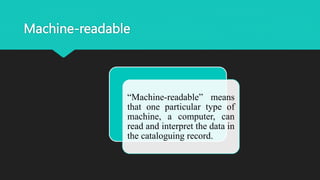
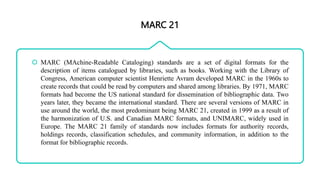
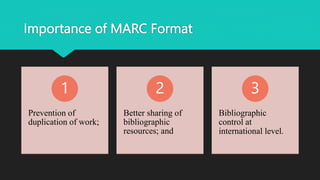
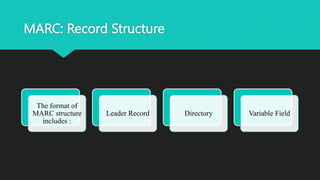
MARC (MAchine-Readable Cataloging) is a format standard that allows bibliographic records to be shared between libraries and read by computers. It was developed in the 1960s and became the US and international standard. MARC 21 is the current predominant version, created in 1999 from the harmonization of US and Canadian MARC formats. A MARC record has three main elements - a record structure that follows international standards, content designators that identify data elements, and the data content itself. Tags, indicators, and subfields are used to encode the different fields within a record. MARC 21 allows for efficient sharing of cataloging records between libraries.