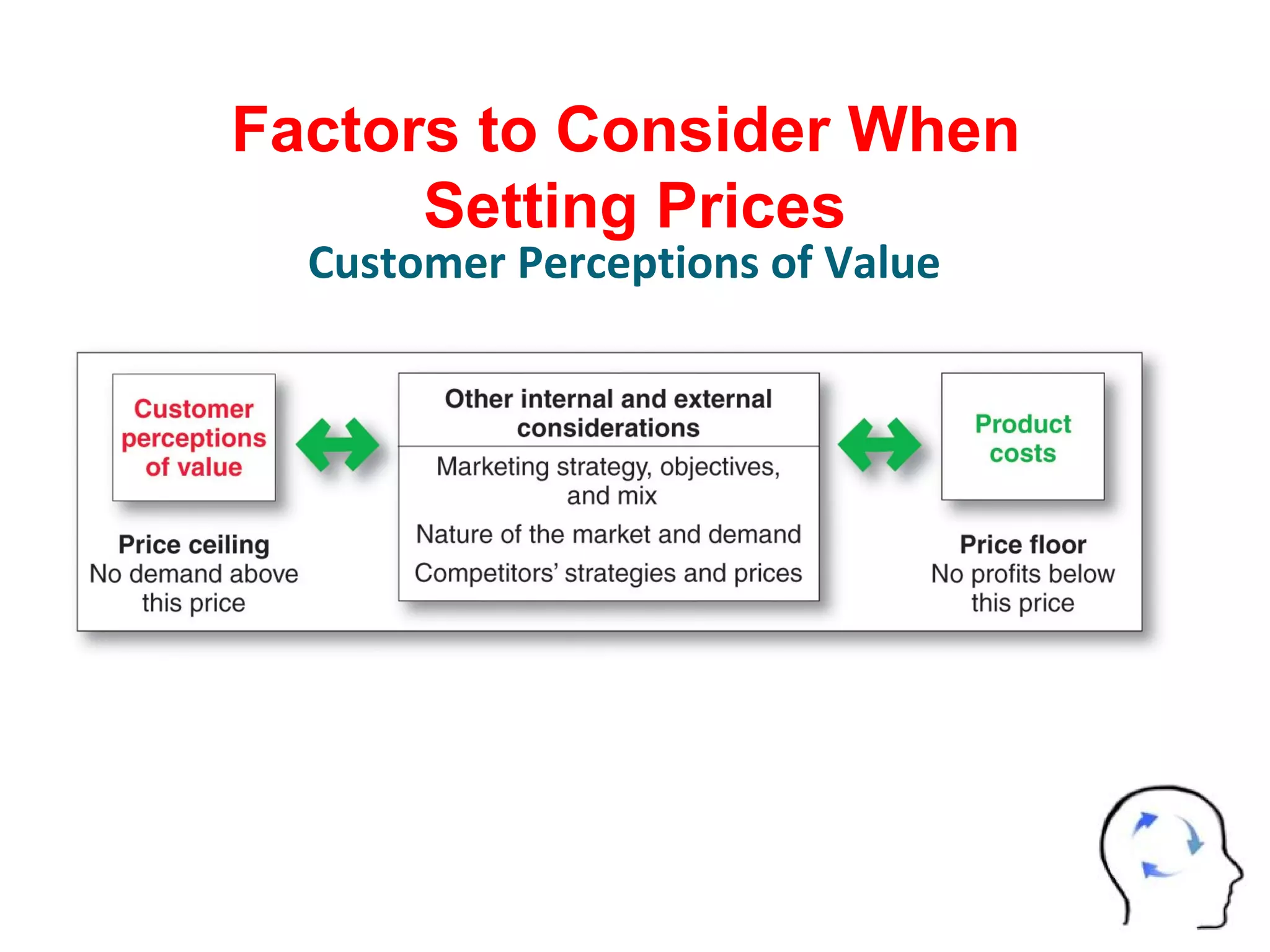
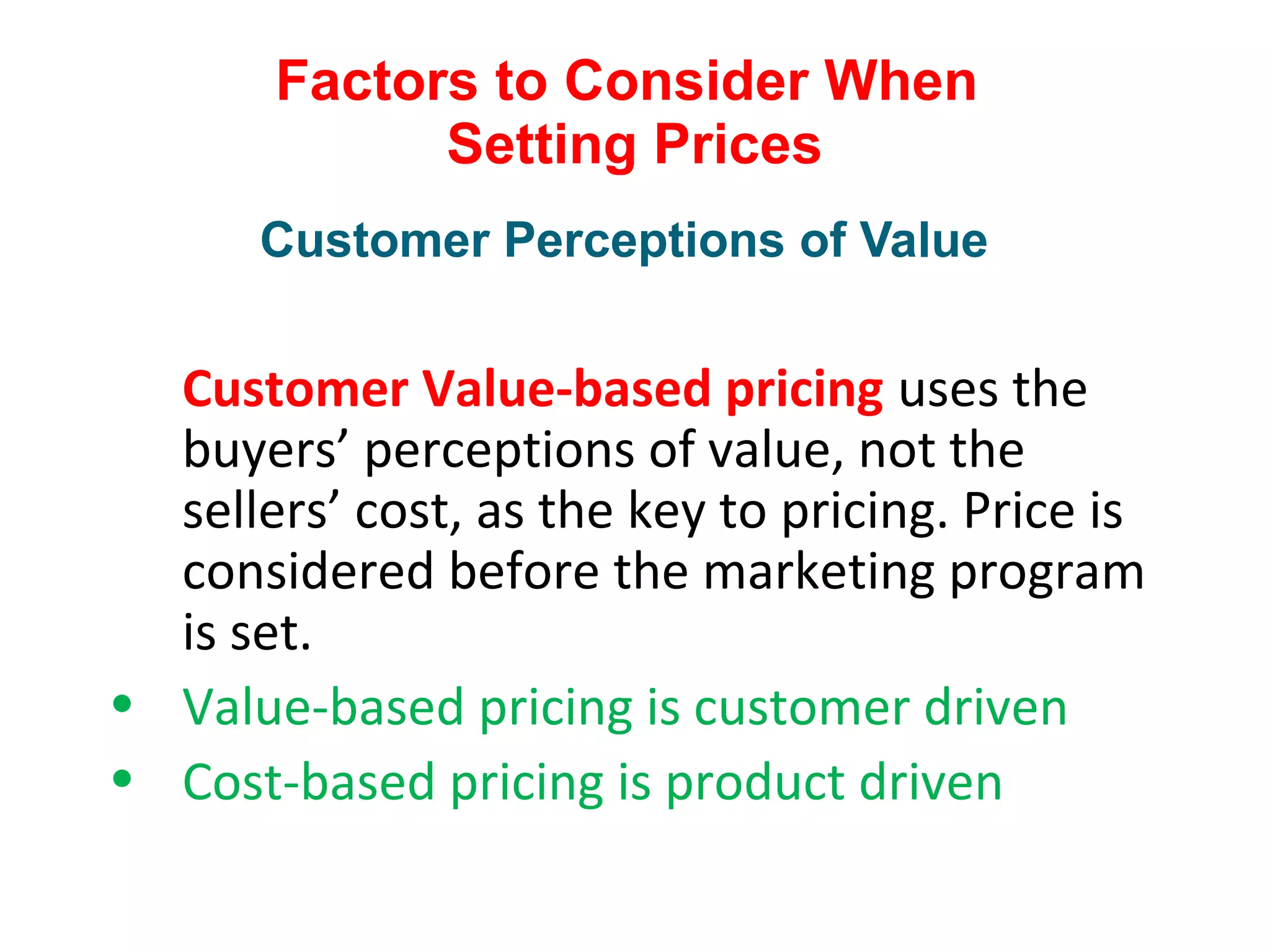
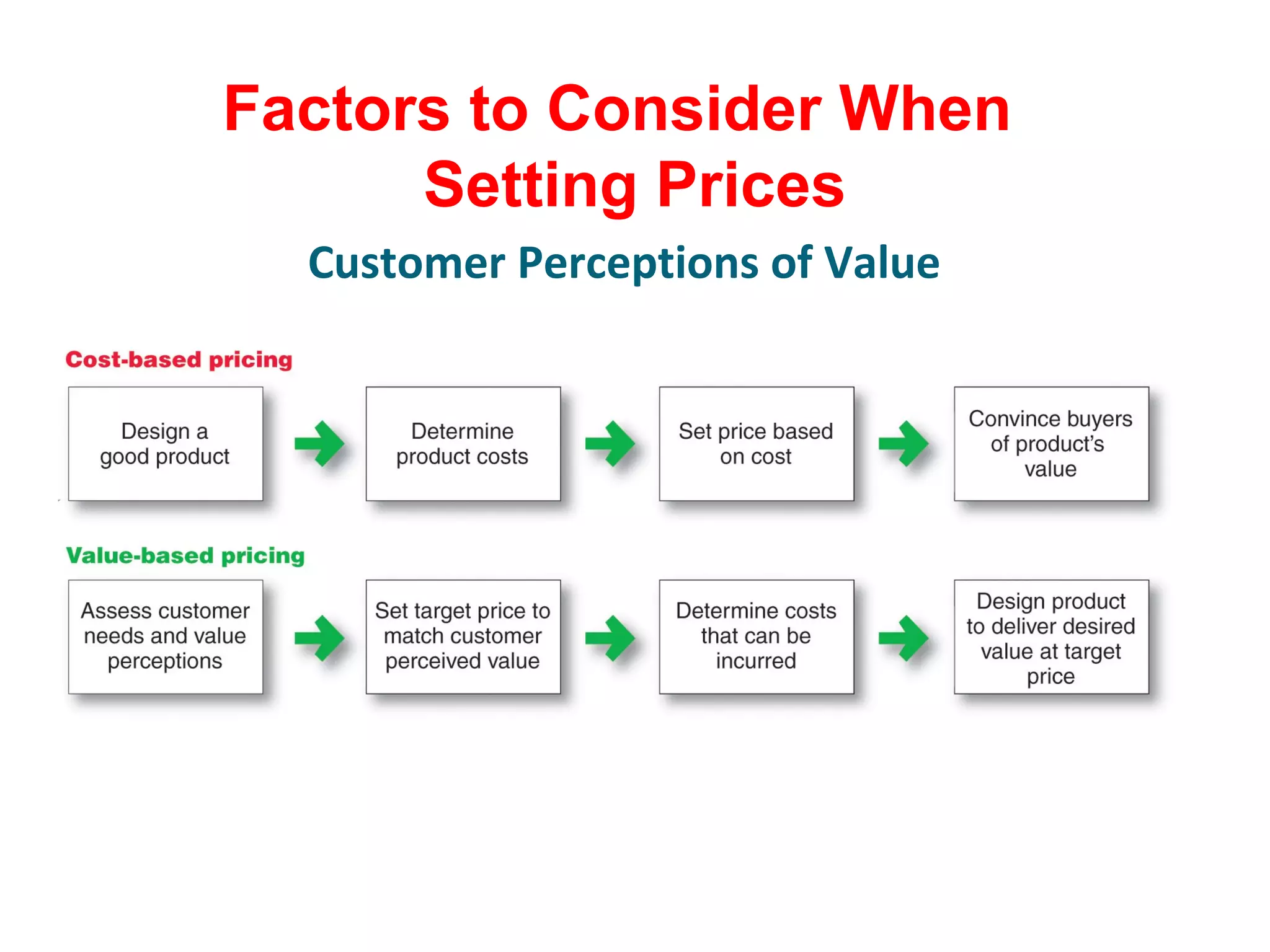
