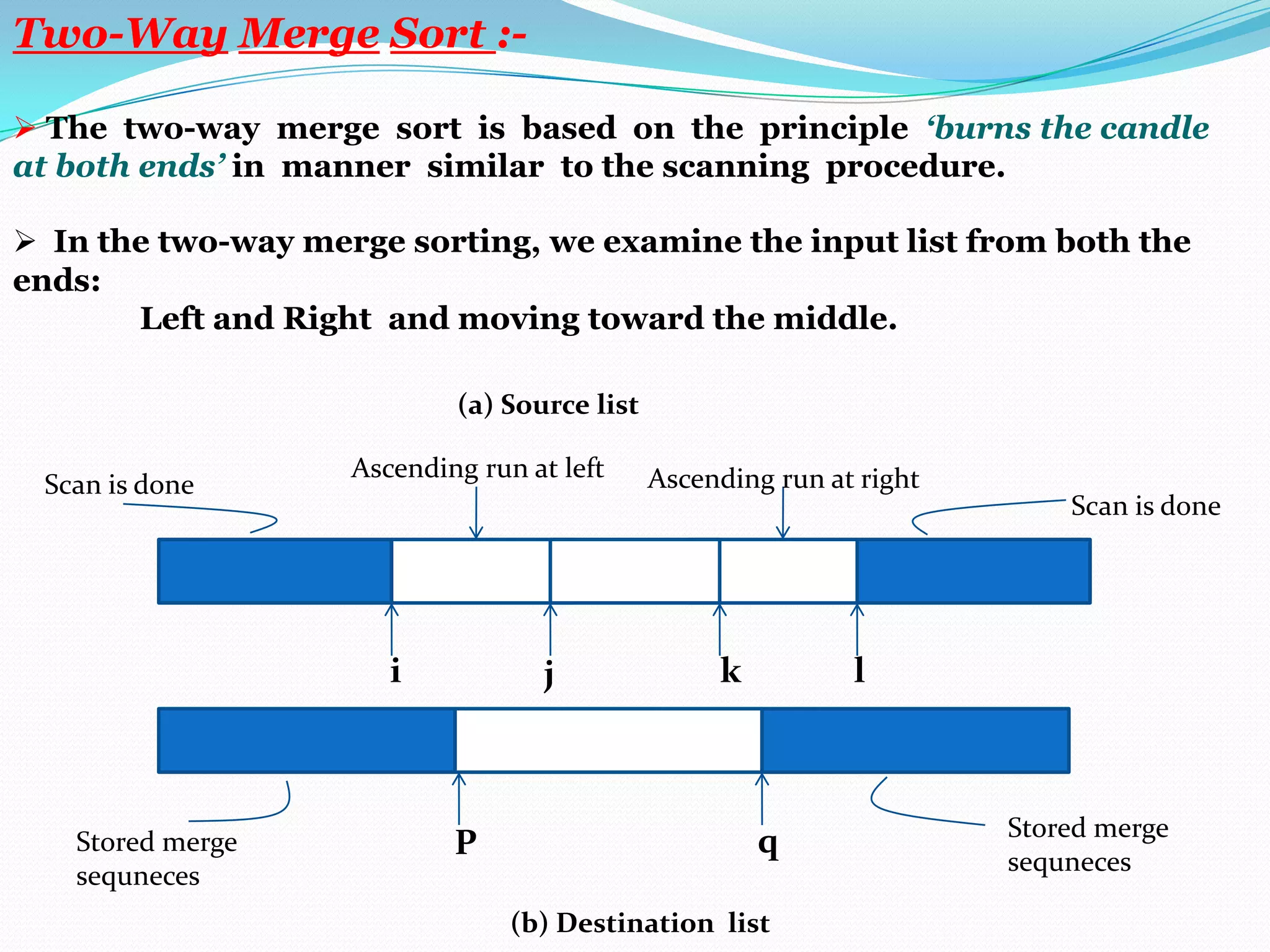
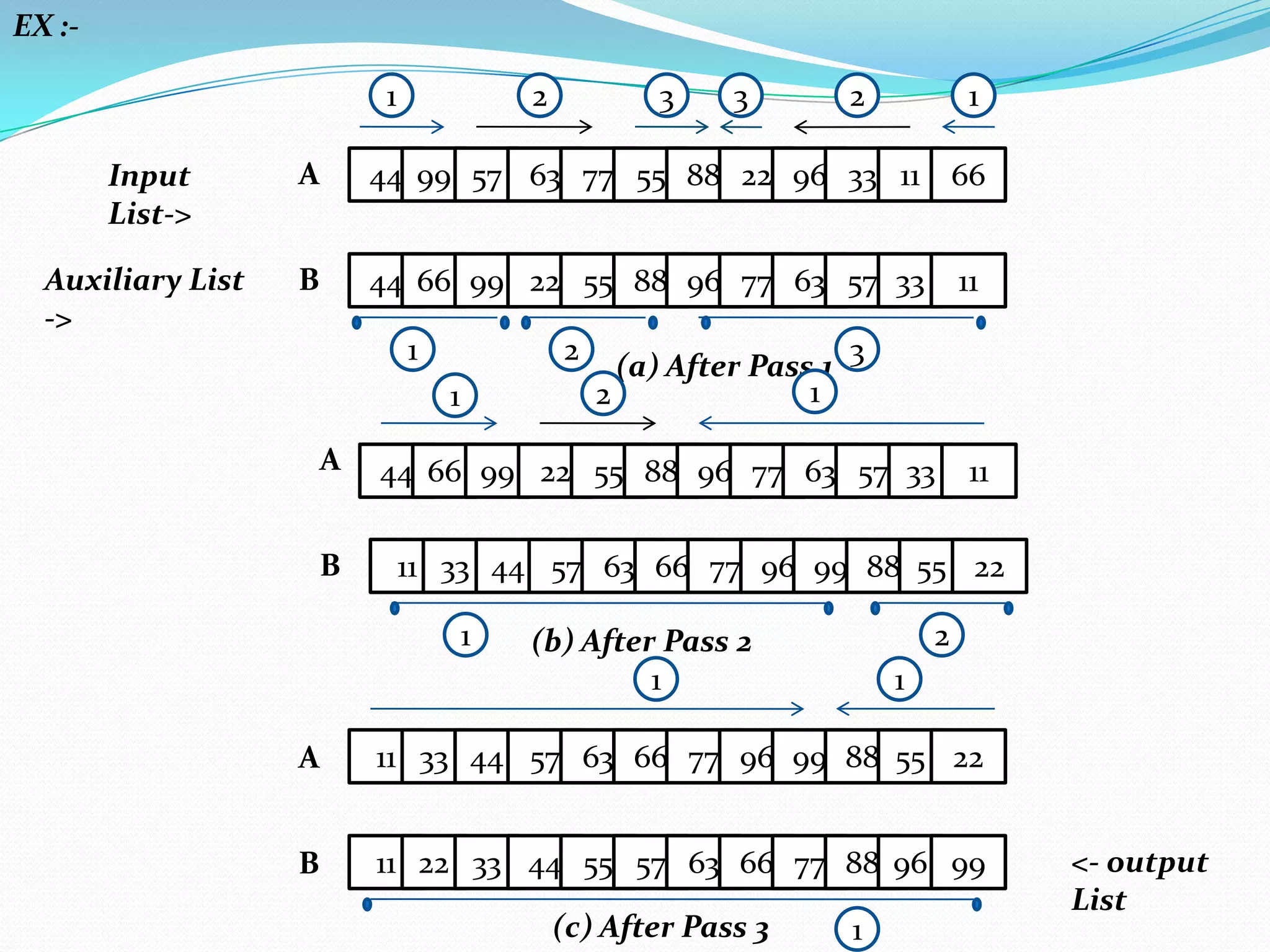
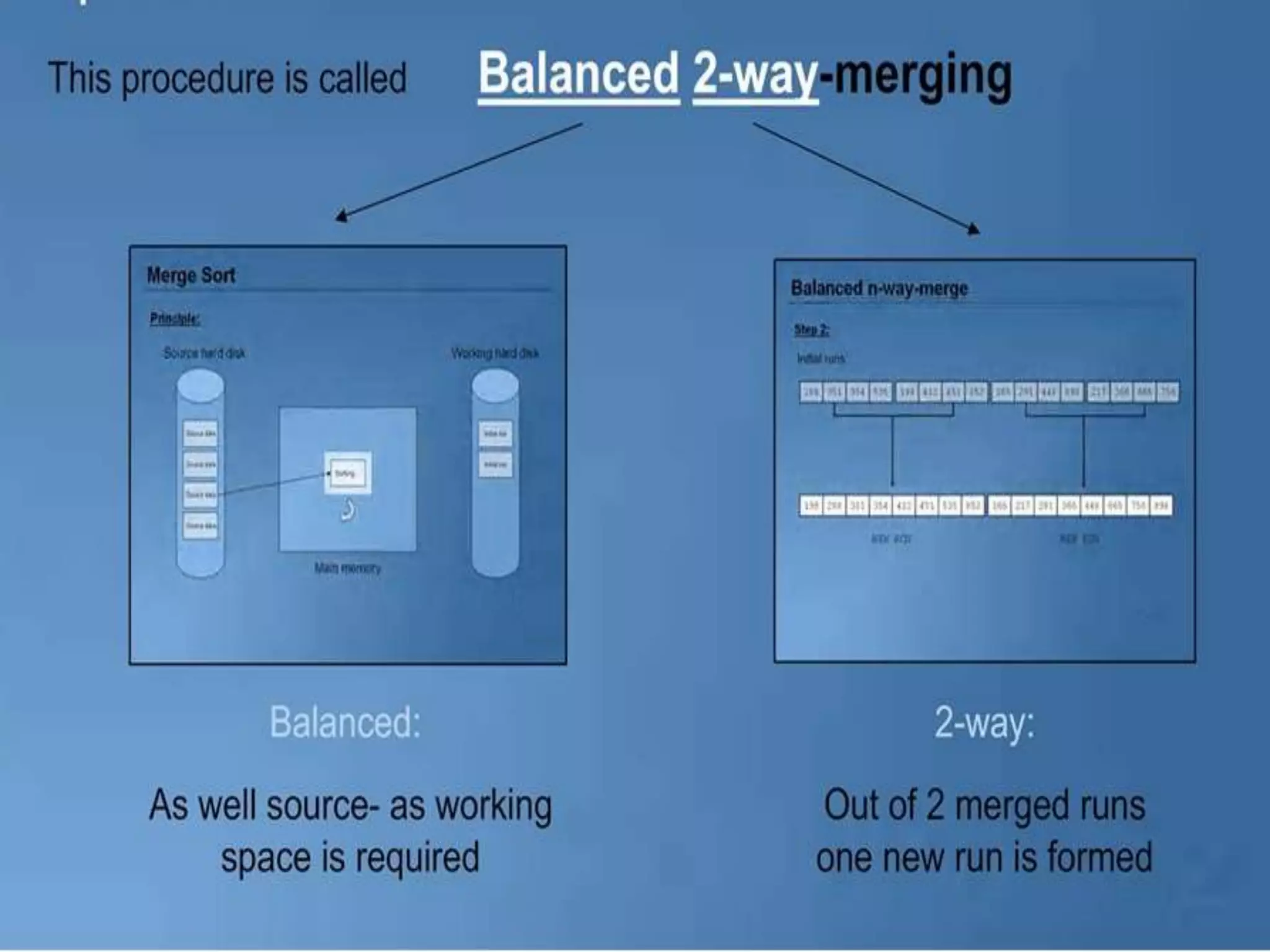
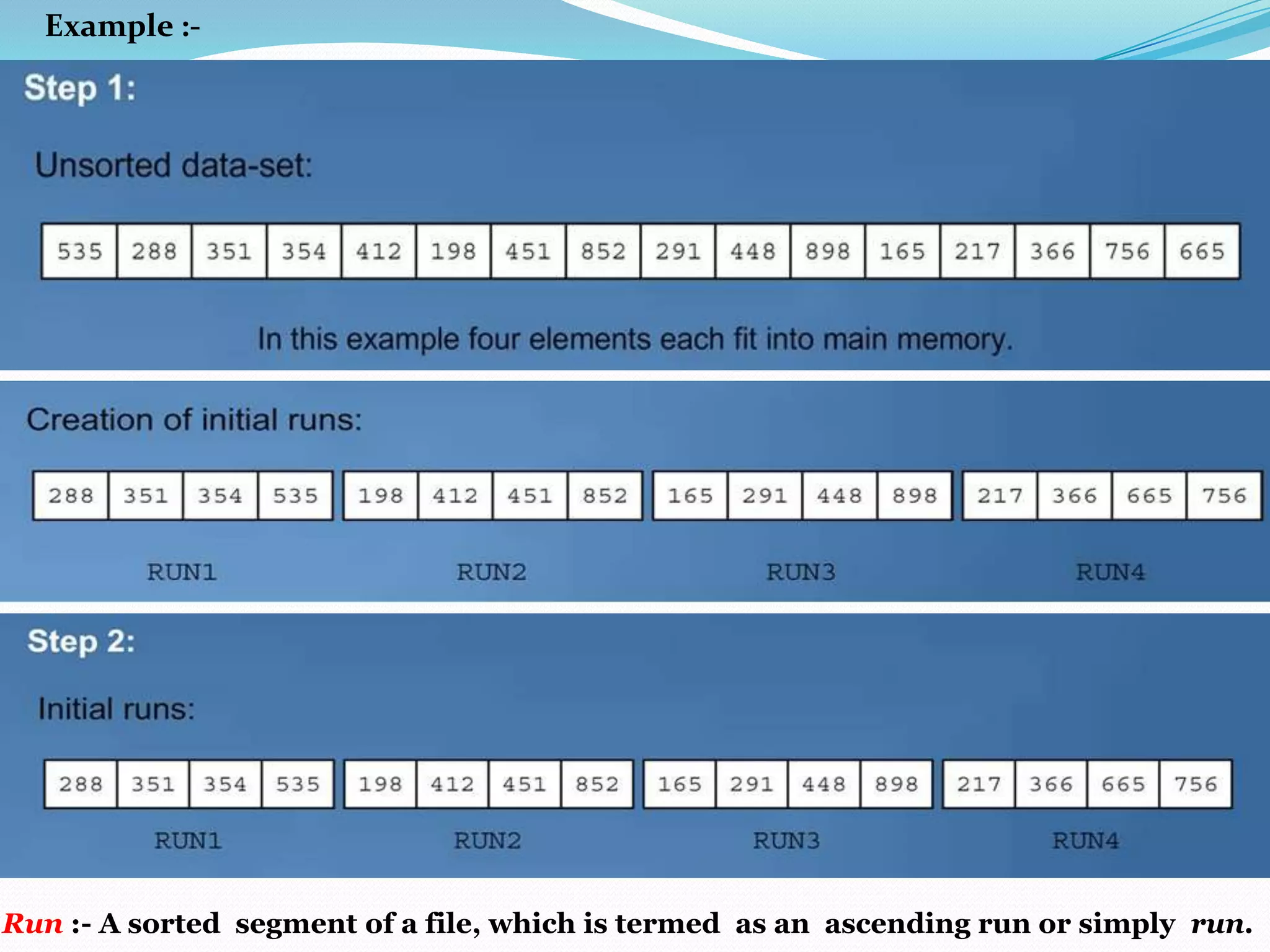
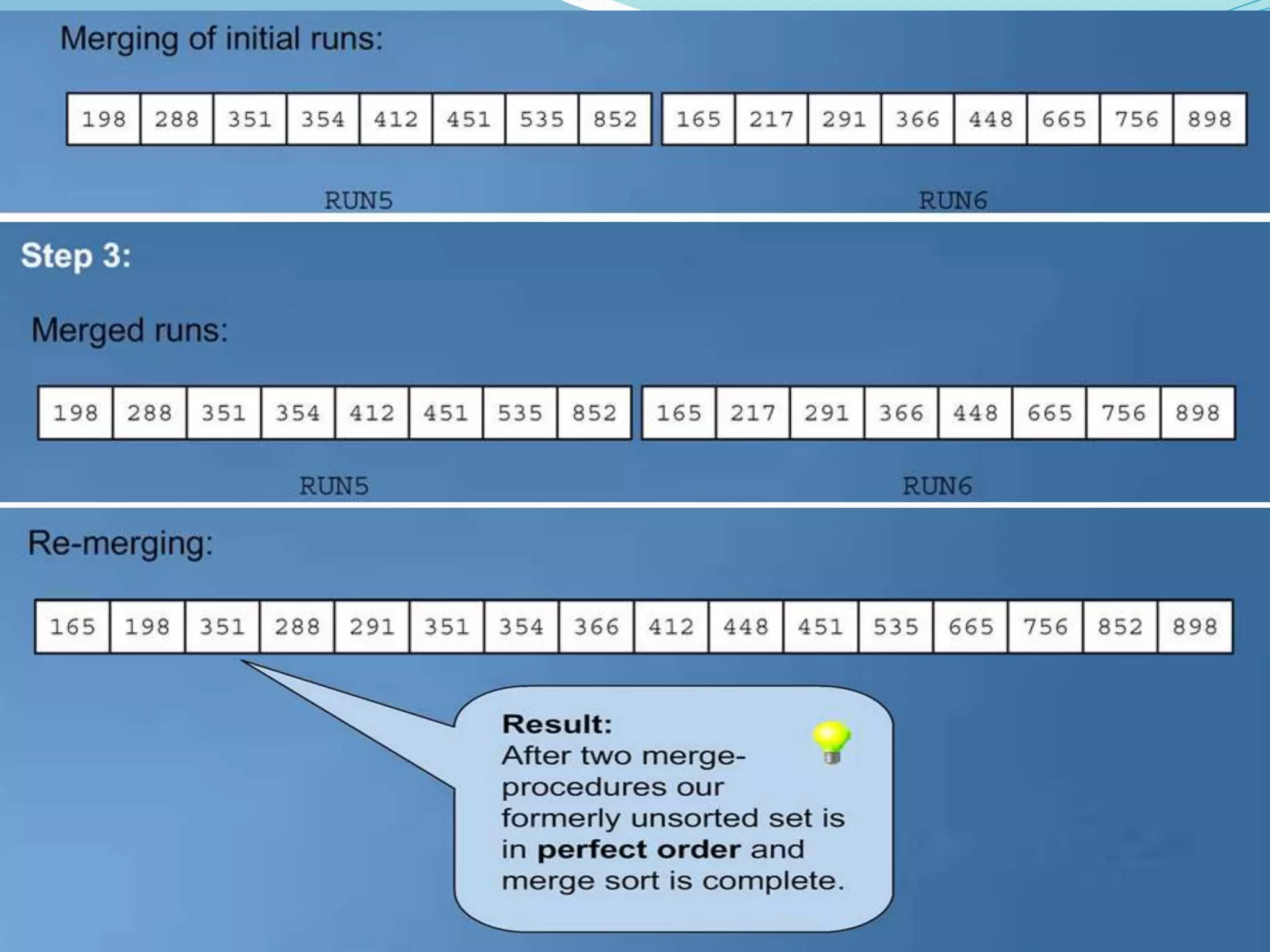
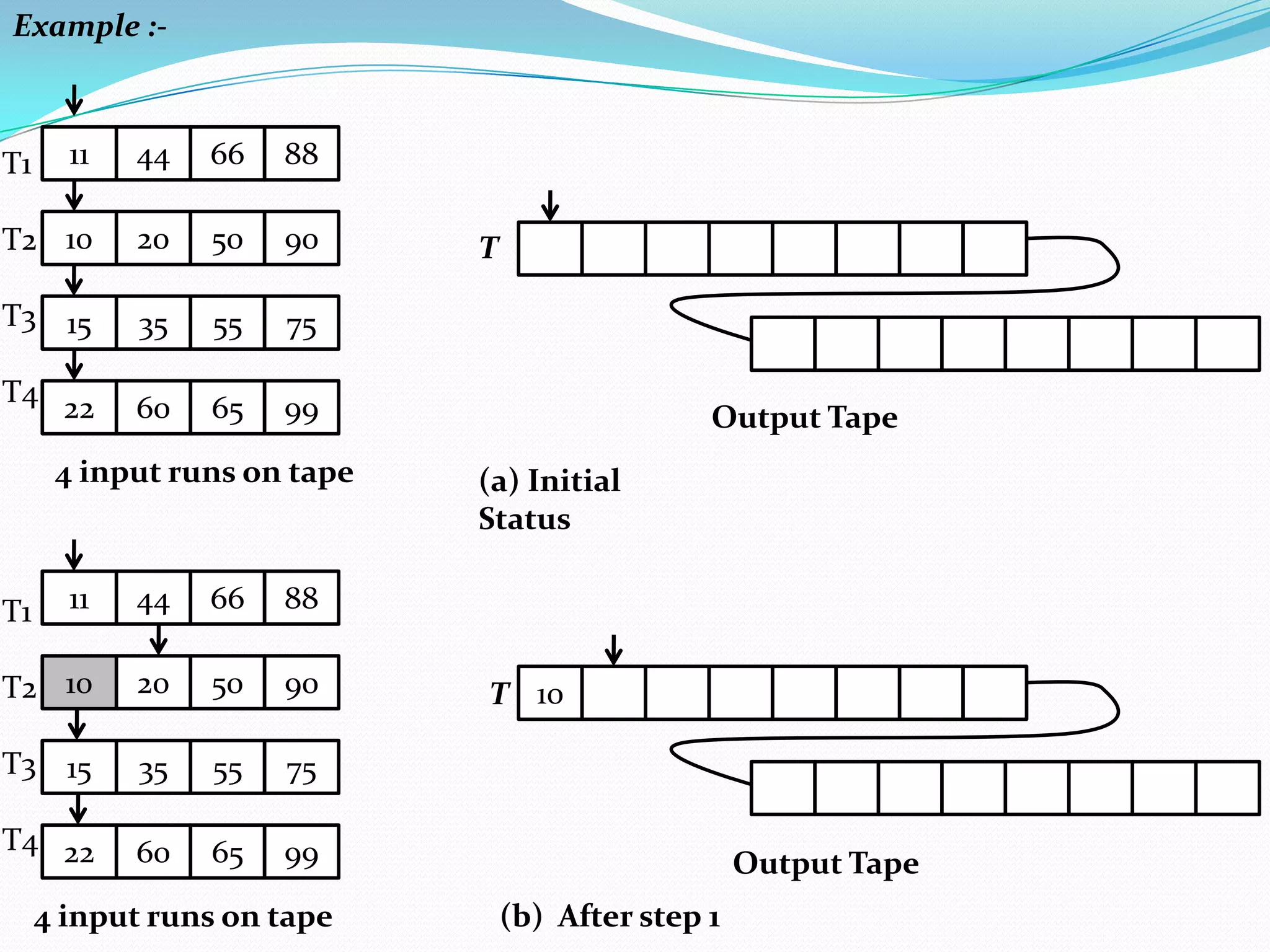
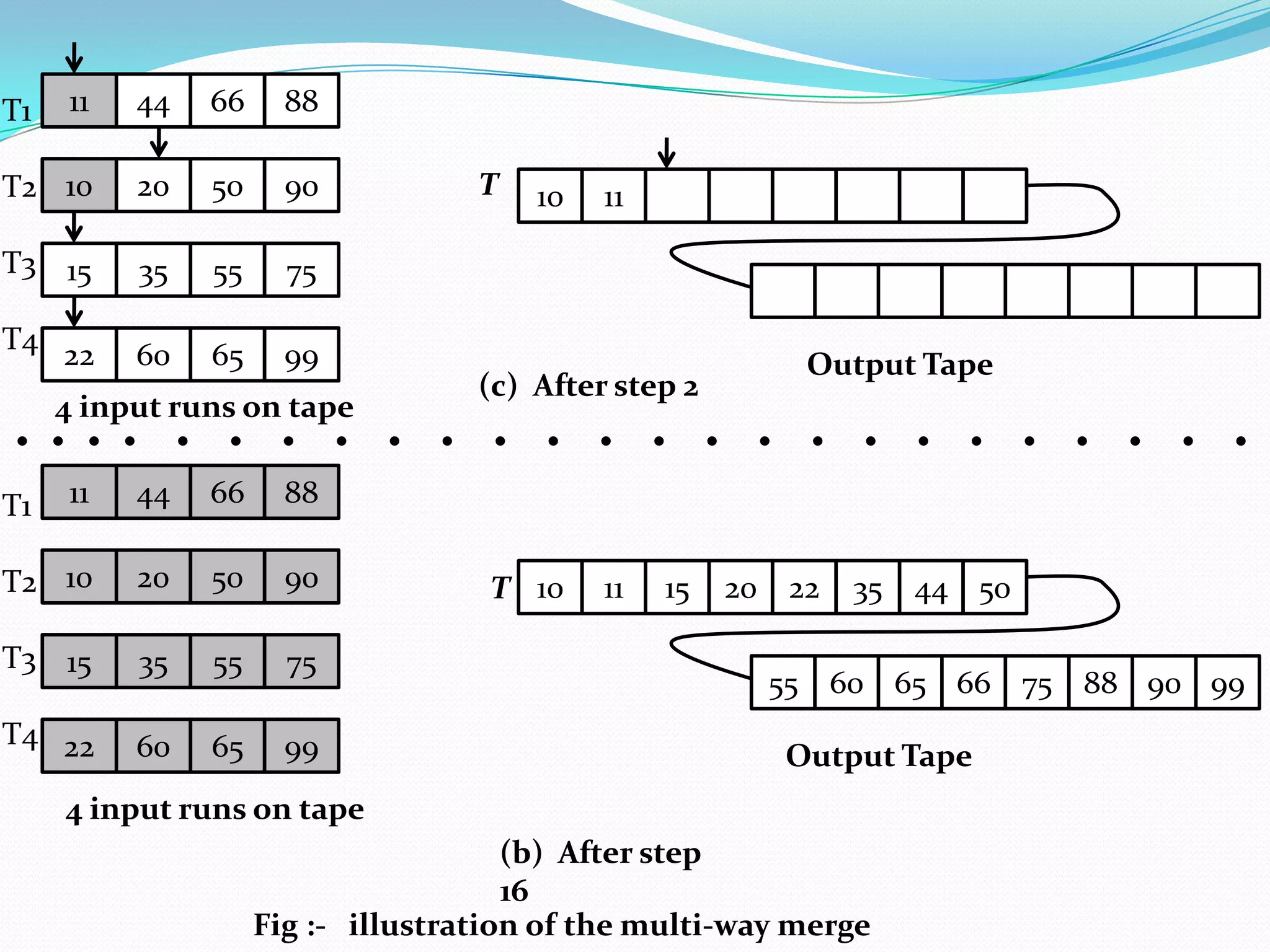
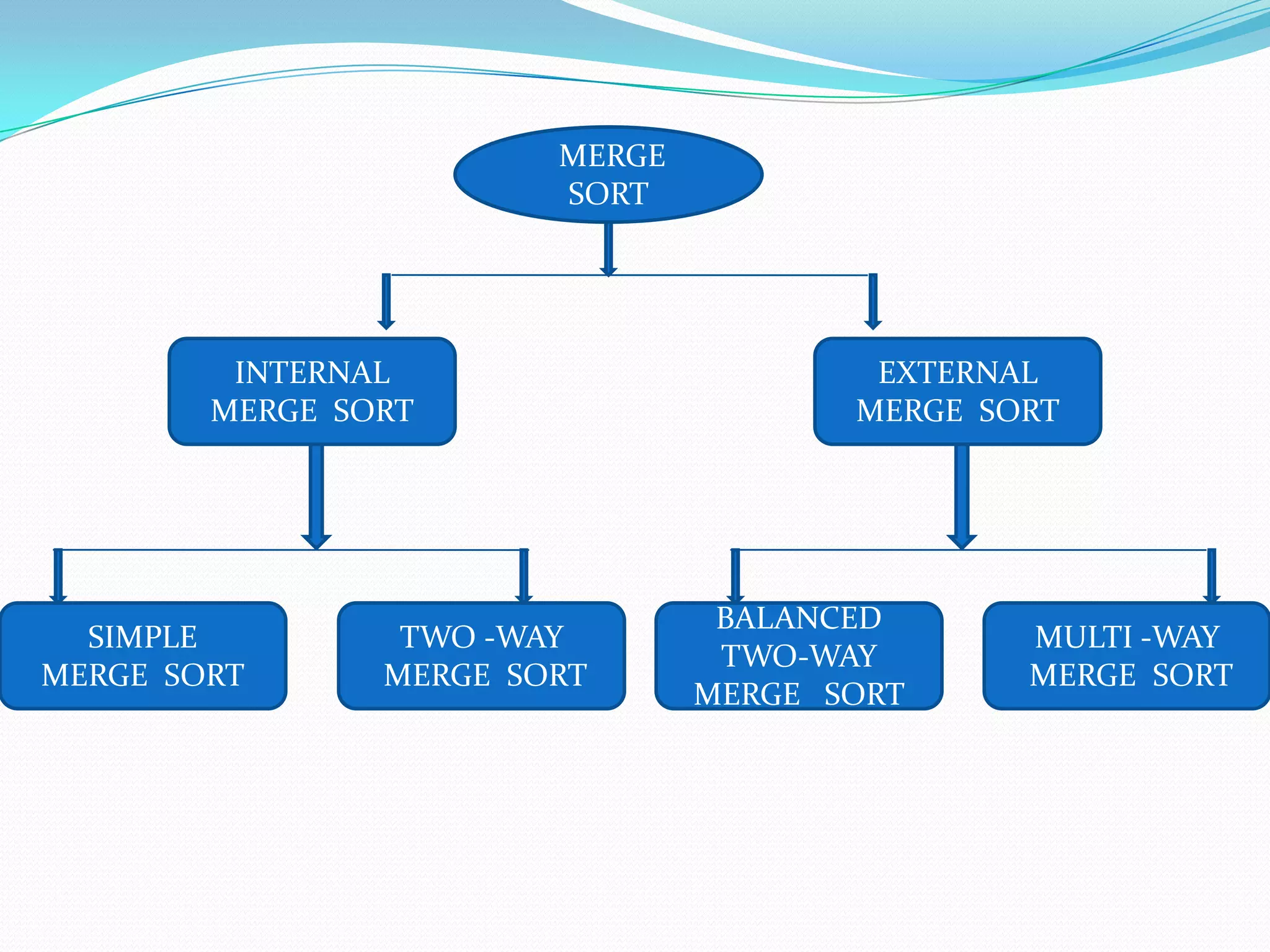
