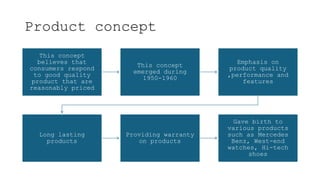
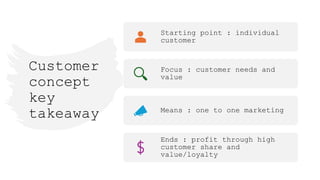
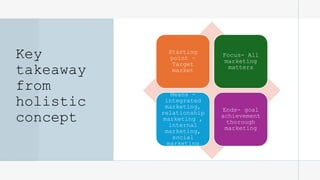
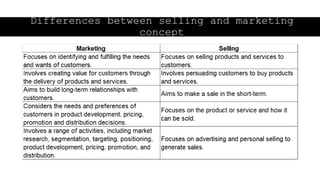
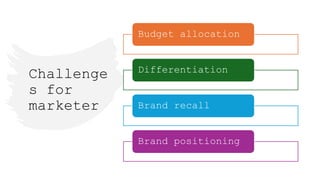
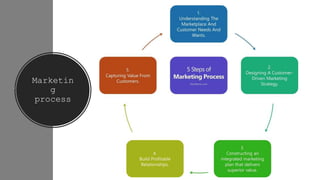
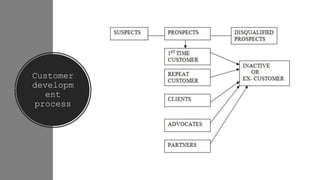
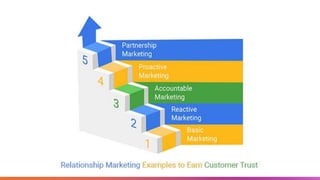
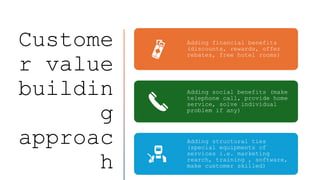
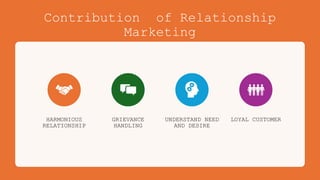
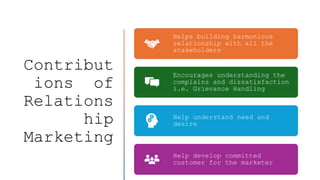
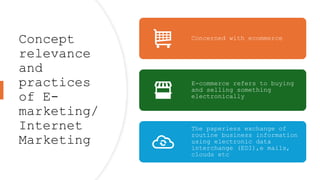
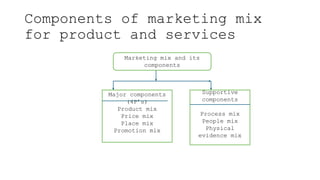
The document outlines the fundamental concepts of marketing, detailing various marketing philosophies including the production, product, selling, marketing, customer, societal, and holistic concepts. It emphasizes the importance of understanding customer needs and the shift towards relationship marketing as a means to build lasting customer connections and enhance satisfaction. Additionally, it addresses contemporary marketing challenges and the significance of integrating marketing efforts across an organization to achieve sustainable success.