MARC (MAchine-Readable Cataloging) is a data format that emerged from a Library of Congress initiative to define a standard for catalog records that enables computers to interpret bibliographic information. MARC records use tags, indicators, and subfields to provide "signposts" that allow computers to distinguish between different elements like title, author, and subjects. Fields in MARC records are either fixed fields that use codes or variable fields for descriptive information. Common fields include titles, authors, and subjects that provide access points for finding records.













![15
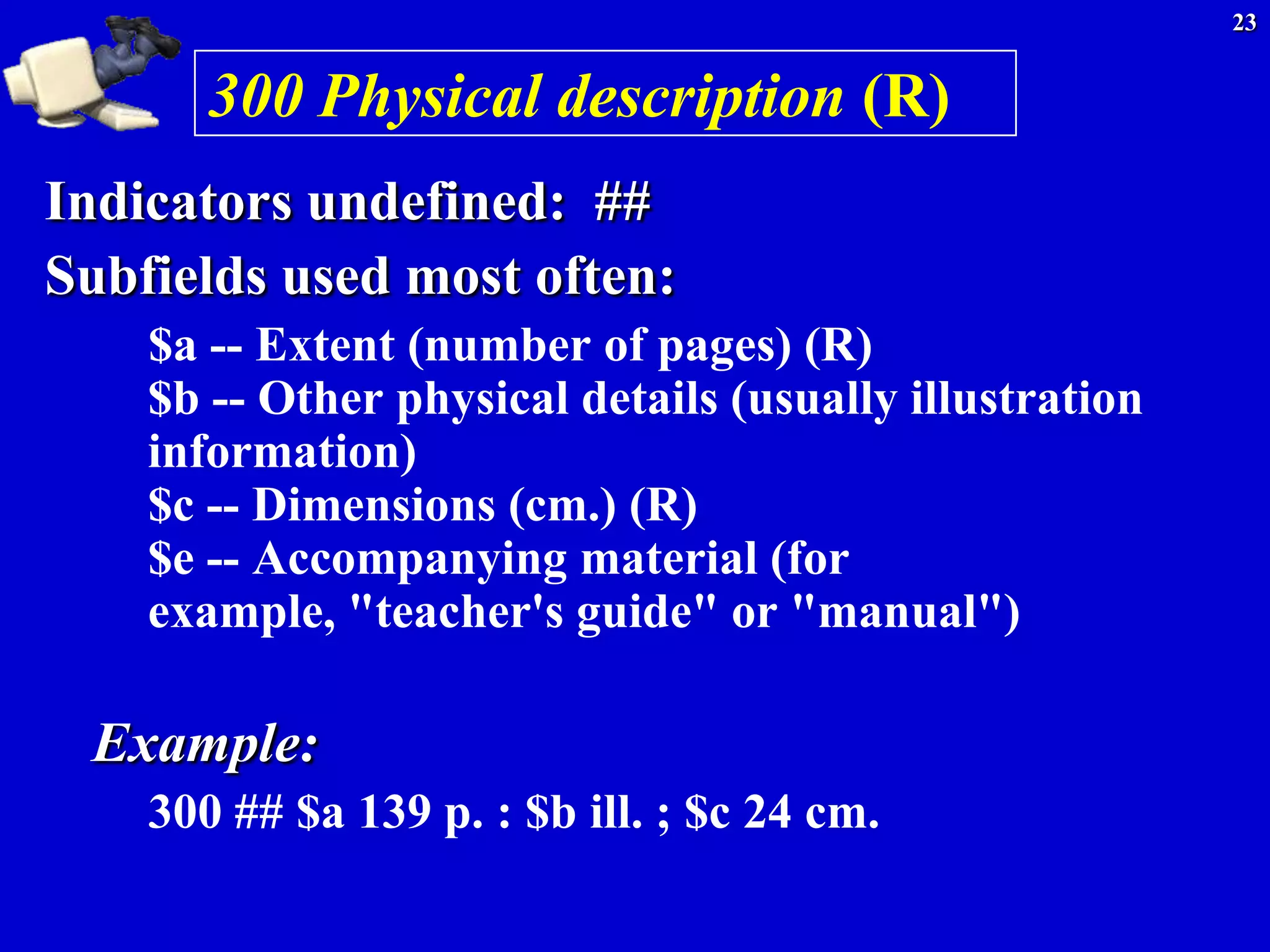
Important fields to be aware of
020 International Standard Book Number -- (ISBN)
(R, or Repeatable i.e. there can be more than one 020 field)
Indicators undefined [entered as ##].
