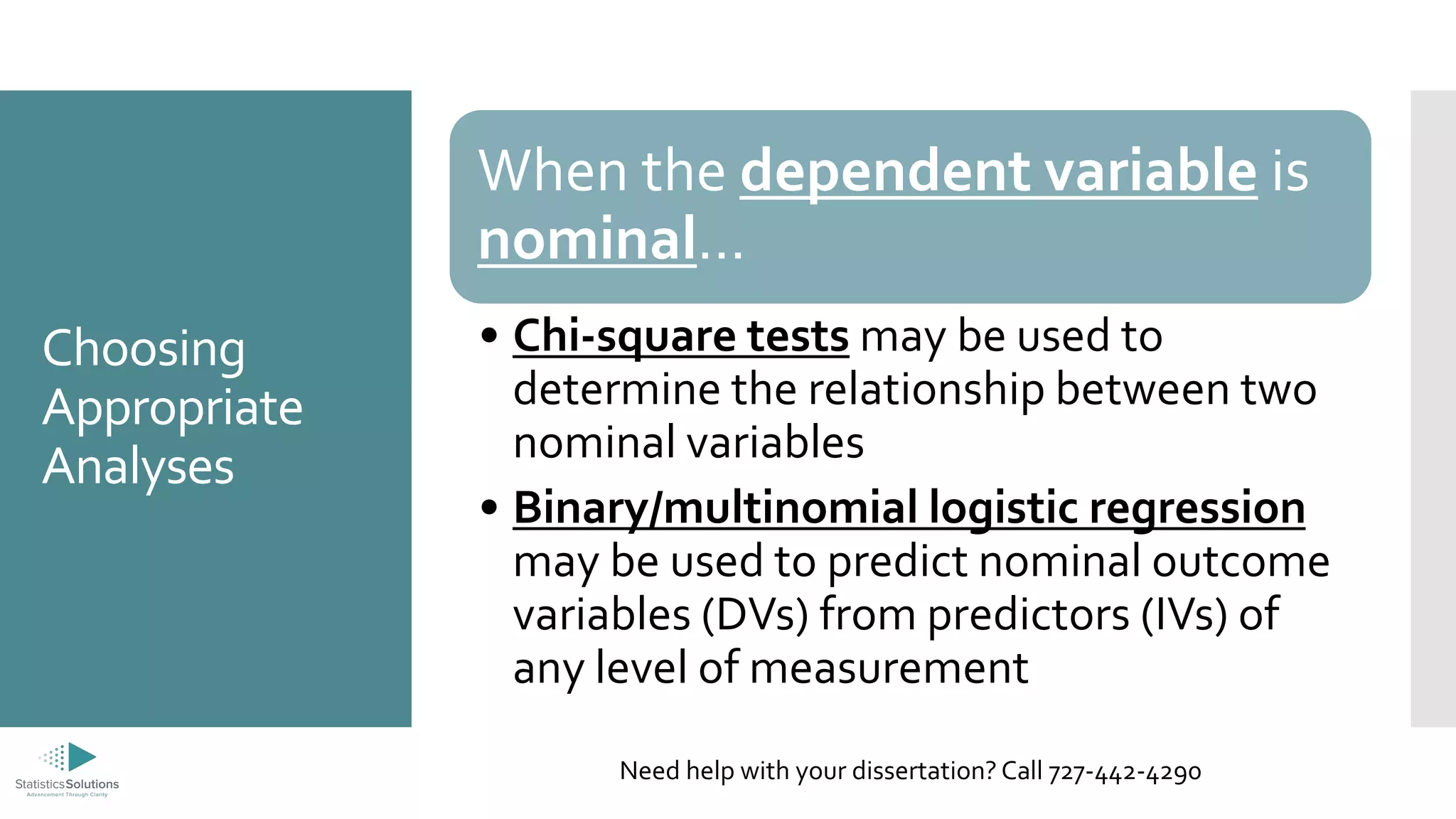
The document outlines the levels of measurement in statistics, including ratio, interval, ordinal, and nominal, and their importance in data analysis. It provides guidelines on selecting appropriate statistical analyses based on these measurement levels, such as t-tests for ratio/interval data and chi-square tests for nominal data. Additionally, it promotes Statistics Solutions as a dissertation consulting service offering editorial support to graduate students.