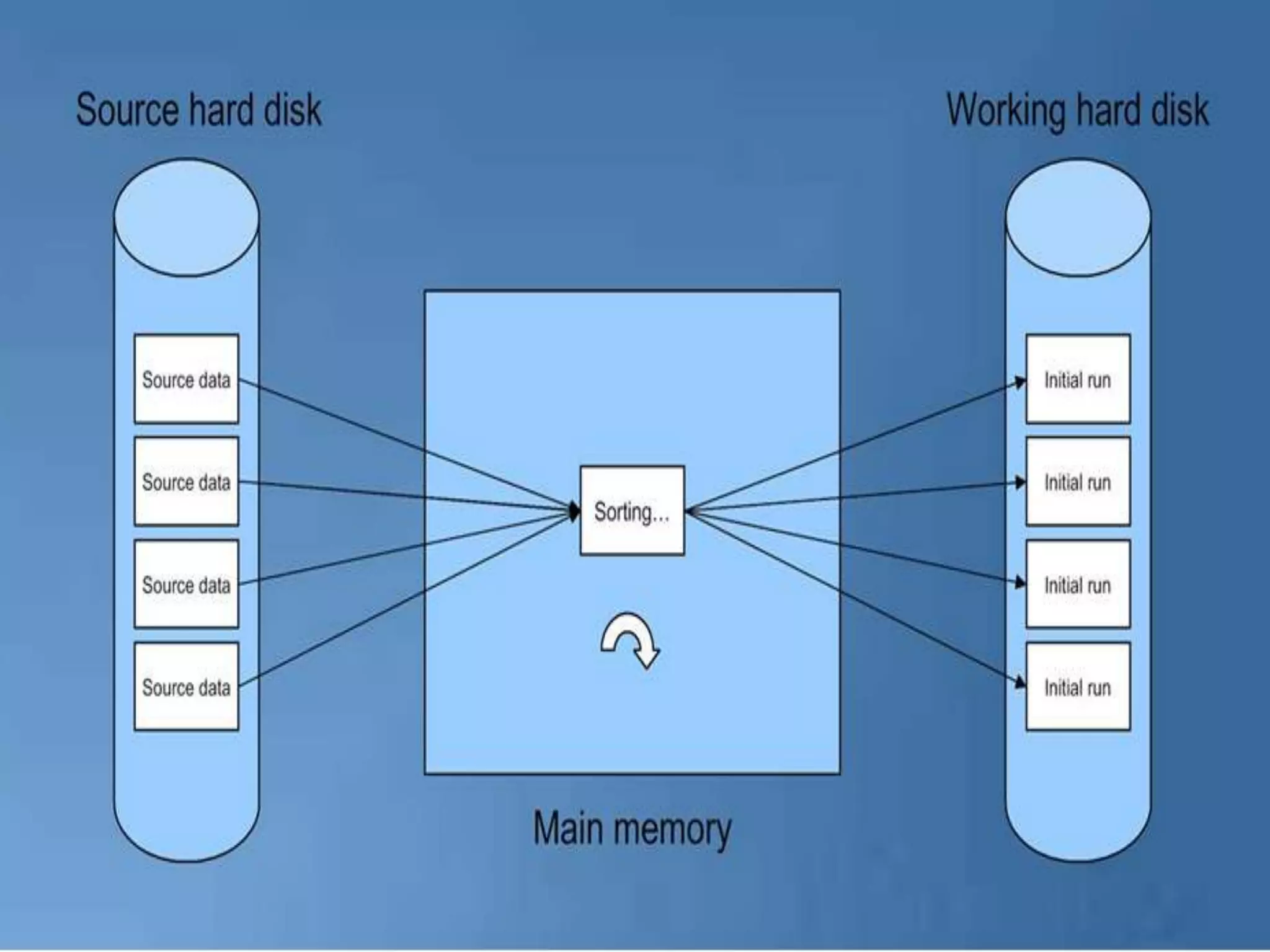
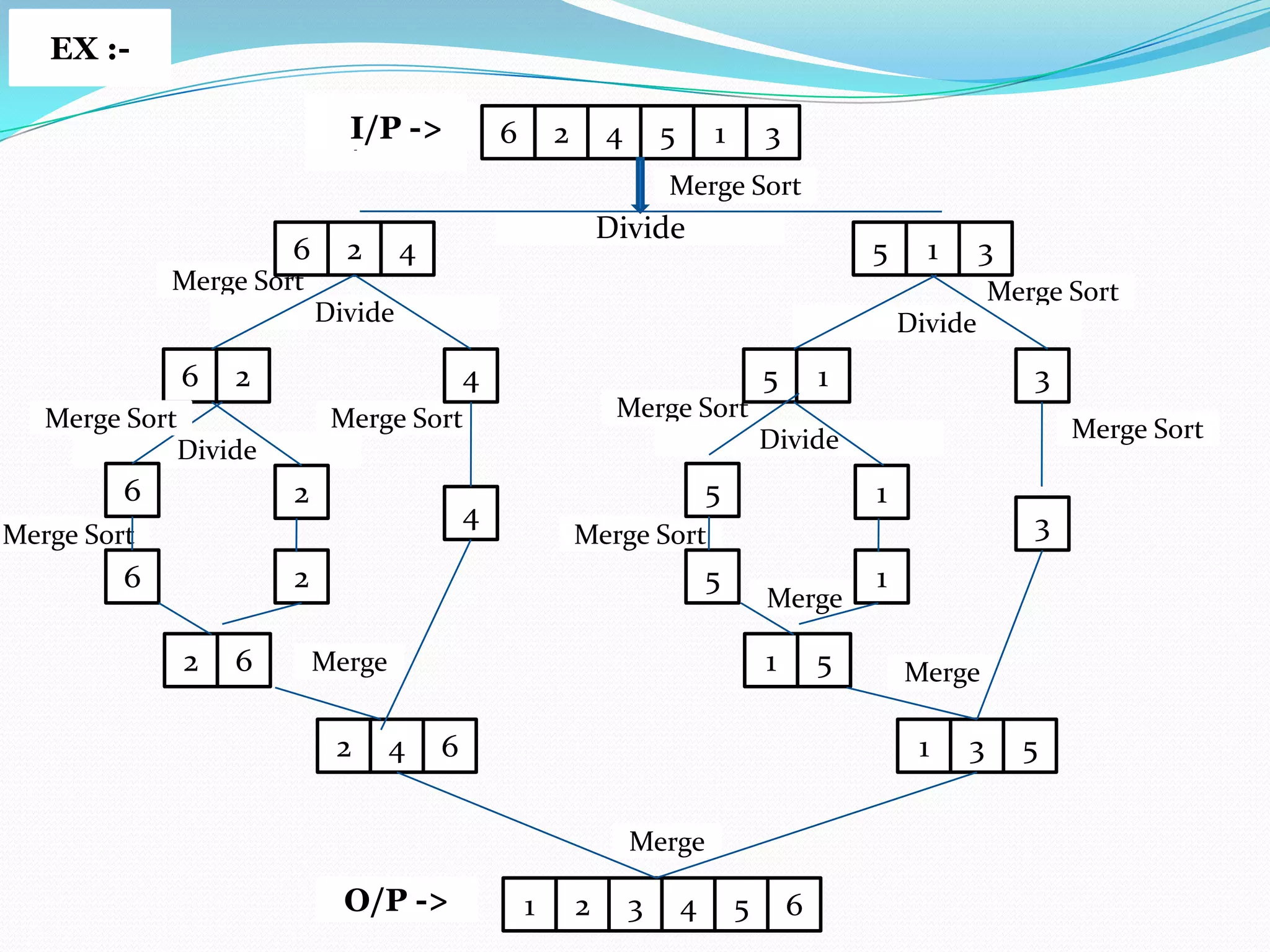
There are two broad categories of sorting methods based on merging: internal merge sort and external merge sort. Internal merge sort handles small lists that fit into primary memory, including simple merge sort and two-way merge sort. External