Subfields used most often:
$a -- International Standard Book Number
$c -- Terms of availability (often a price)
$z -- Cancelled/invalid ISBN (R)
Example:
020 ## $a 0877547637
The computer is programmed to recognize that field 020 means
the standard number and that $a in this field stands for ISBN, so
it will display or print that out as ISBN:0877547637](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/divingintomarc-130406195208-phpapp01/75/Diving-into-MARC-What-s-MARC-got-to-do-with-it-15-2048.jpg)

![17
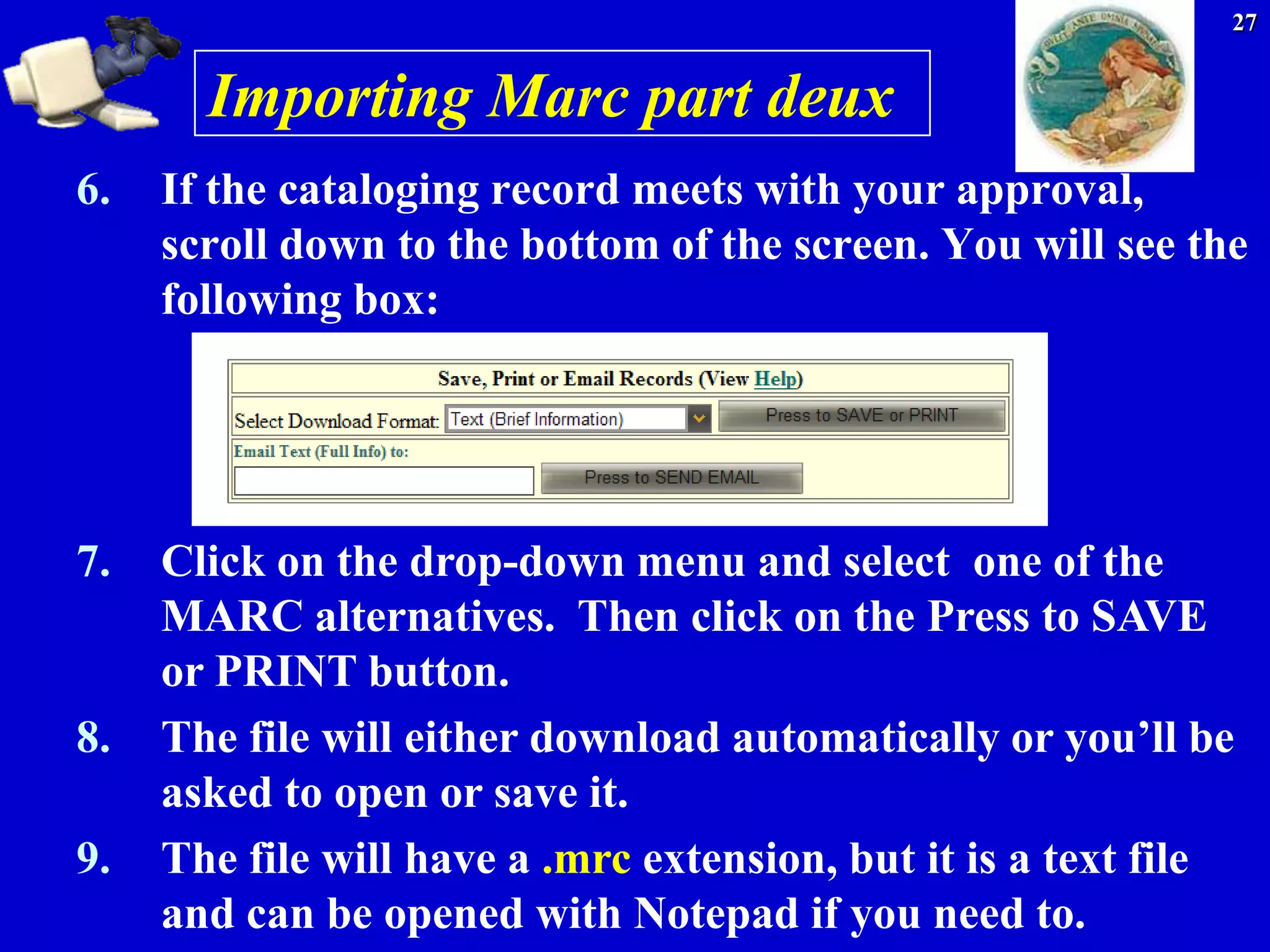
Two more 245 examples
245 00$aLibrary evaluation :$ba casebook and can-do
guide /$cDanny P. Wallace, Connie Van Fleet, editors.
Library evaluation : a casebook and can-do guide /
Danny P. Wallace, Connie Van Fleet, editors.
245 00$aWorld Book millennium 2000$h[computer
file].
World Book millenium 2000 [computer file].
