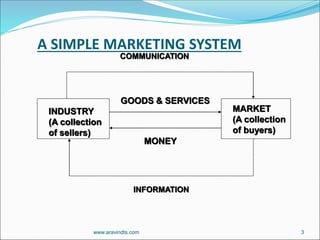
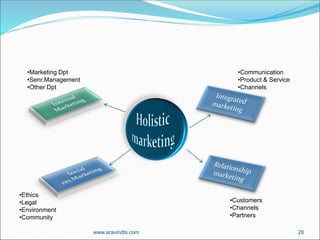
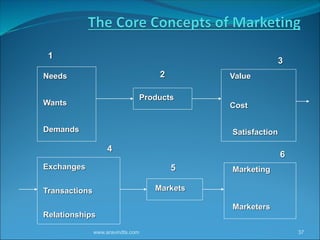
The document outlines various marketing concepts and elements, including the types of entities involved in marketing and key concepts such as exchange, production, product, selling, and marketing concepts. It emphasizes the importance of understanding consumer needs and creating value while incorporating societal responsibilities and integrated marketing practices. Additionally, it discusses the role of relationship marketing and differentiates between responsive, anticipative, and creative marketing strategies.