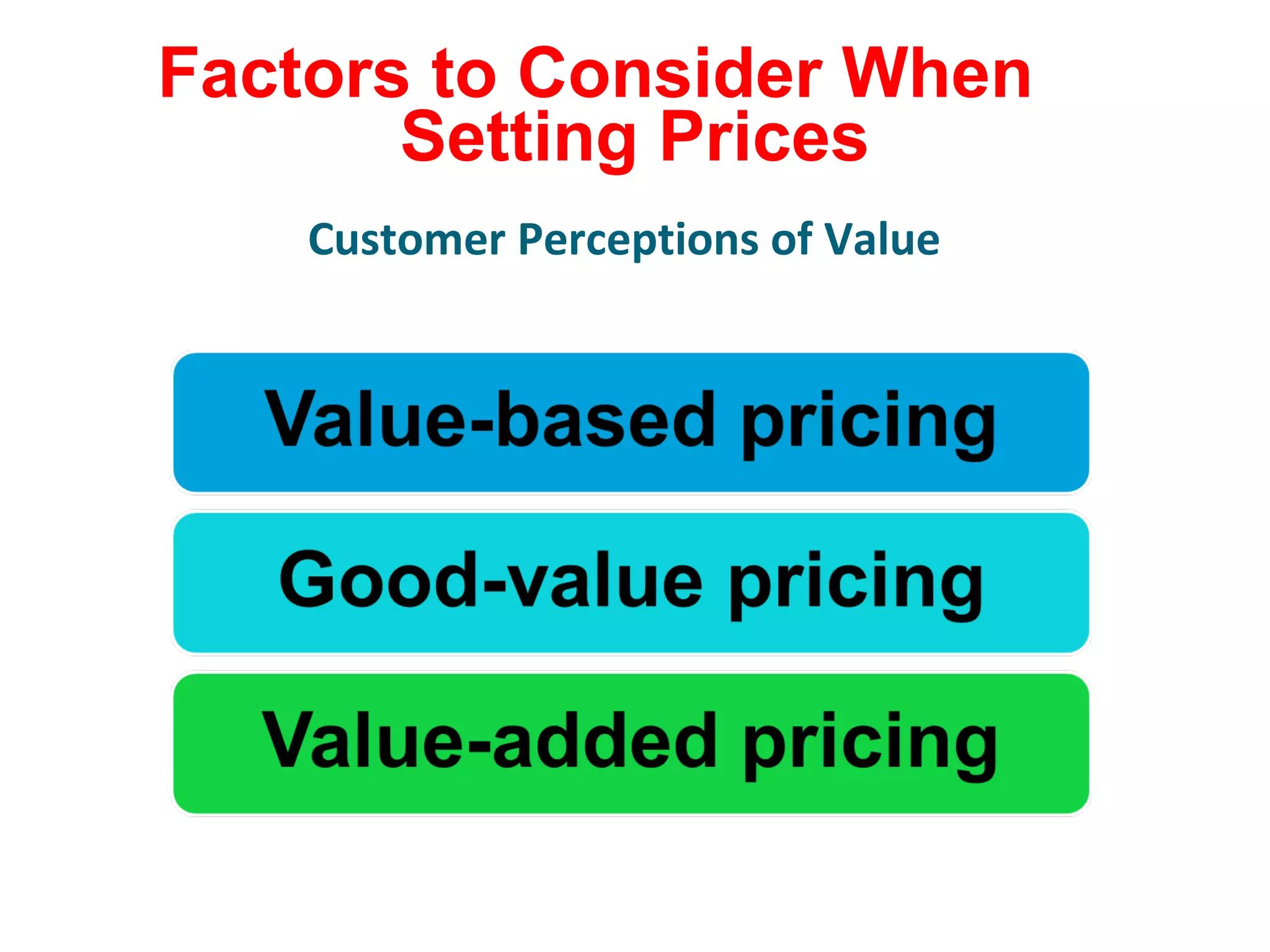
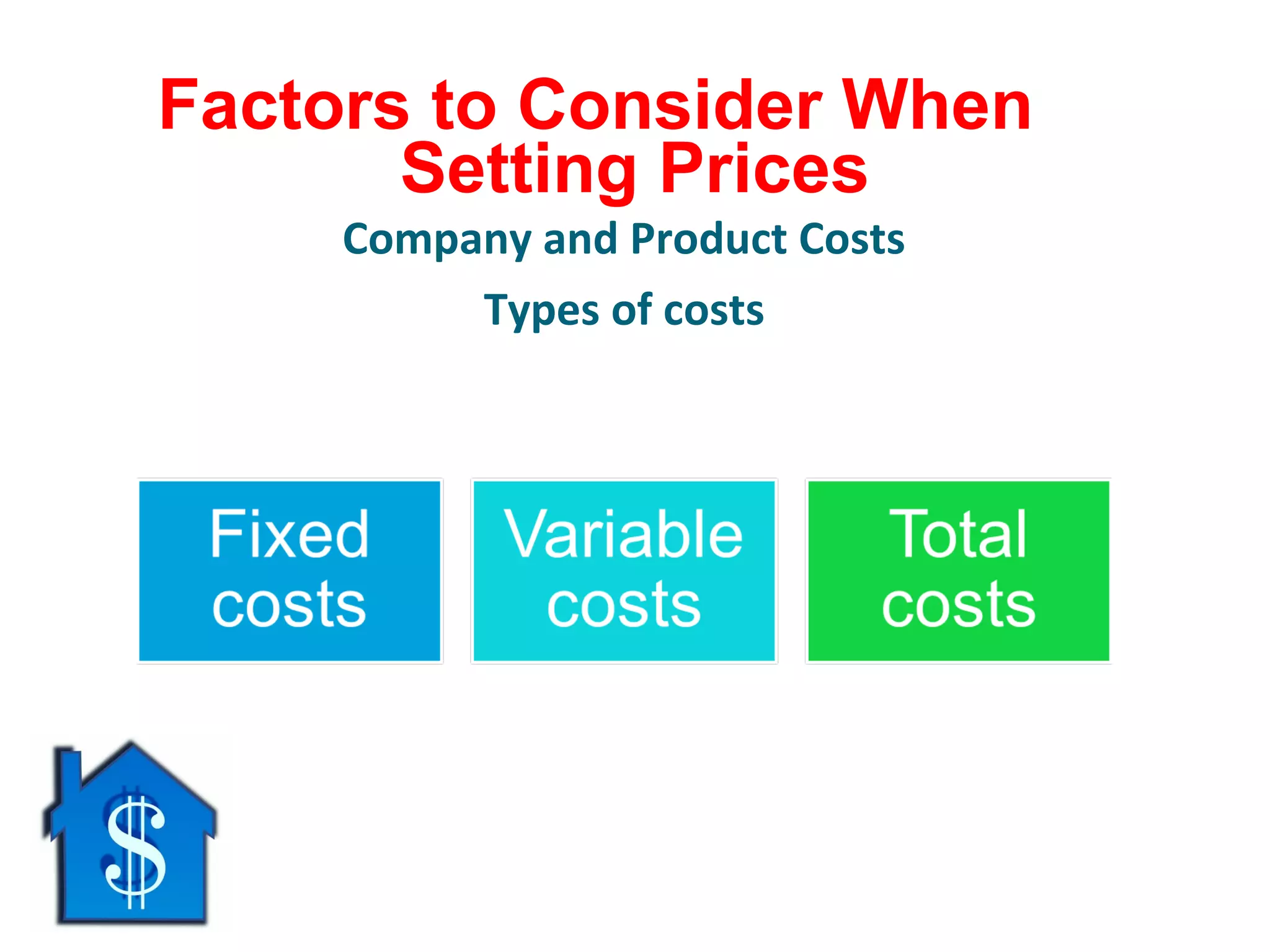
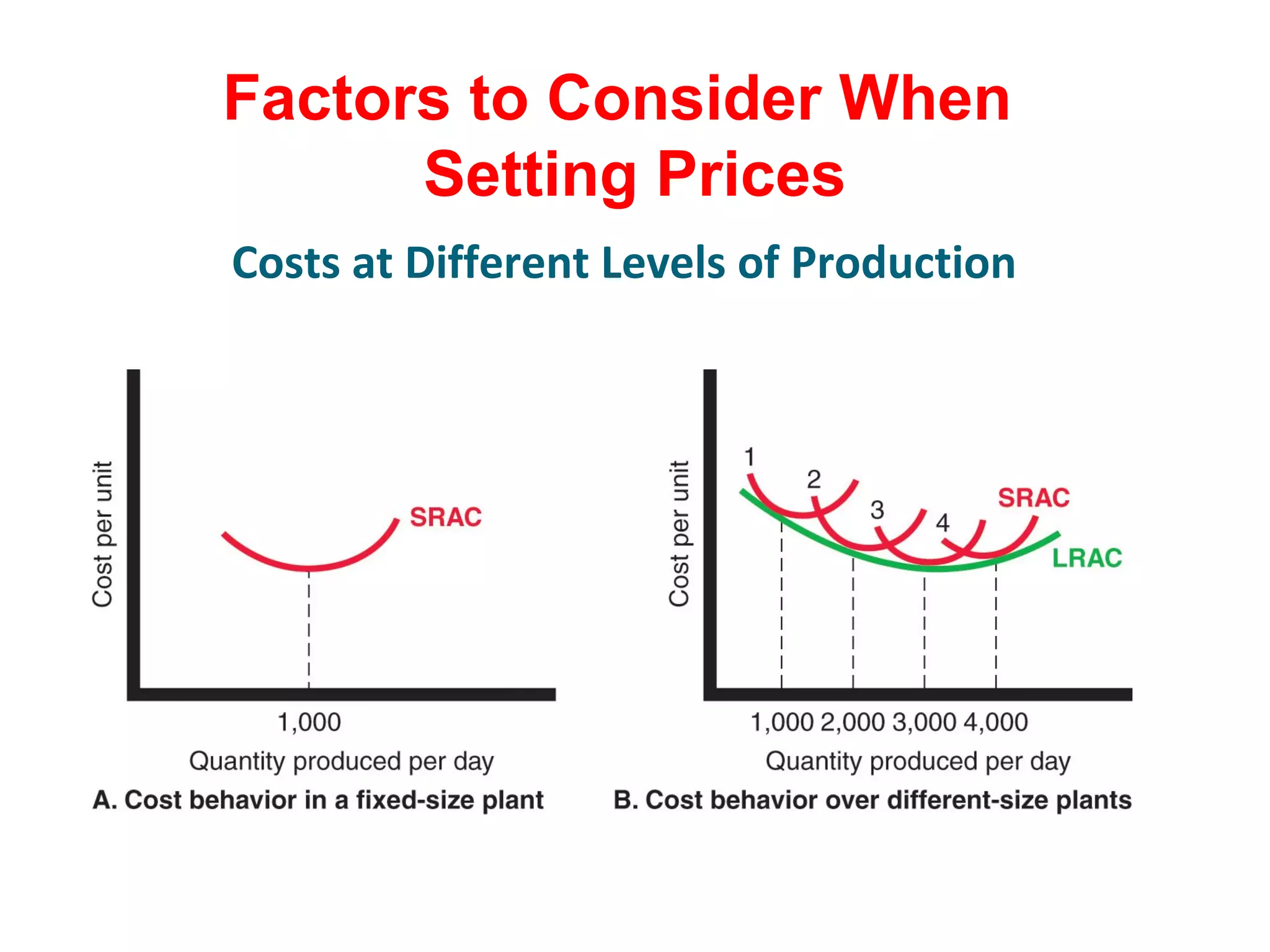