Notice here that the GMD [General Material Designation] is
included, since that’s part of the title and statement of
responsibility area, and this isn’t a book](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/divingintomarc-130406195208-phpapp01/75/Diving-into-MARC-What-s-MARC-got-to-do-with-it-17-2048.jpg)

![19
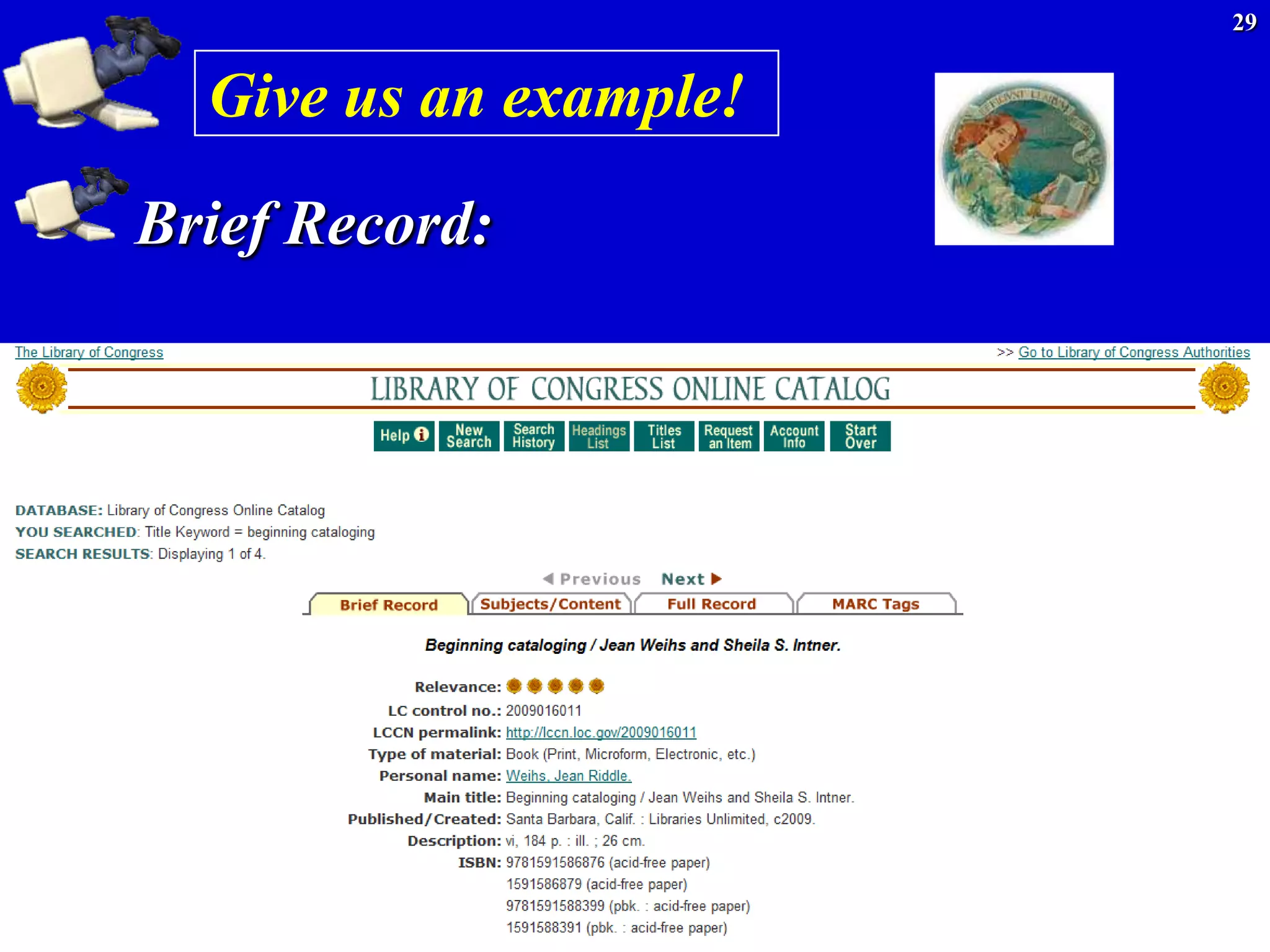
100 Main entry -- Personal name -- (primary author)
(NR [not repeatable]; there can be only one main entry)
Indicator 1: Type of personal name entry element
0 -- Forename
1 -- Surname (this is the most common form)
3 -- Family name
Indicator 2 undefined.
Indicator 2 became obsolete in 1990. Older records may display 0 or 1
Subfields used most often:
$a -- Personal name
$b -- Numeration
$c -- Titles and other words associated with a name (R)
$q -- Fuller form of name
$d -- Dates associated with a name (generally, year of birth)
Example:
100 1# $a Gregory, Ruth W. $q (Ruth Wilhelme), $d 1910-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/divingintomarc-130406195208-phpapp01/75/Diving-into-MARC-What-s-MARC-got-to-do-with-it-19-2048.jpg)