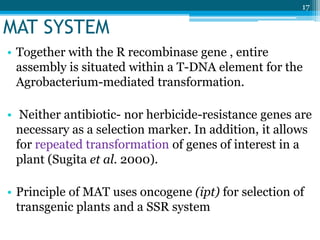
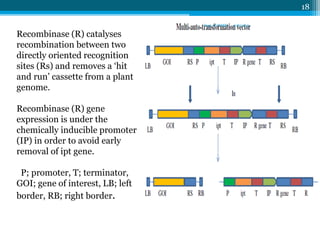
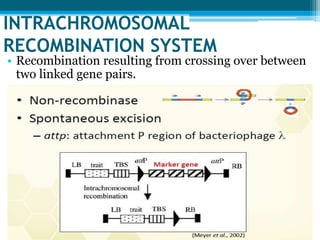
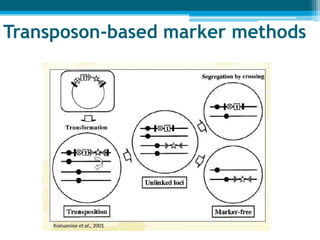
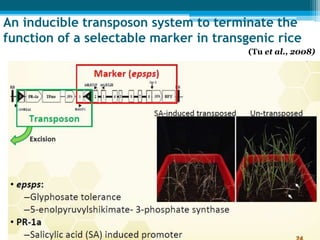
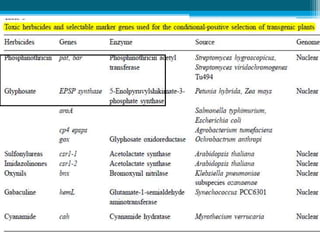
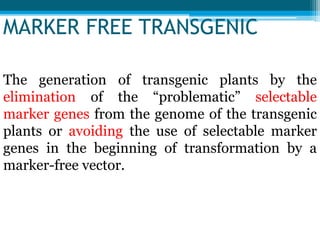
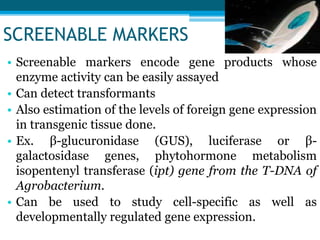
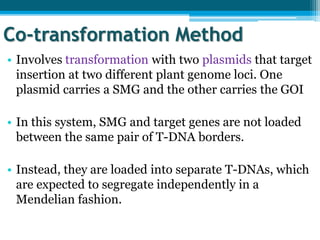
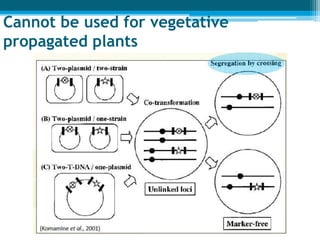
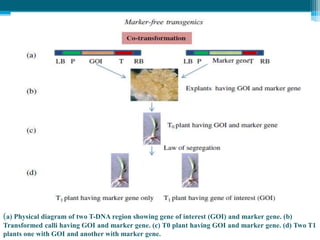
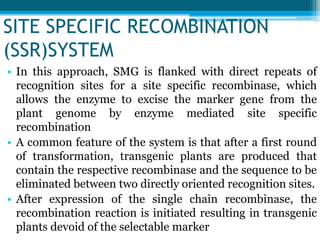
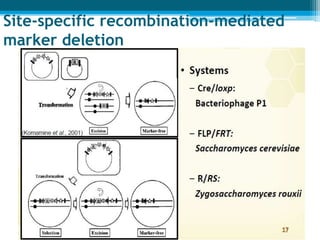
This document discusses marker-free transgenics, which aim to generate transgenic plants without selectable marker genes. It describes various strategies to produce marker-free plants, including using screenable markers, co-transformation, site-specific recombination, multi-autotransformation vectors, intrachromosomal recombination, and transposon-based methods. The document concludes that developing marker-free transgenic crops could help advance crop improvement efforts and increase public acceptance of transgenic technologies.




![• A positive selection system
• Unique as it uses morphological changes caused by
oncogene [ipt gene] or rhizogene (the rol gene) of A.
Tumefaciens which control the endogenous levels of plant
hormones and the cell responses to PGR as the selection
marker
• A chosen GOI is placed adjacent to a multigenic element
flanked by RS recombination sites. A copy of the selectable
ipt gene from A.tumefaciens is inserted between these
sites
16
MAT SYSTEM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arpitamarkerfree-150608091909-lva1-app6892/85/Marker-free-transgenic-development-16-320.jpg)