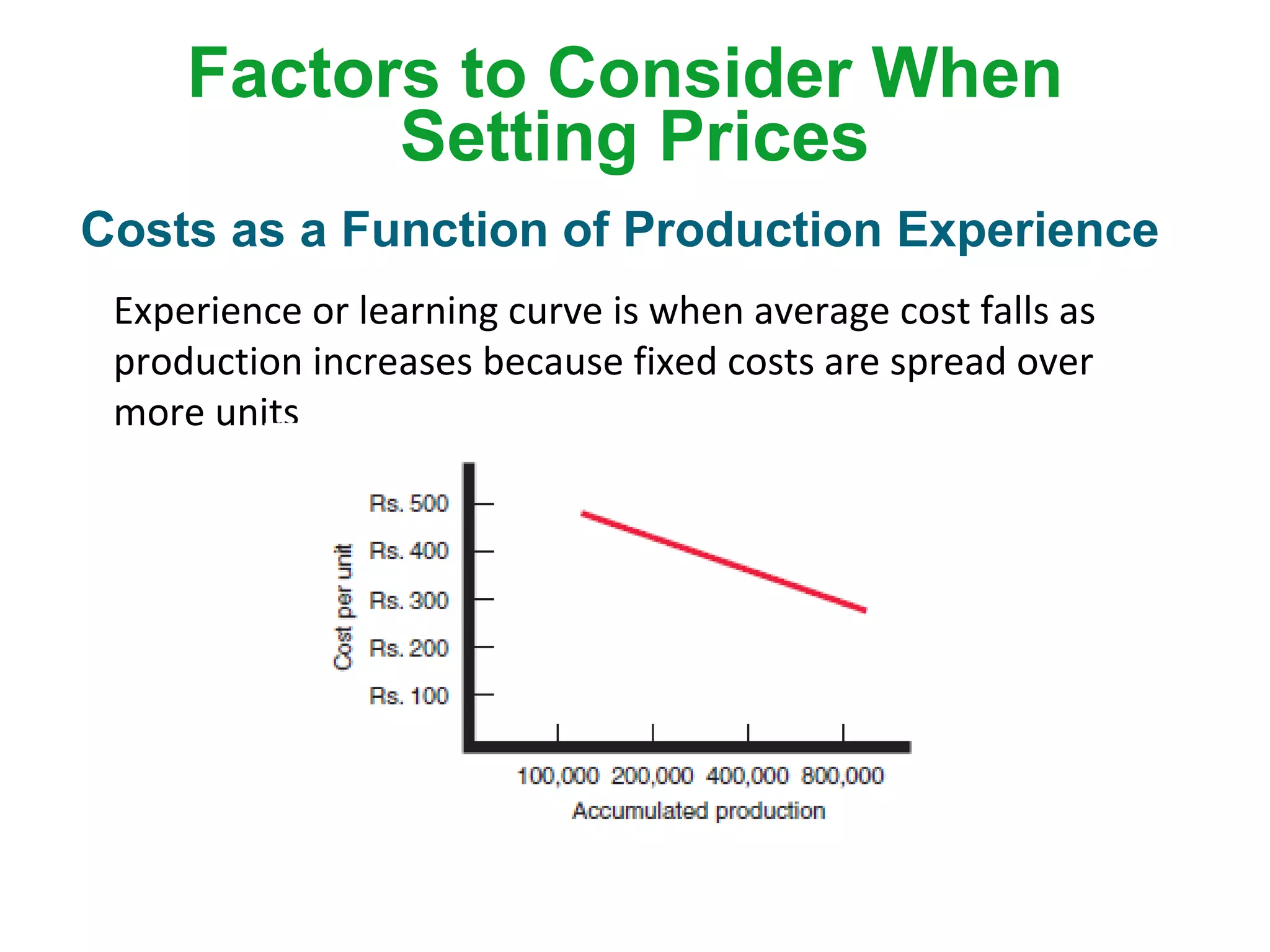
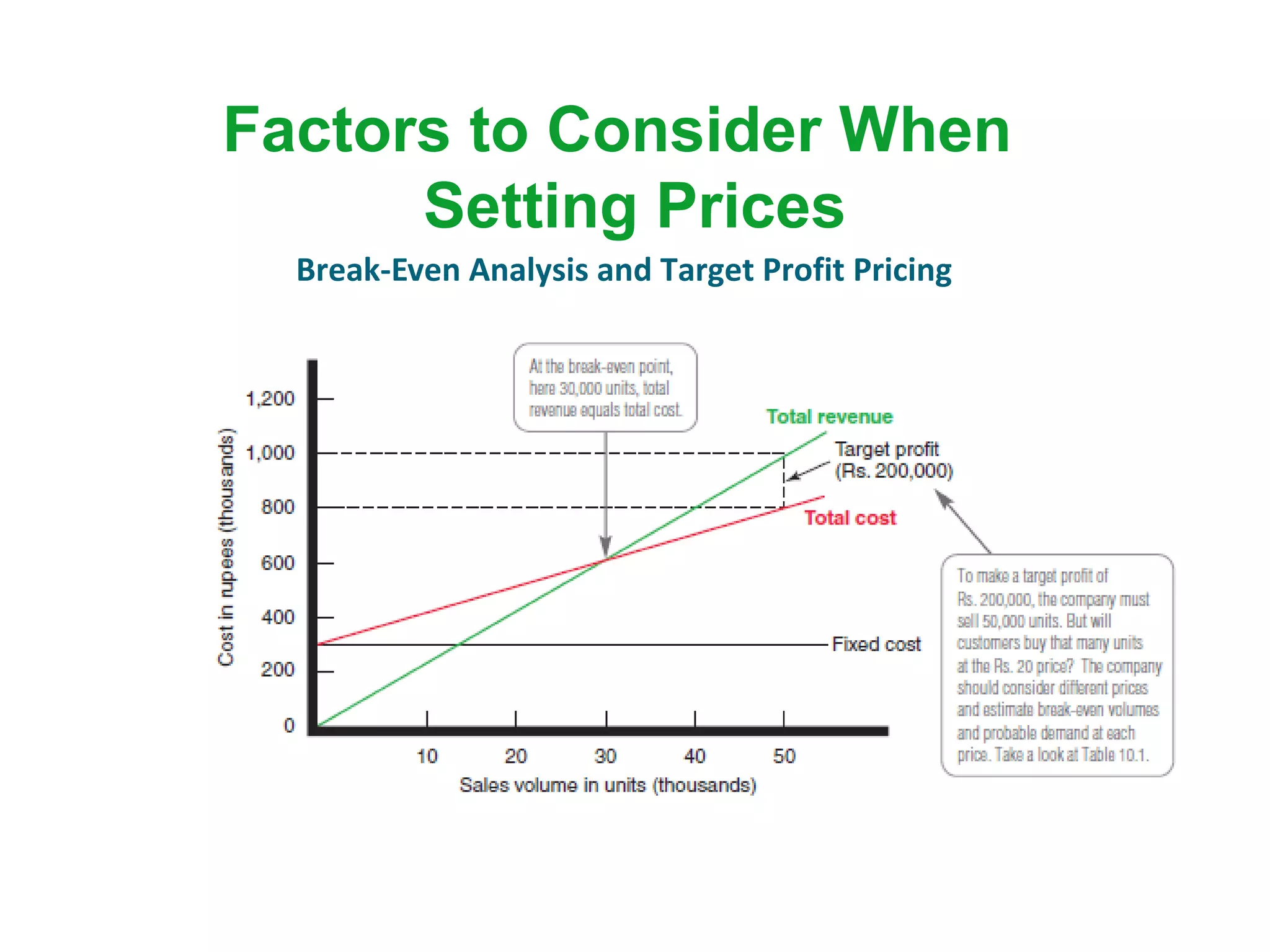
