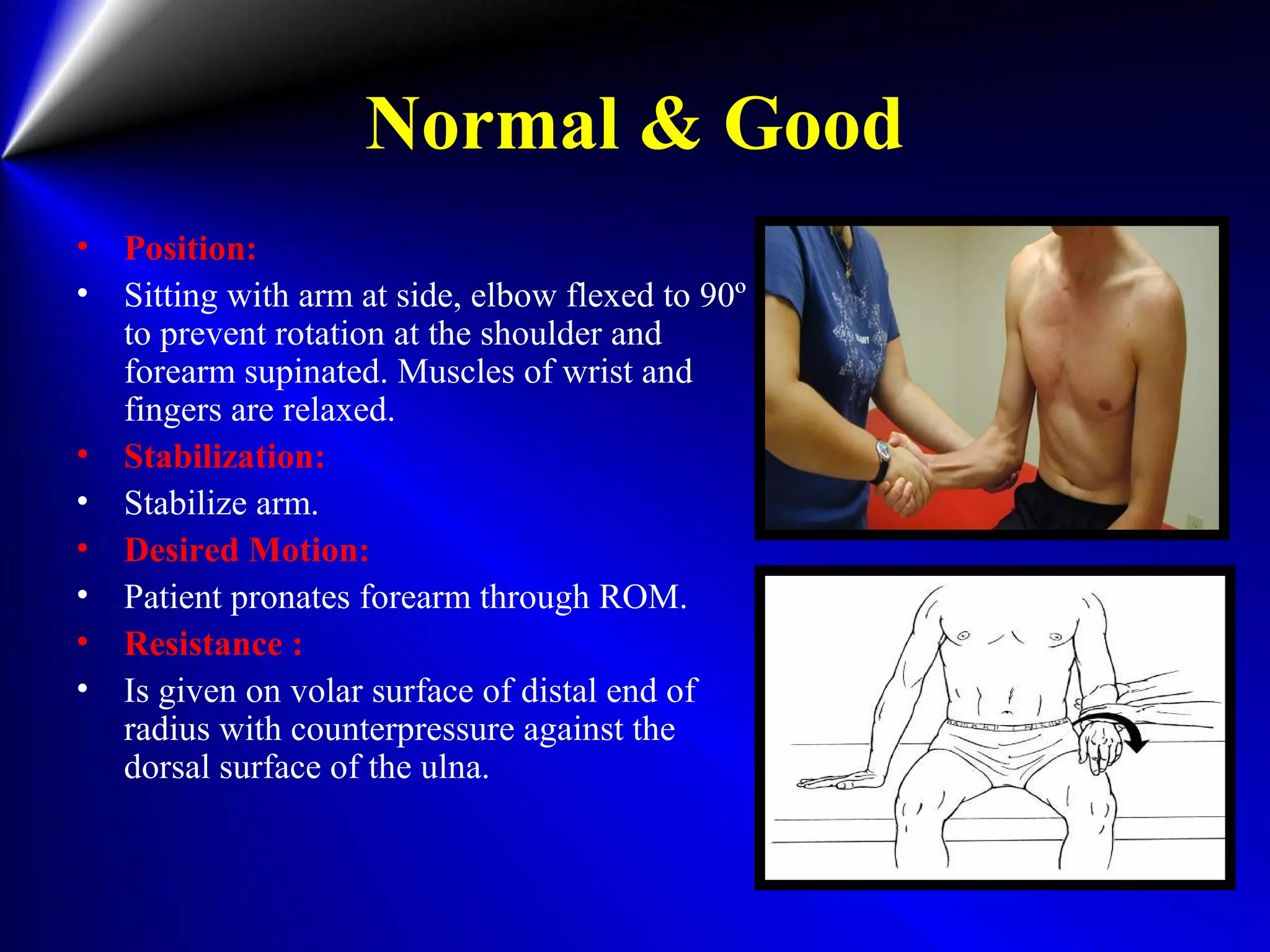
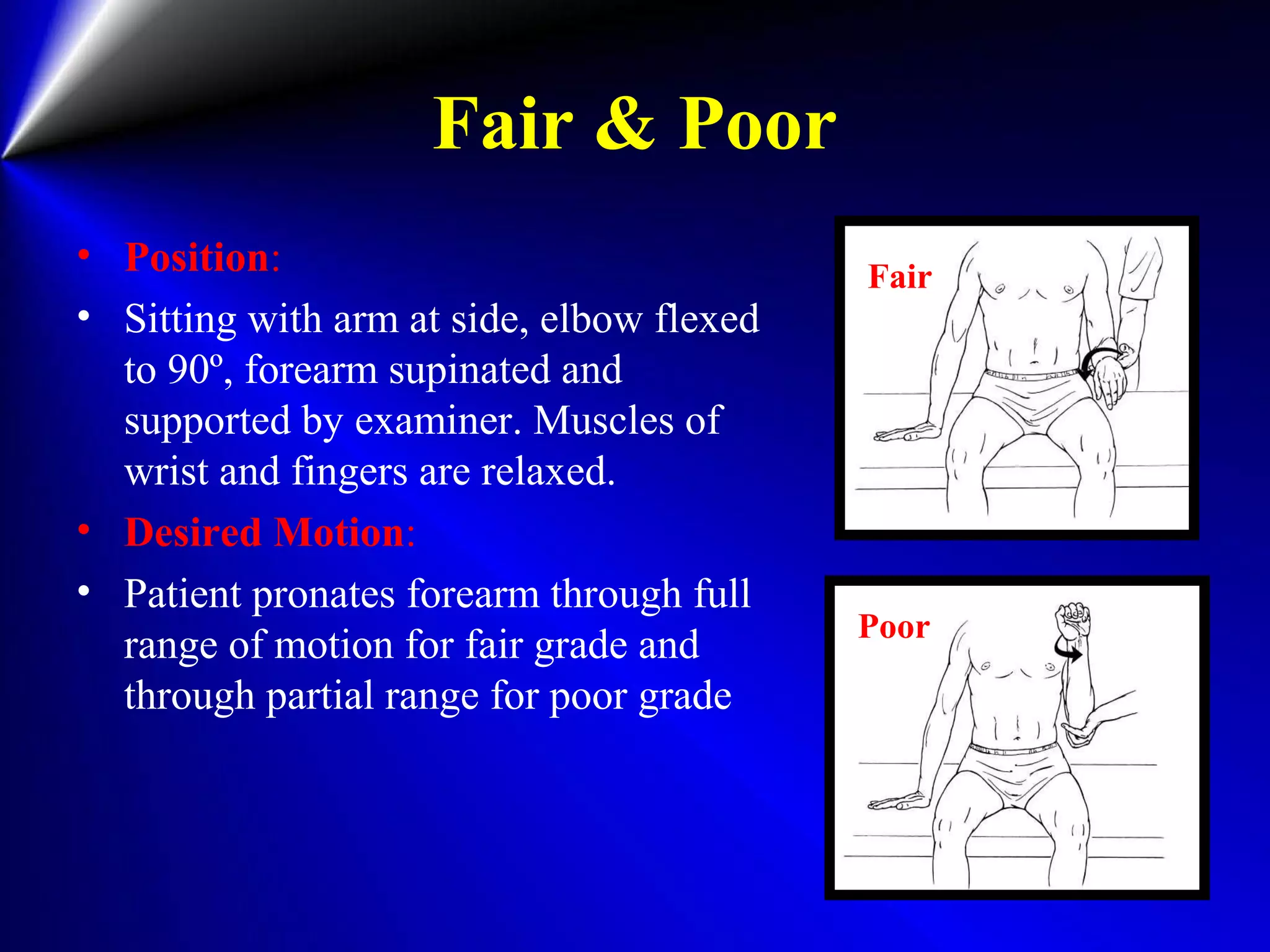