merge sort is for very large lists that exceed primary memory, including balanced two-way merge sort and multi-way merge sort. The simple merge sort uses a divide-and-conquer approach to recursively split lists in half, sort each sublist, and then merge the sorted sublists.


![SIMPLE MERGE SORT : The simple merge sort (or merge sort) technique closely follows the
divide –and-conqure paradigm.
let a list of n elements to be sorted with l and r being the position
of leftmost and rightmost element in the list.
The three tasks in this divided-and-conqure technique are as
followed :-
[
]
1. Divide :- Partition the list midway ,that is ,at (l+r)/2 into two
sub lists with (n/2) elements in each, if n is even or
[n/2] and [n/2]-1 element if n is odd .
2. Conquer :- Sort the two lists recursively using the merge sort.
3. Combine :- Merge the sort sub listed to obtain the sorted output.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mainds-140130082205-phpapp01/75/Marge-Sort-5-2048.jpg)
![Combine
Conqure
Divide
l
r
.........................................................................
.
[(l+r)/2]
.................................. ..................................
.
.
Sort this left-part by merge sort Sort this right-part by merge sort
...................................
...................................
Merge the two list
Sorted List
Fig. Divide-and-conqure strategy in the merge
sort](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mainds-140130082205-phpapp01/75/Marge-Sort-6-2048.jpg)
![Algorithm Merge sort
Input :- An array A[l…r] where l and r are the lower and upper index
of A.
Output :- Array a[l…r] with all element arranged in ascending order .
Steps:
1. if(r<=l) then
2.
Return
3. else
4.
Mid=[(l+r)/2]
5.
MergeSort(A[l…mid])
6.
MergeSort(A[mid+1…r])
7.
Merge(A,L,mid,r)
8. Endif
9. Stop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mainds-140130082205-phpapp01/75/Marge-Sort-8-2048.jpg)