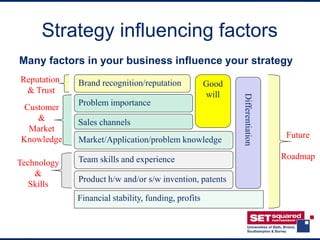
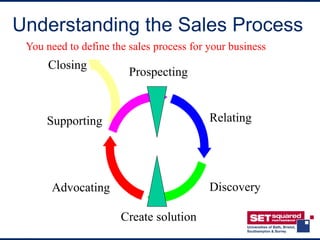
The document discusses key aspects of developing marketing and sales strategies for a business plan. It covers defining marketing, conducting market research, choosing a target market, understanding competition, developing a marketing strategy and plan, marketing communications, and developing a sales strategy and process. The key points are that an effective marketing plan should define specific activities to achieve objectives, and the sales process must be understood as it affects key investment factors like costs, growth and profitability. Investors will focus on how the company will take the product to market and deliver business objectives.