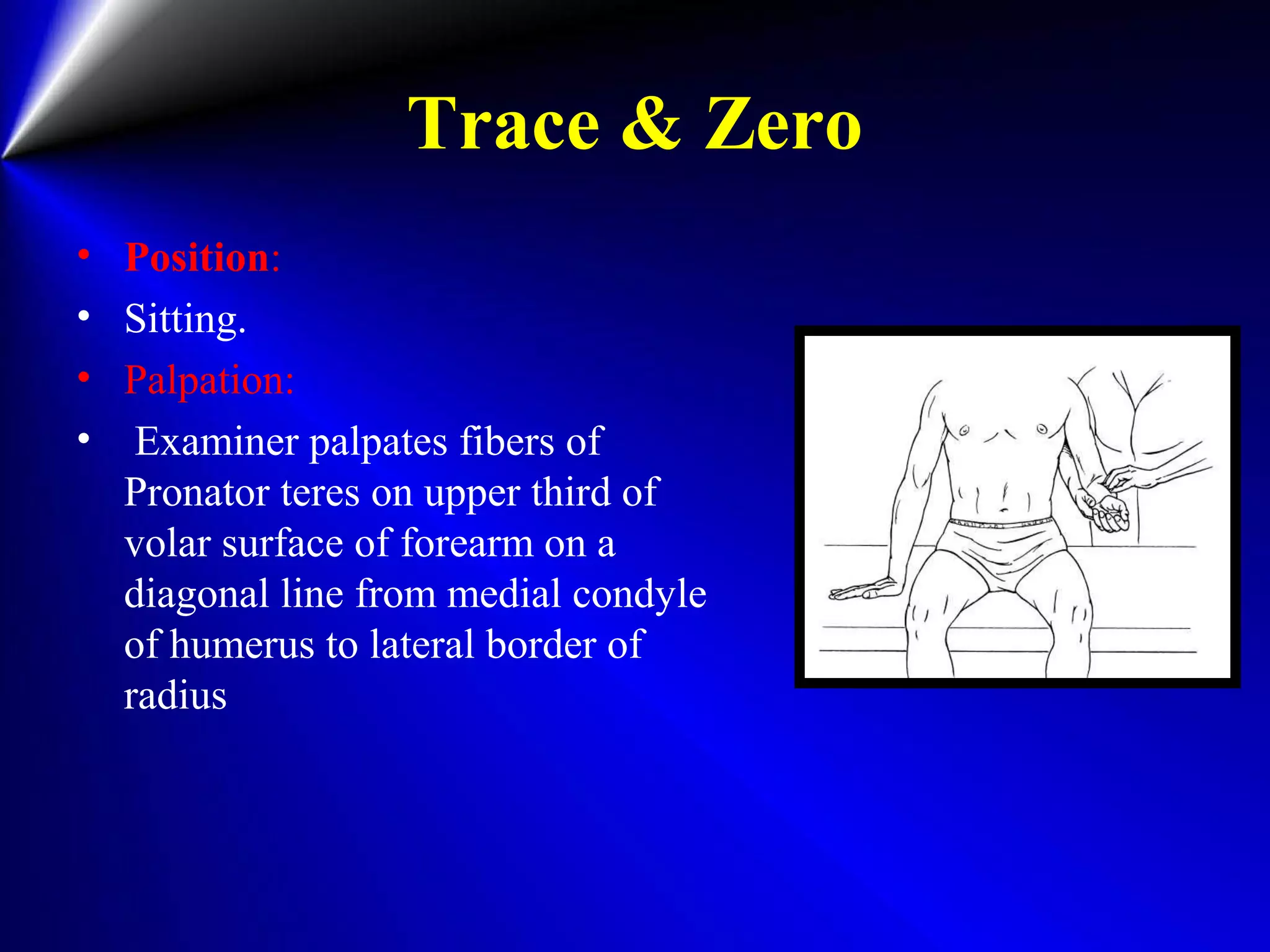
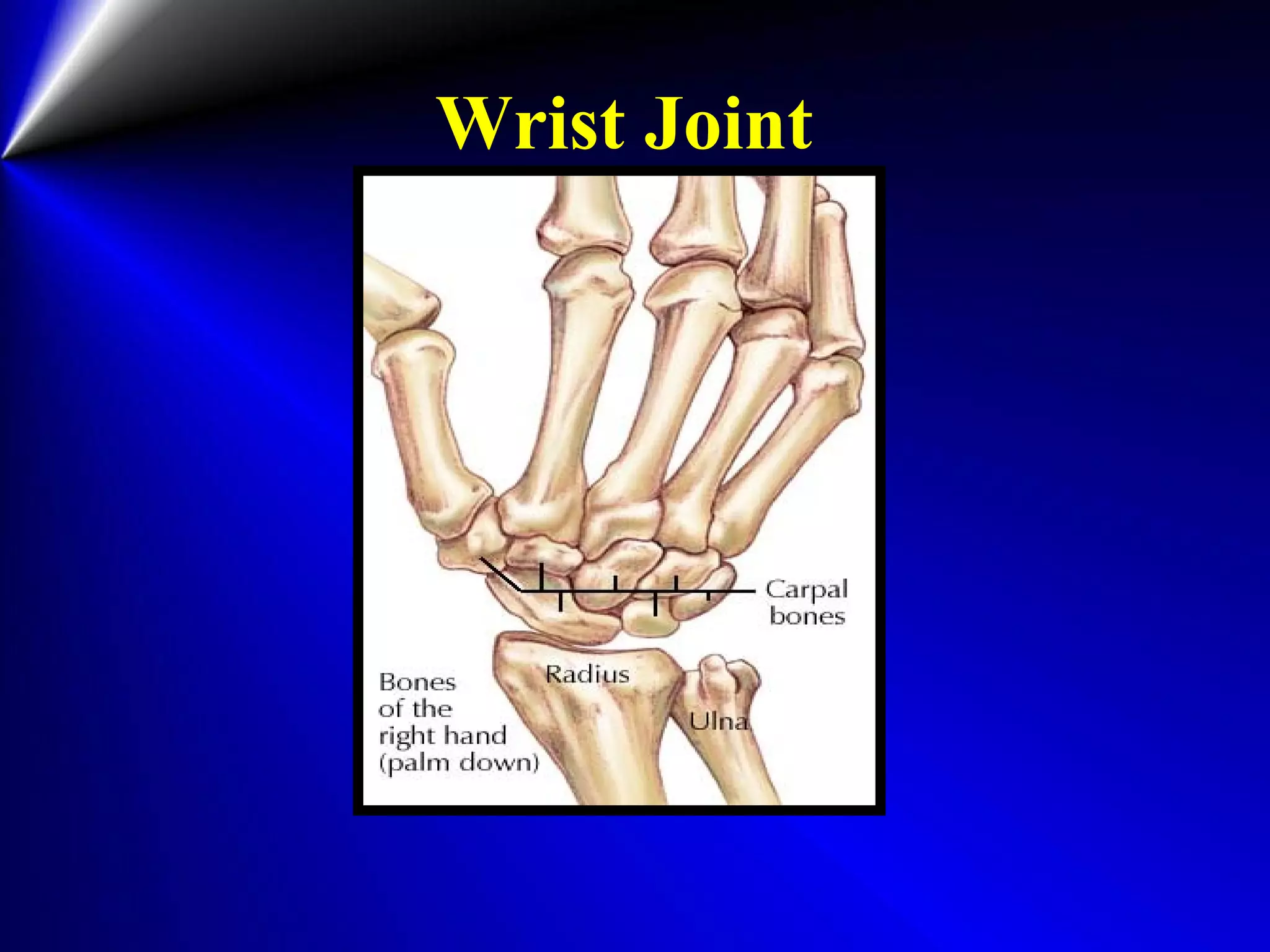
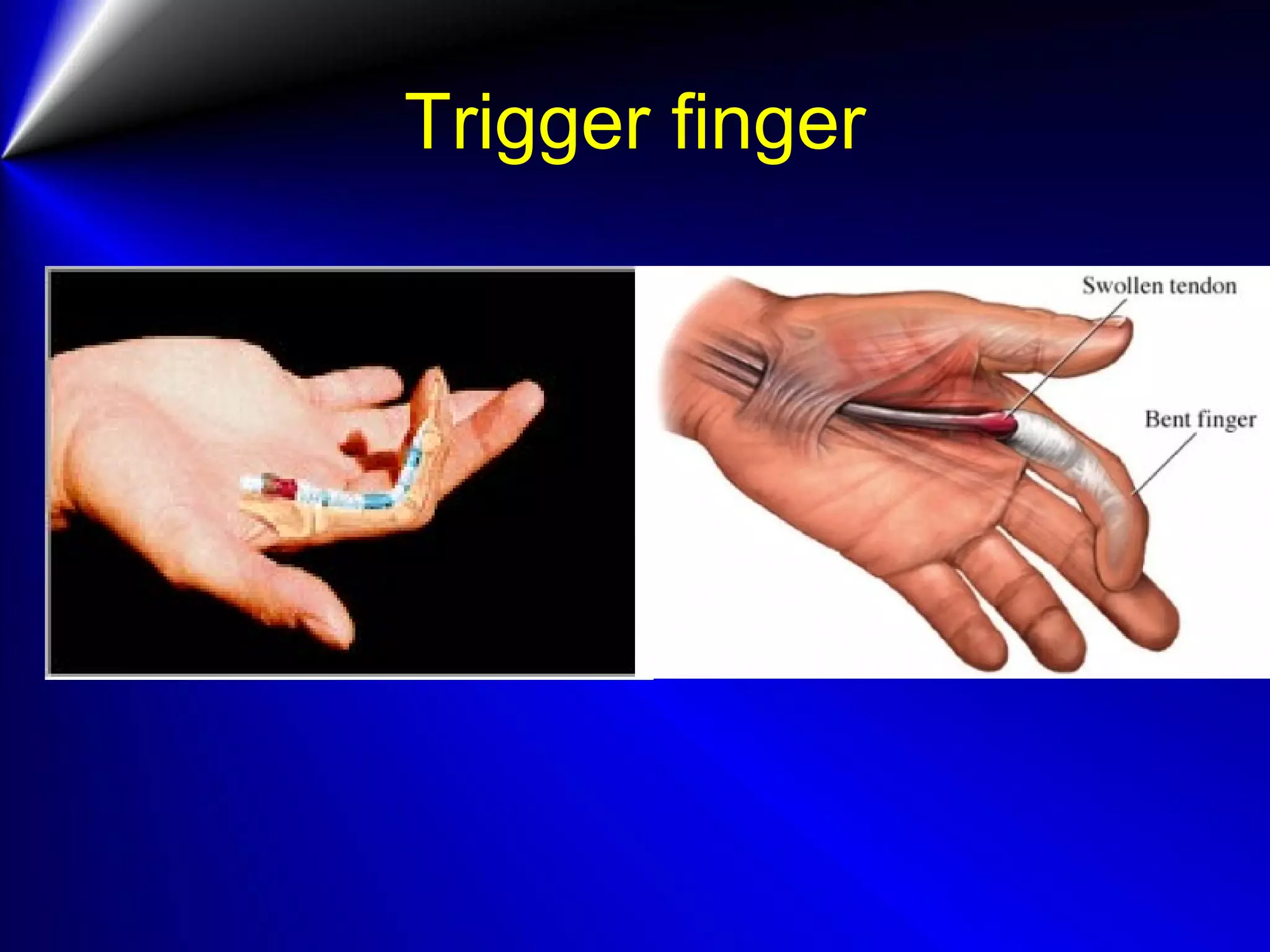