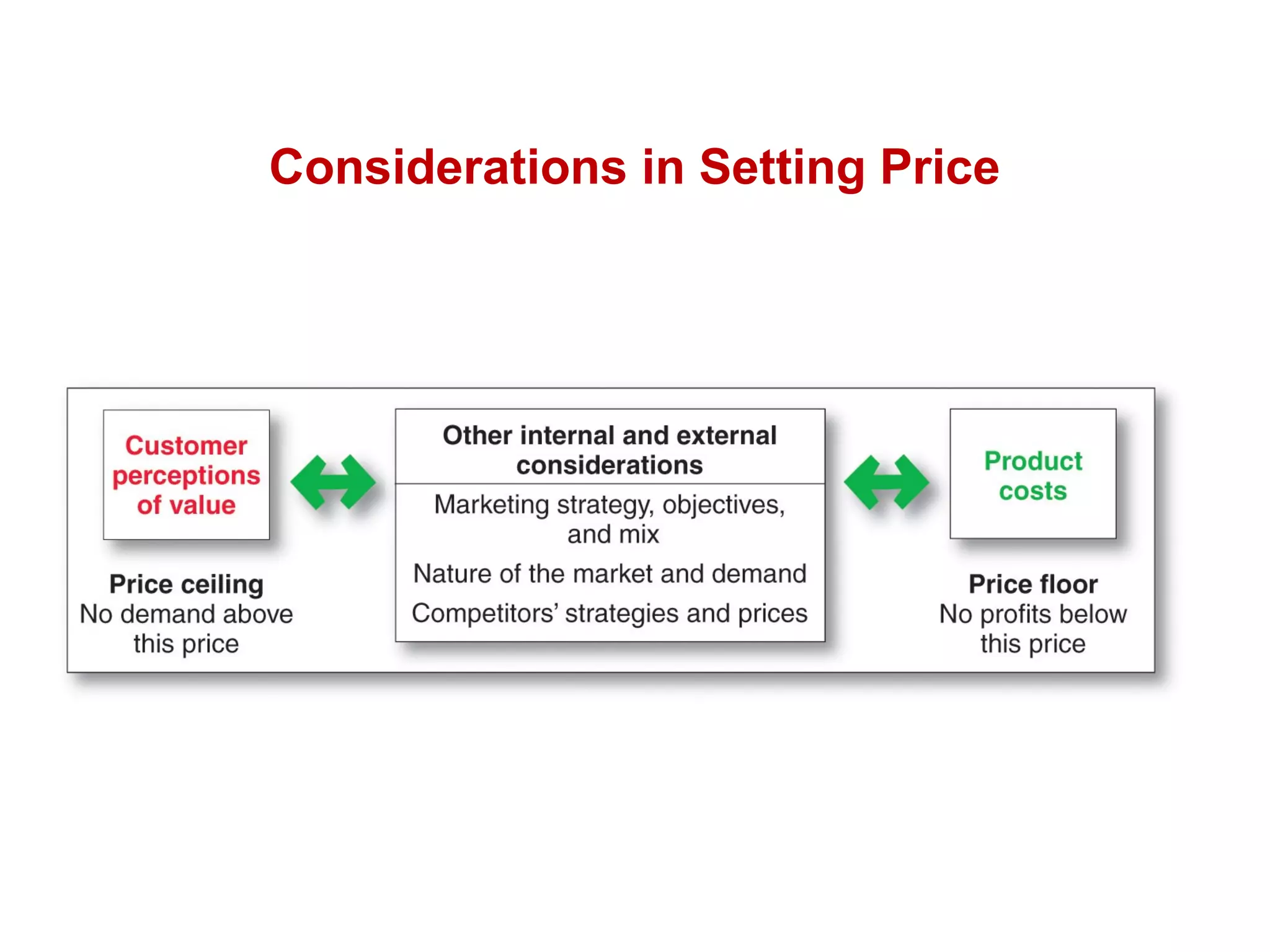
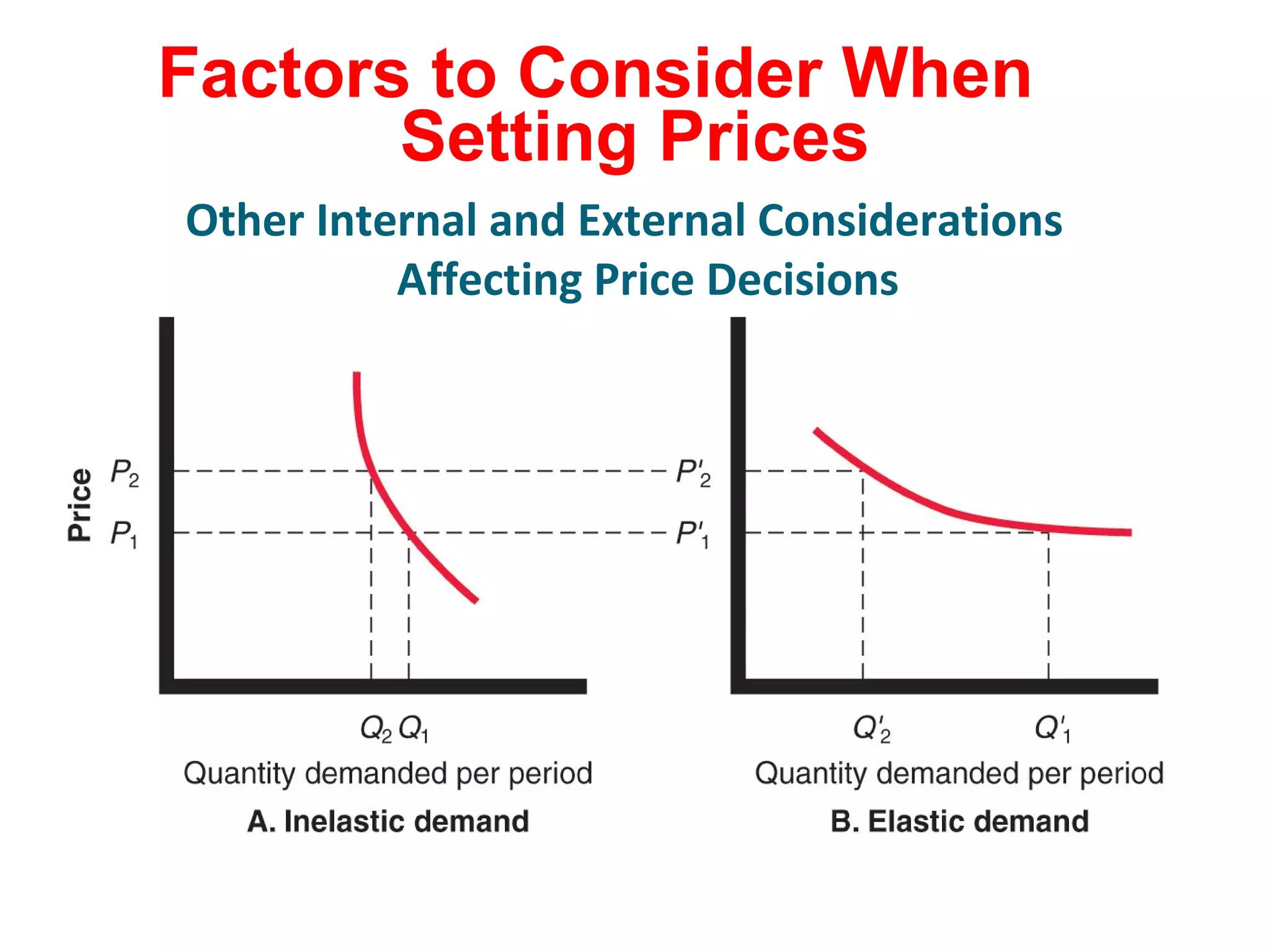
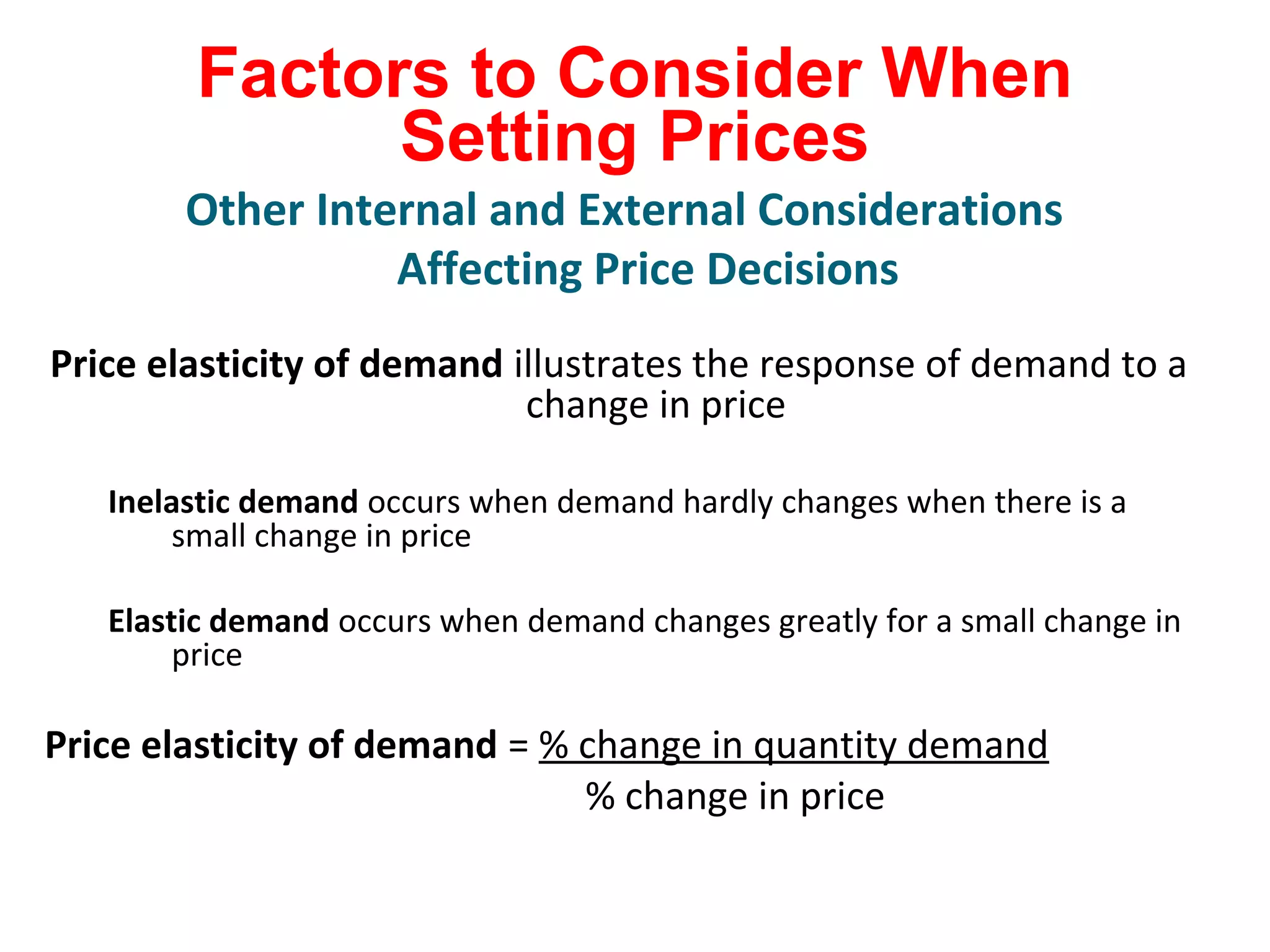
The document discusses pricing strategies in marketing, highlighting the importance of understanding customer perceptions of value when setting prices. It differentiates between customer value-based pricing, cost-based pricing, and competitor-based pricing while considering internal and external factors influencing price decisions. Key concepts include pricing power, cost structures (fixed and variable), and the relationship between price elasticity and demand.