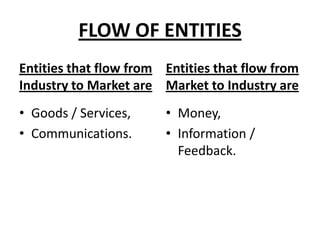
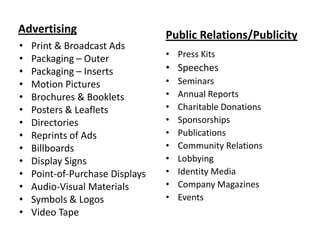
The document discusses the theoretical aspects of marketing communications, detailing various entities involved in marketing such as goods, services, events, and ideas. It emphasizes the importance of communication as a key component in the marketing process for engaging with stakeholders and consumers. Additionally, it outlines the modern marketing communications mix, which includes tools like advertising, public relations, personal selling, and direct marketing.