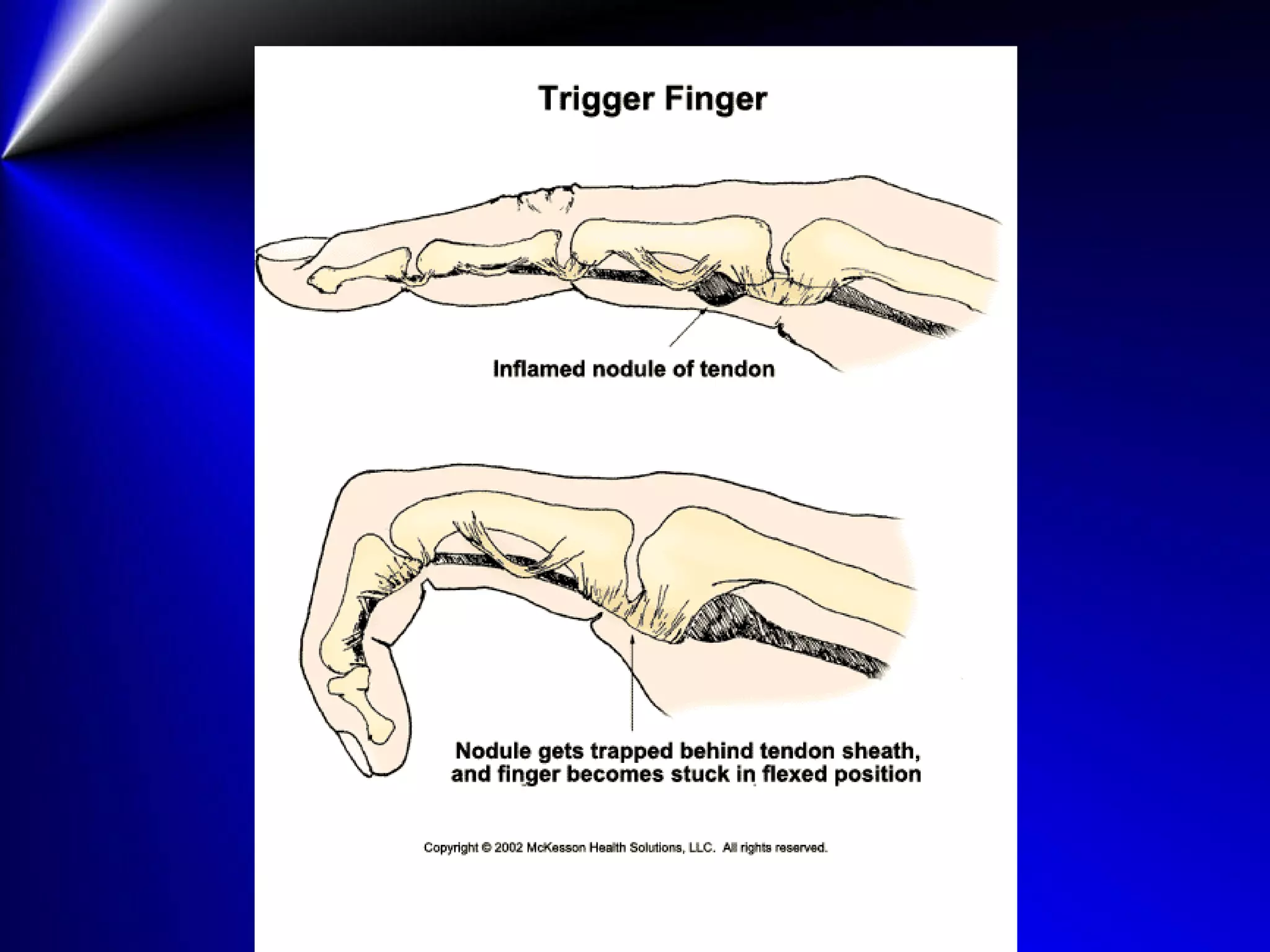
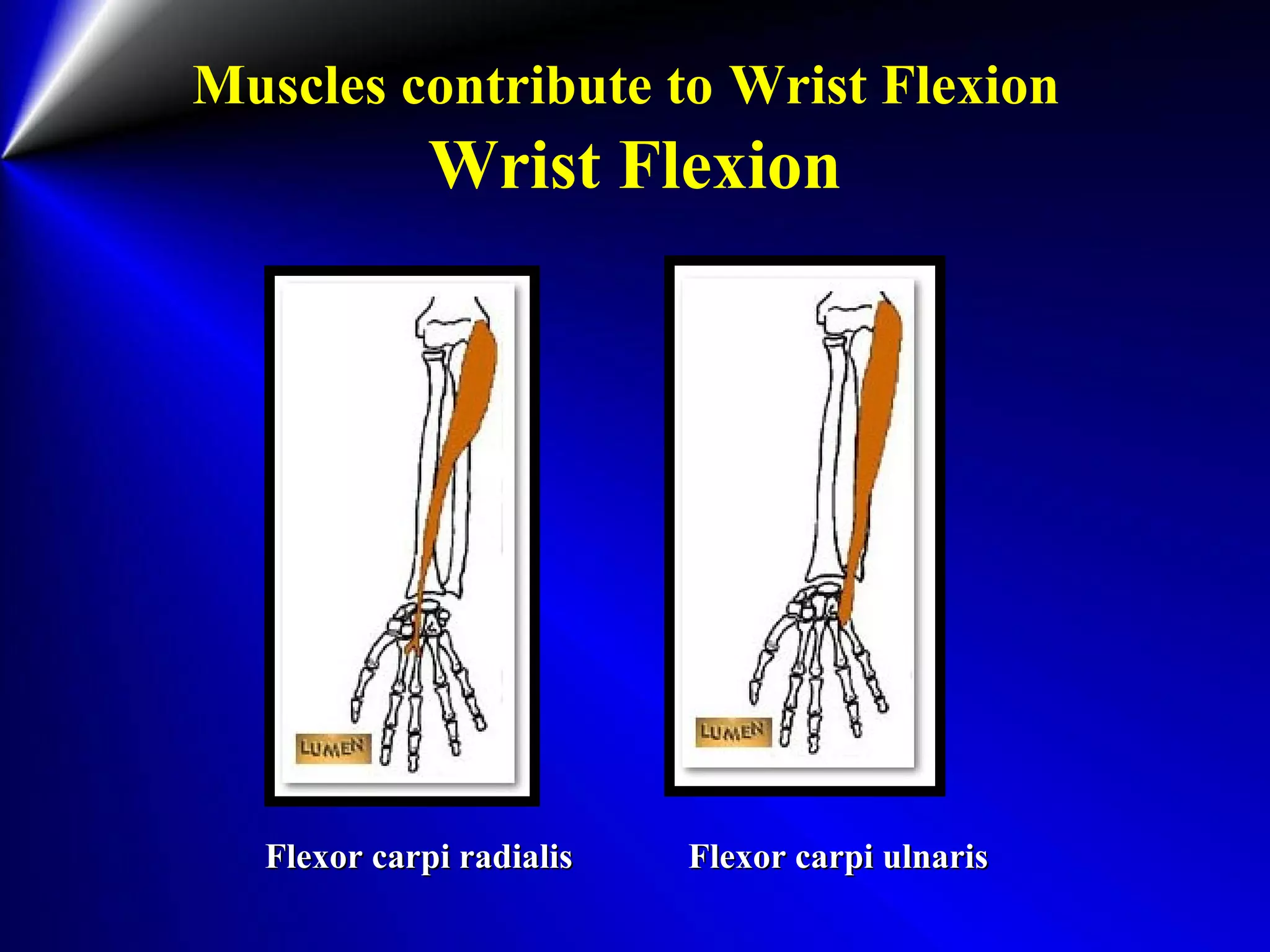
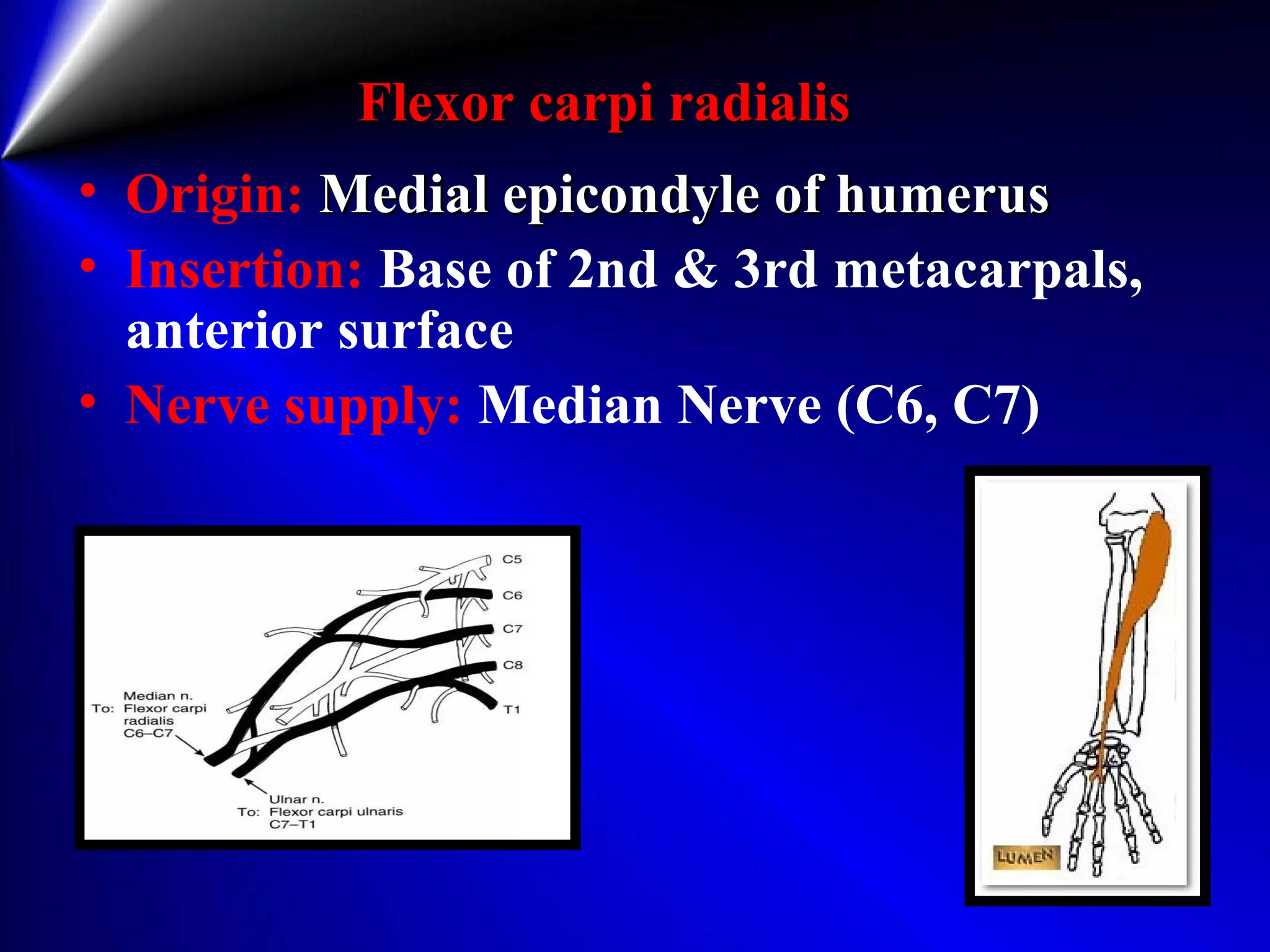
