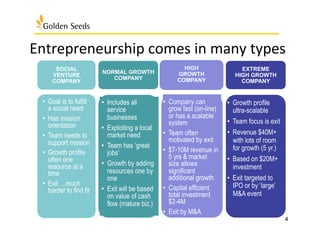
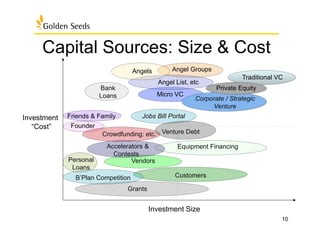
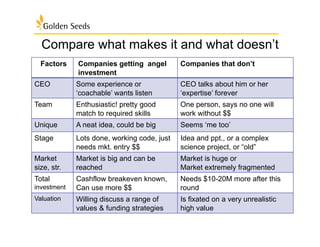
The document outlines various funding sources and strategies for women entrepreneurs, highlighting different types of companies (normal, high, extreme growth, and social ventures) and their unique financing paths. It emphasizes the importance of understanding capital requirements, preparing an effective pitch, and the roles of equity and debt in securing funding. Furthermore, it addresses what potential investors look for in a business, including product differentiation, market strategy, and team capability.