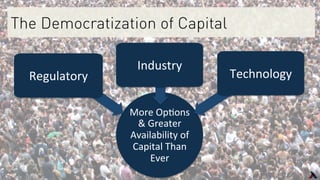
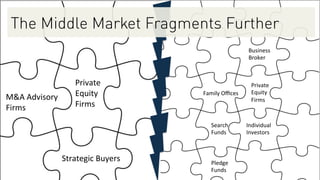
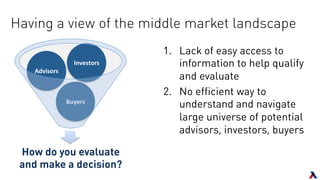
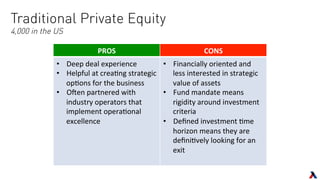
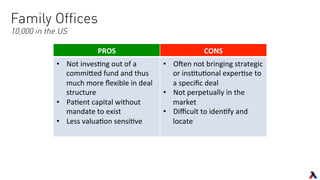
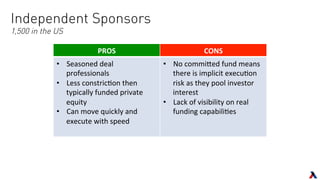
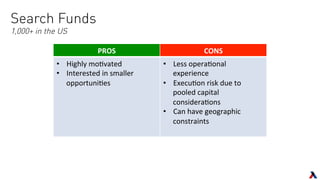
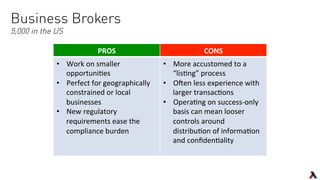
The document provides an overview of key players in the middle market, including trends, buyers, and advisors. It notes that the middle market has become more fragmented with the rise of specialized private equity firms and independent sponsors. There is also greater availability of capital from a more diverse set of investors like family offices and search funds. New technologies are helping bridge information gaps and connect middle market participants.