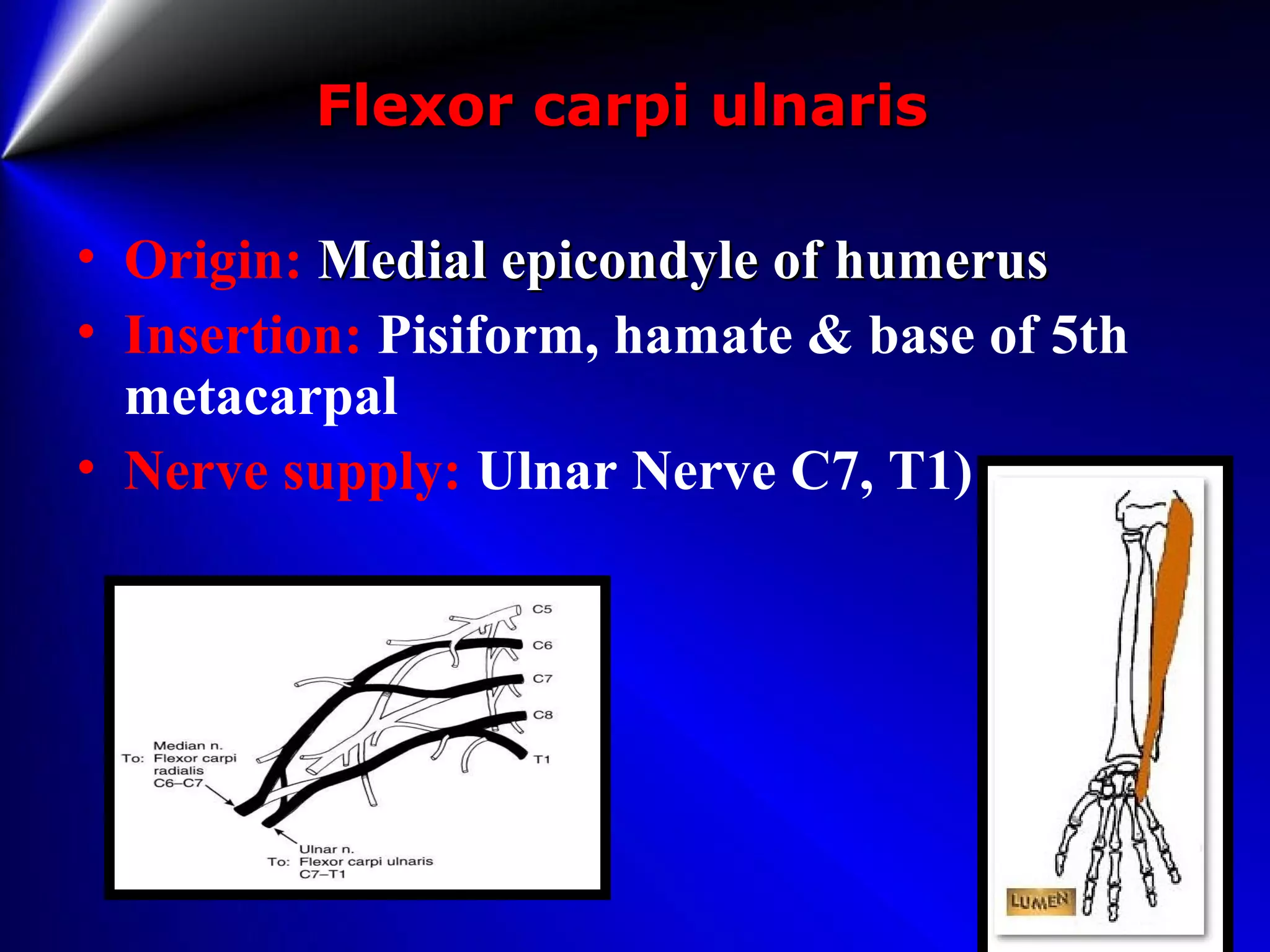
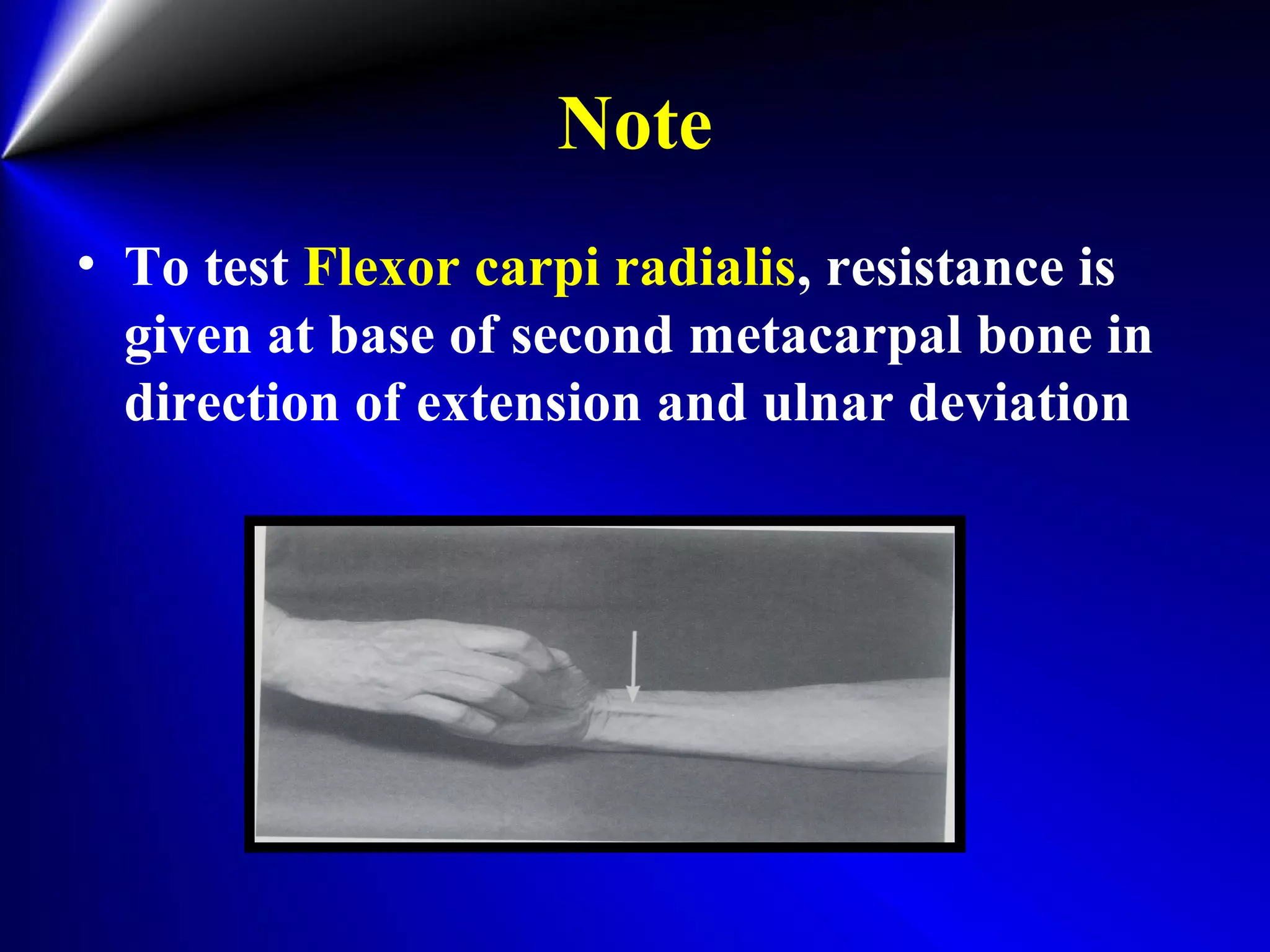
