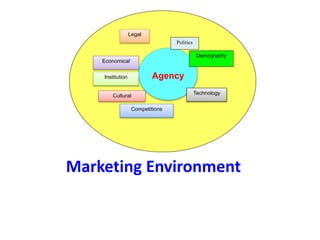
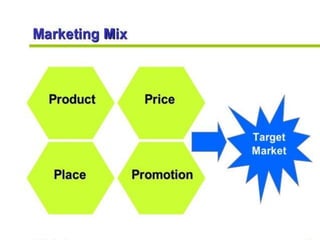
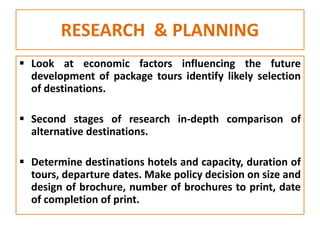
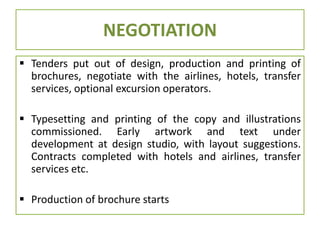
This document discusses marketing and the marketing mix model. It defines marketing and explores various elements of the marketing environment including economic, legal, political, demographic, competitive, cultural, institutional, and technological factors. It then explains the marketing mix model using the four Ps - product, price, place, and promotion. Specific questions are provided for each P to help define marketing strategies. The document also discusses tools and instruments used for tourism marketing, including various forms of advertising, public relations, trade shows, and word-of-mouth promotion.