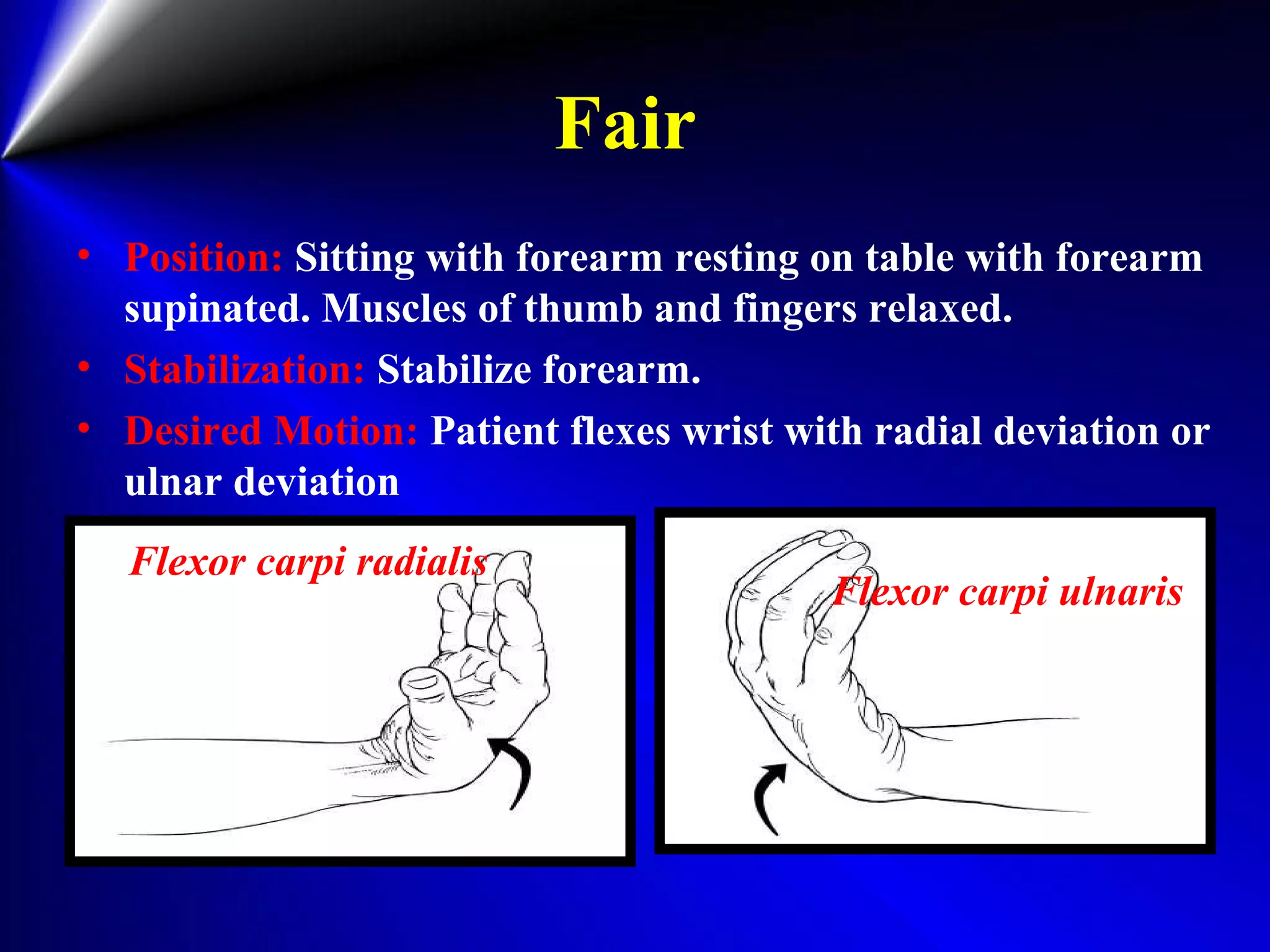
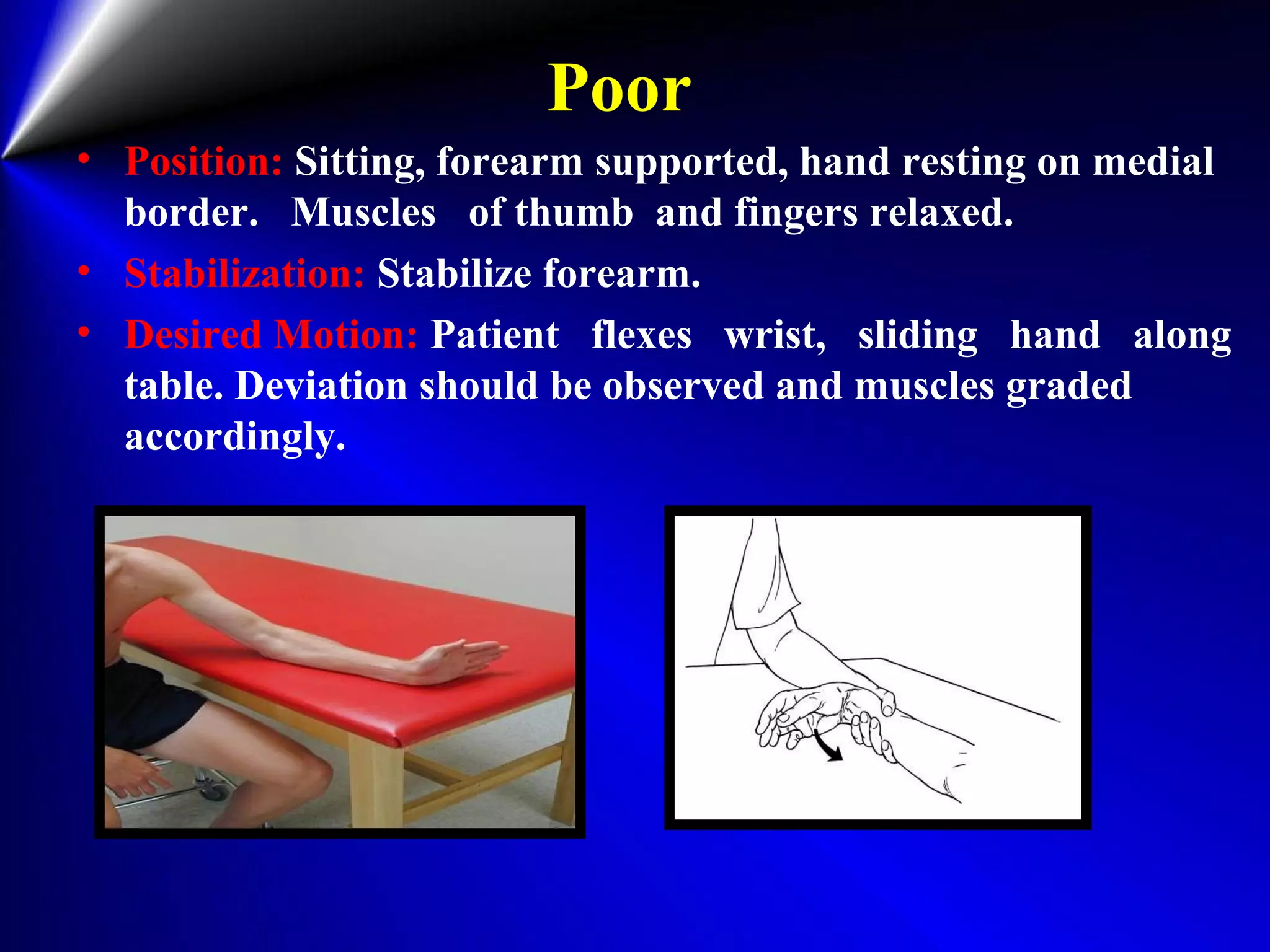
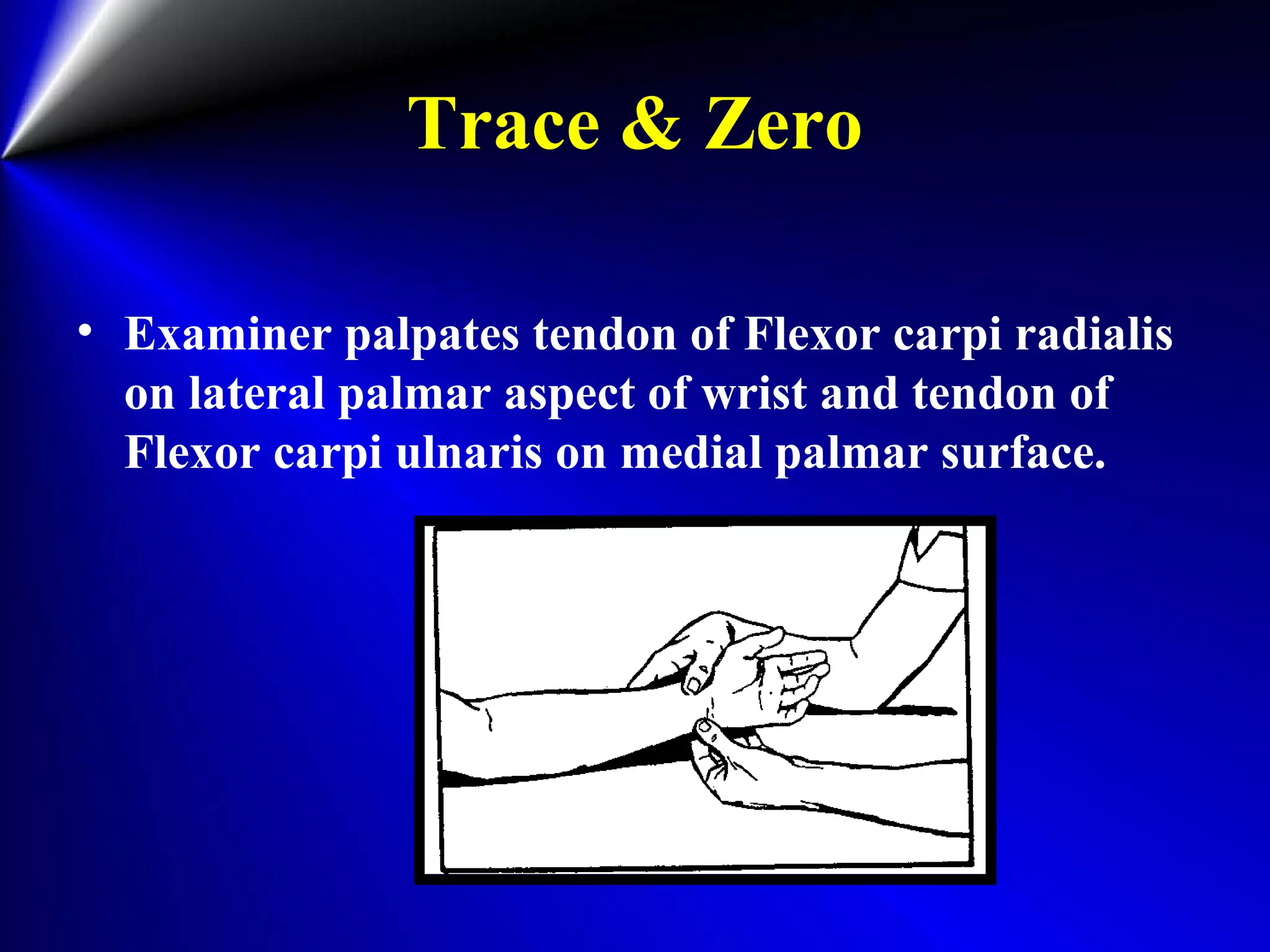
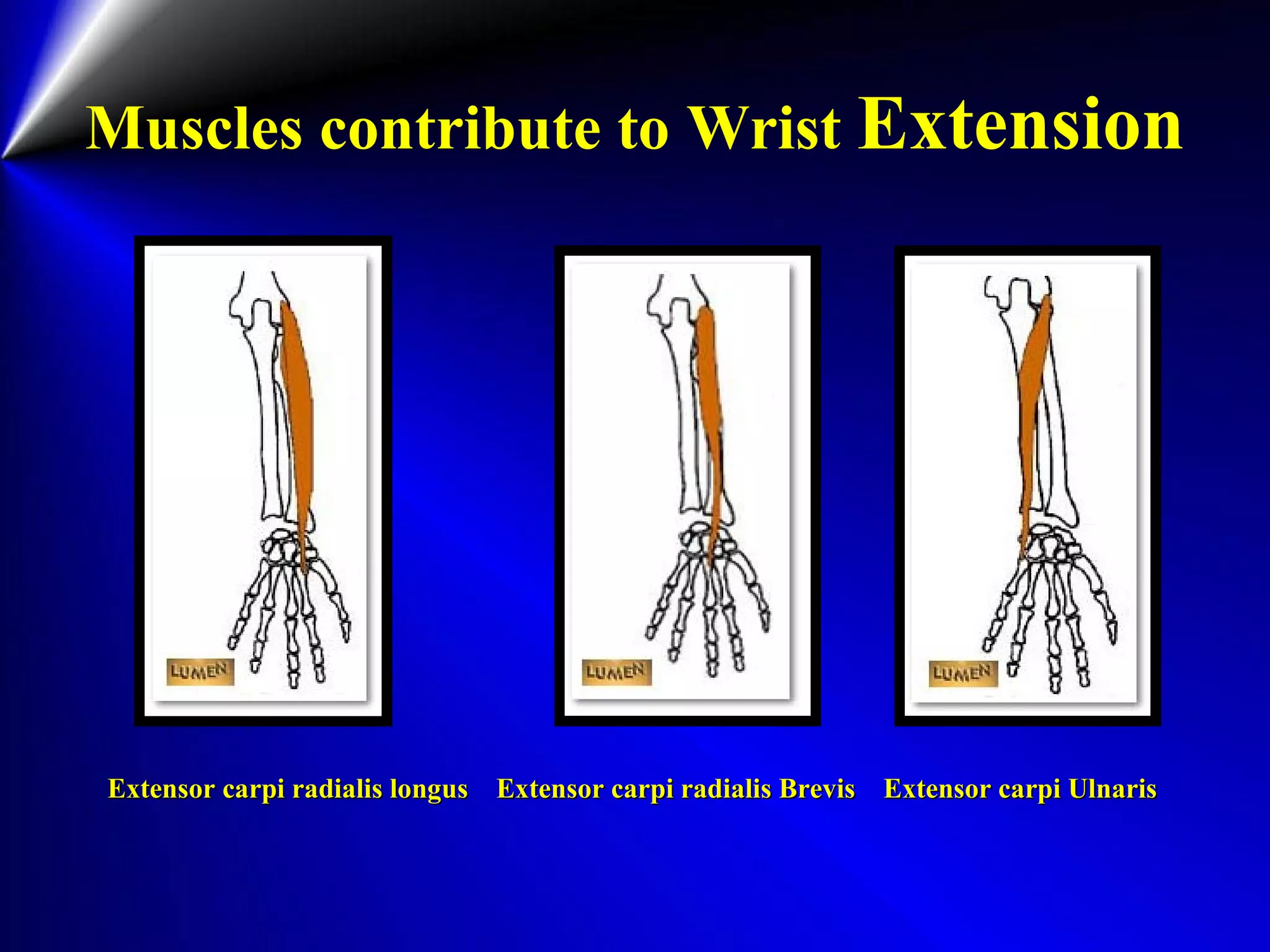
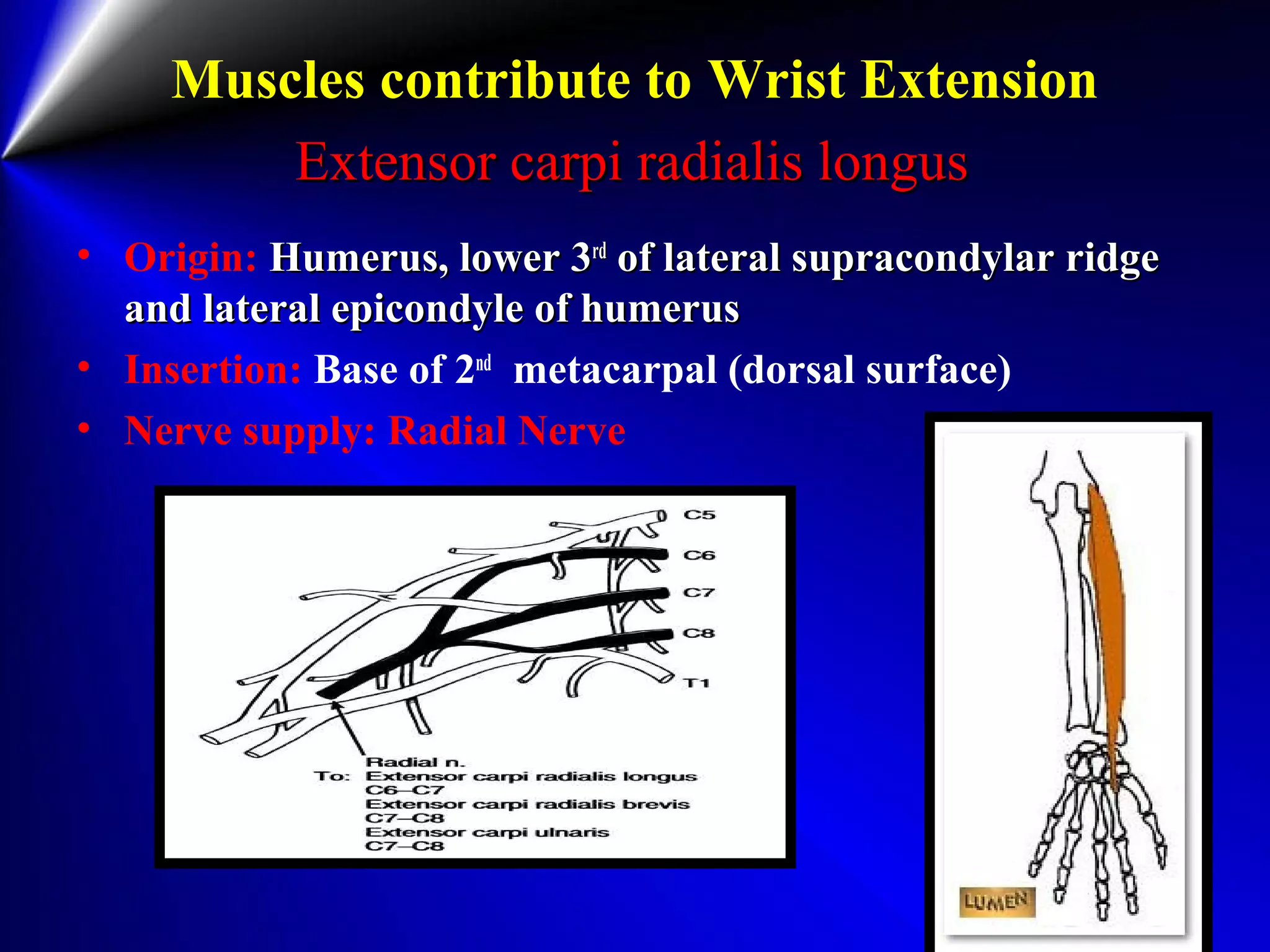
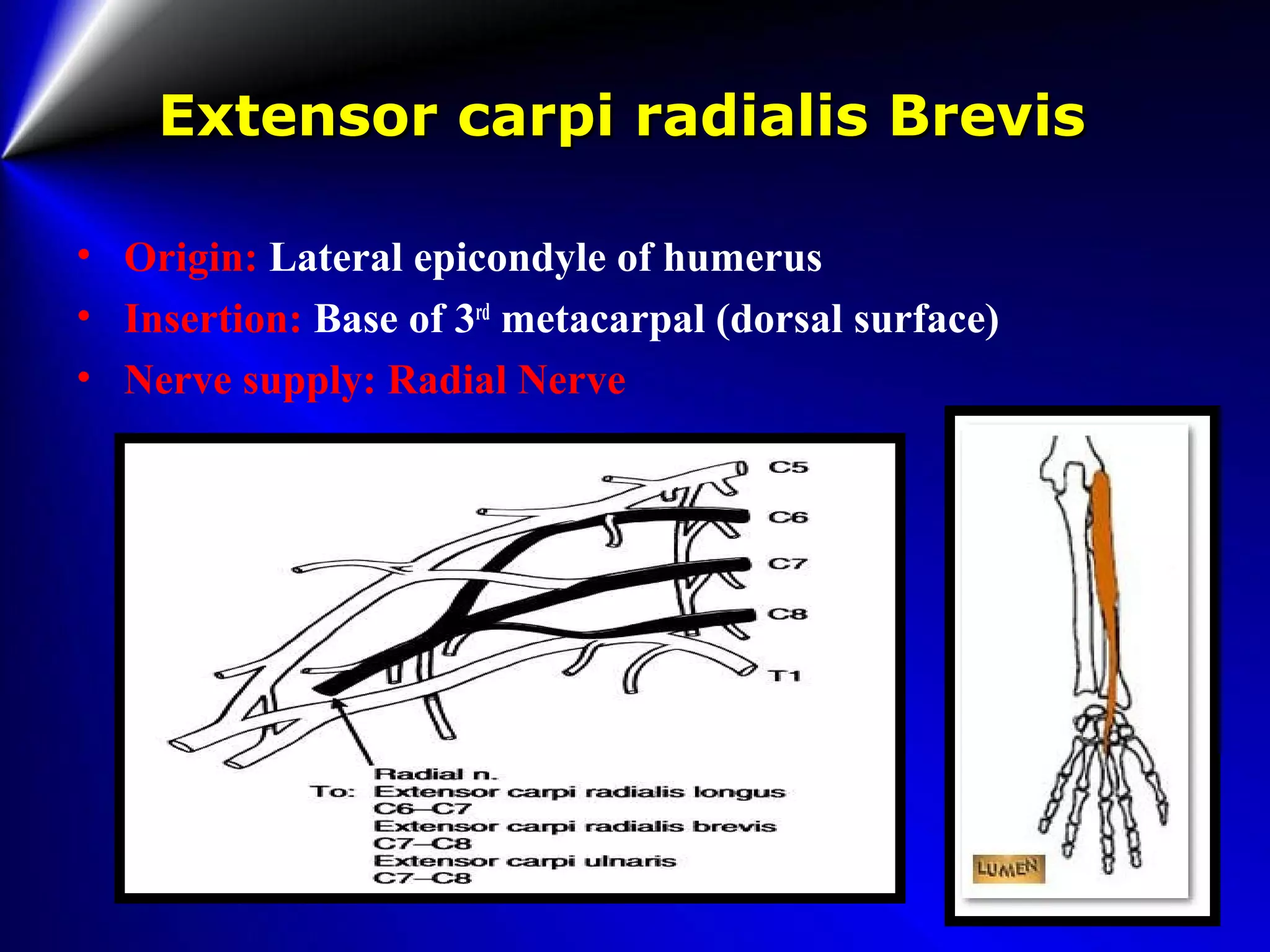
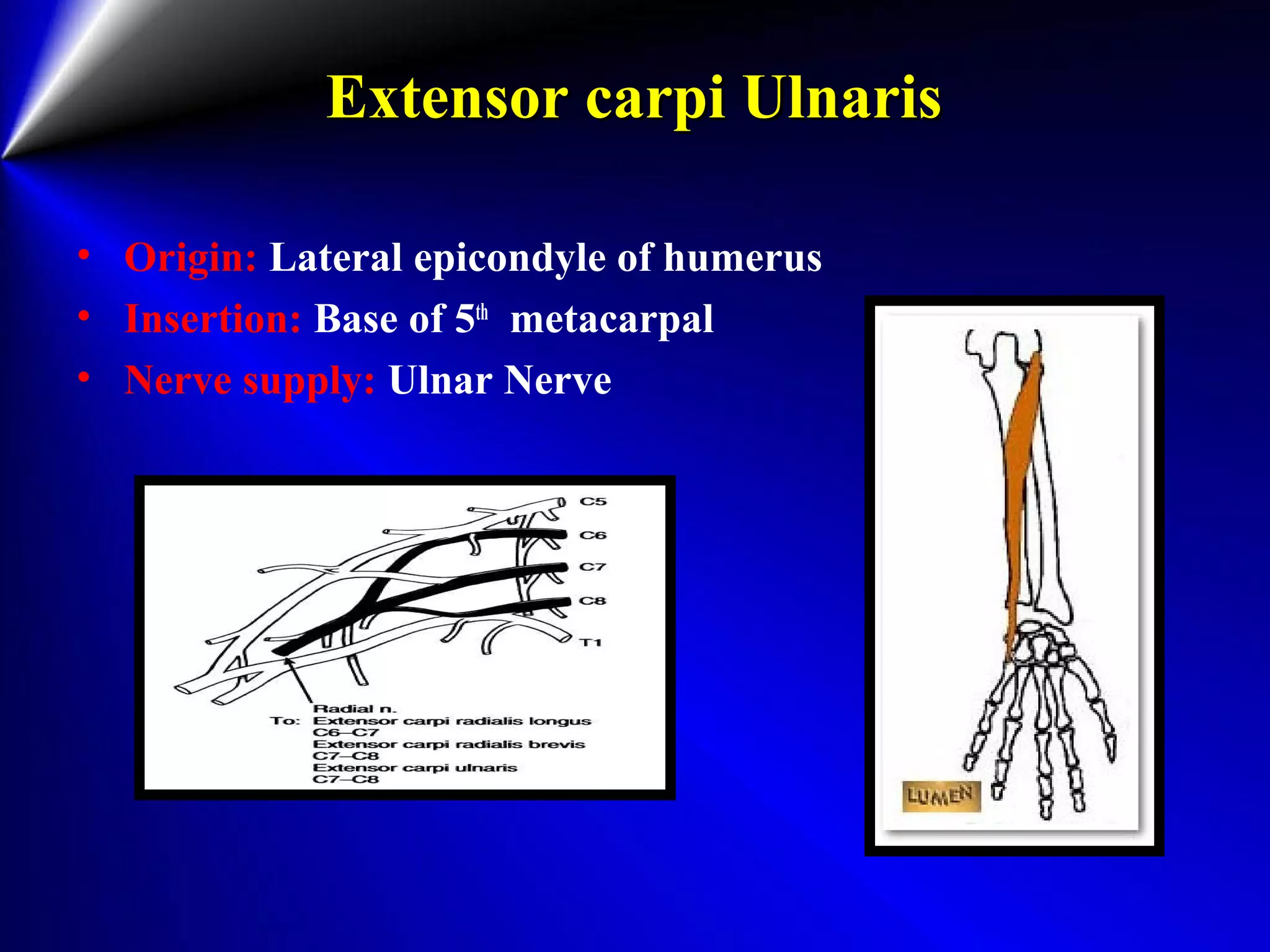
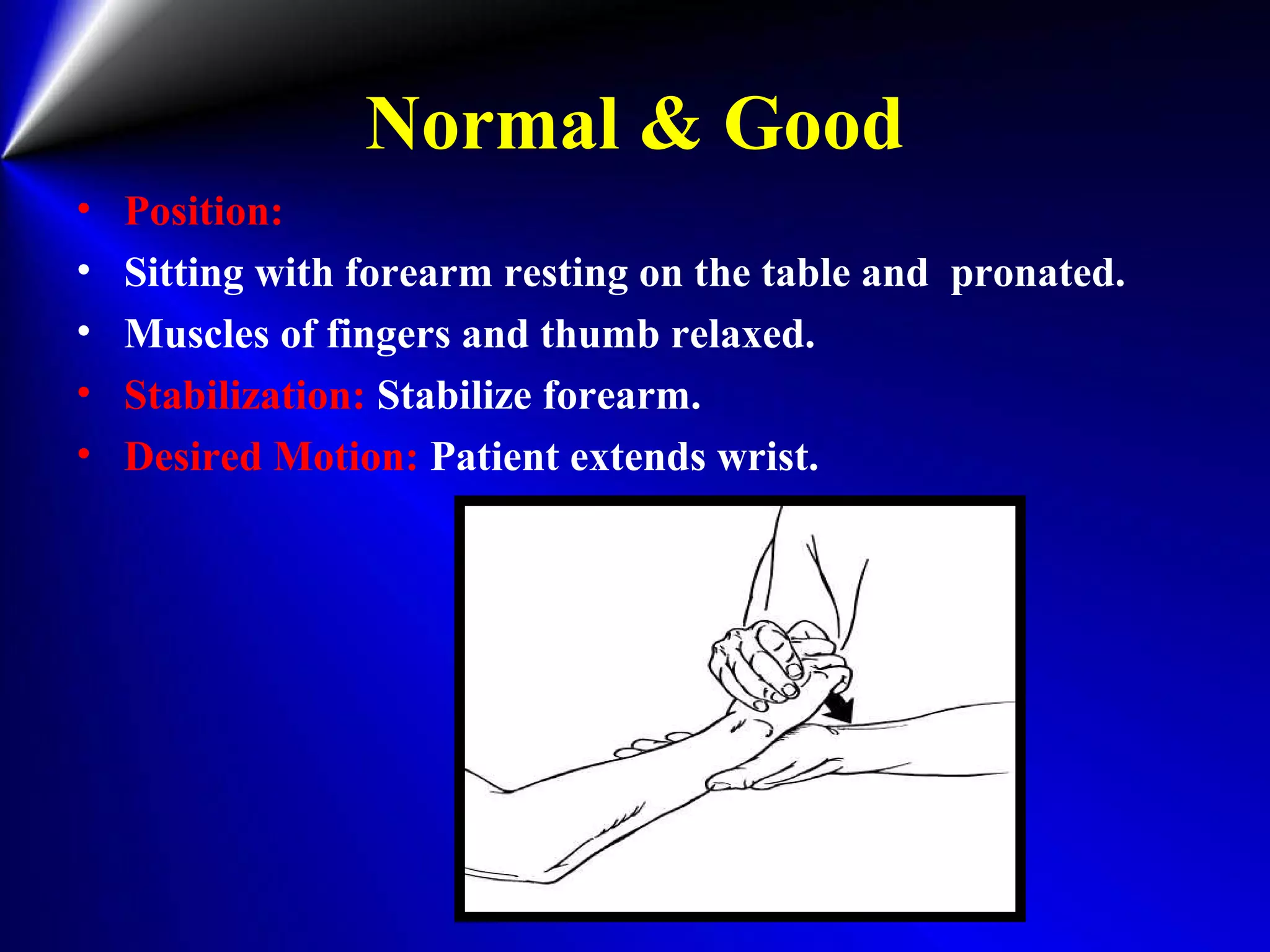
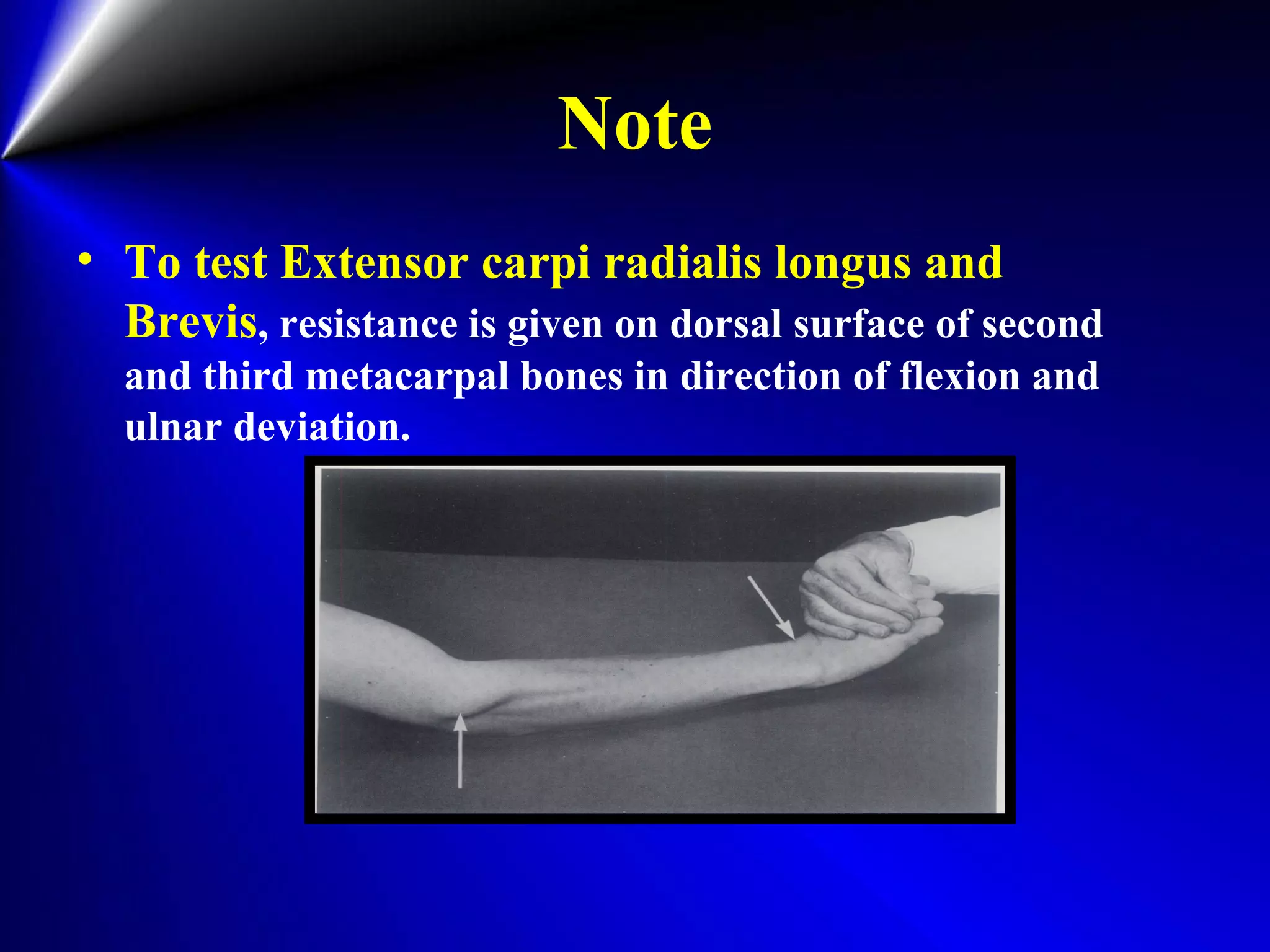
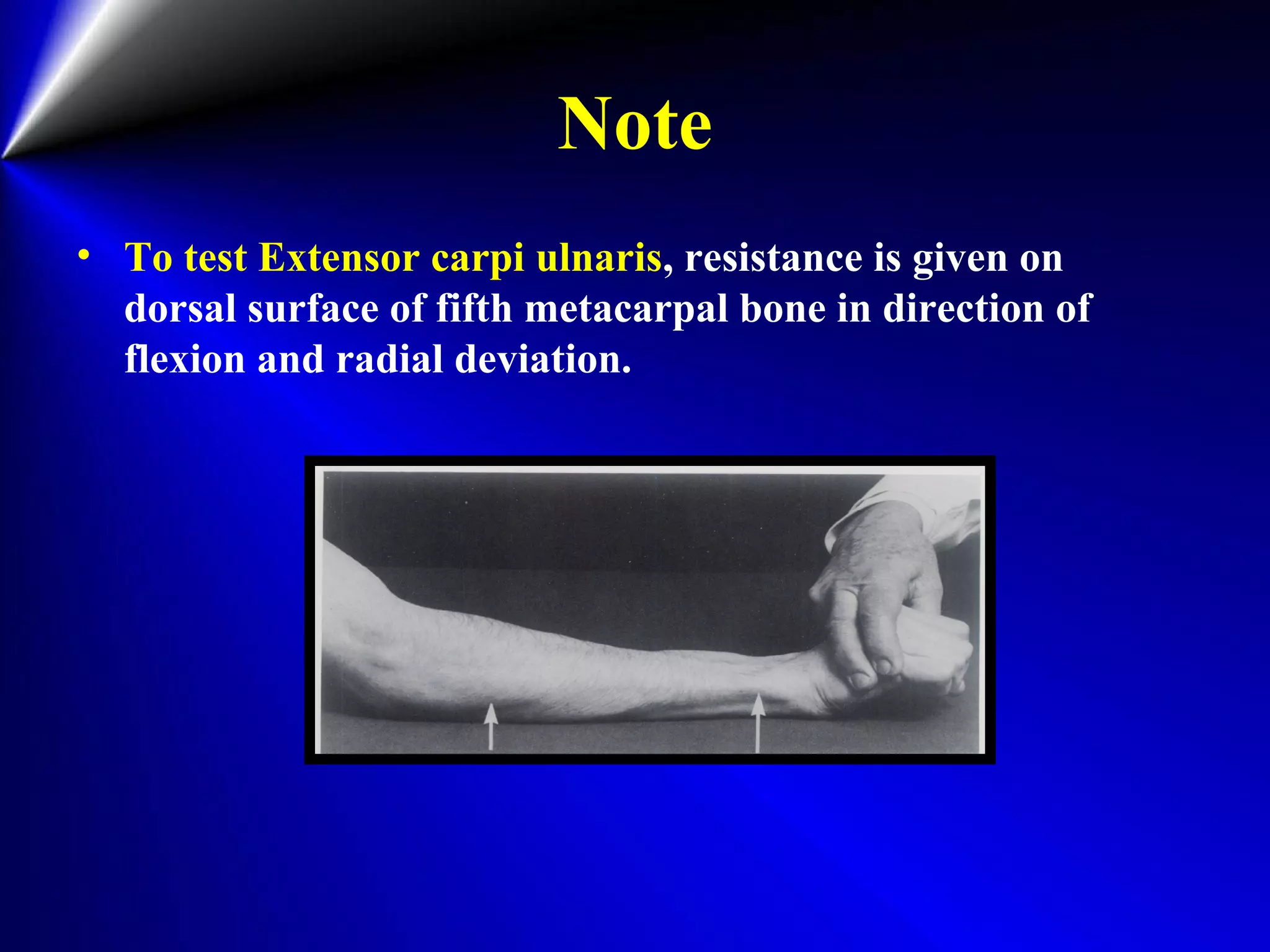
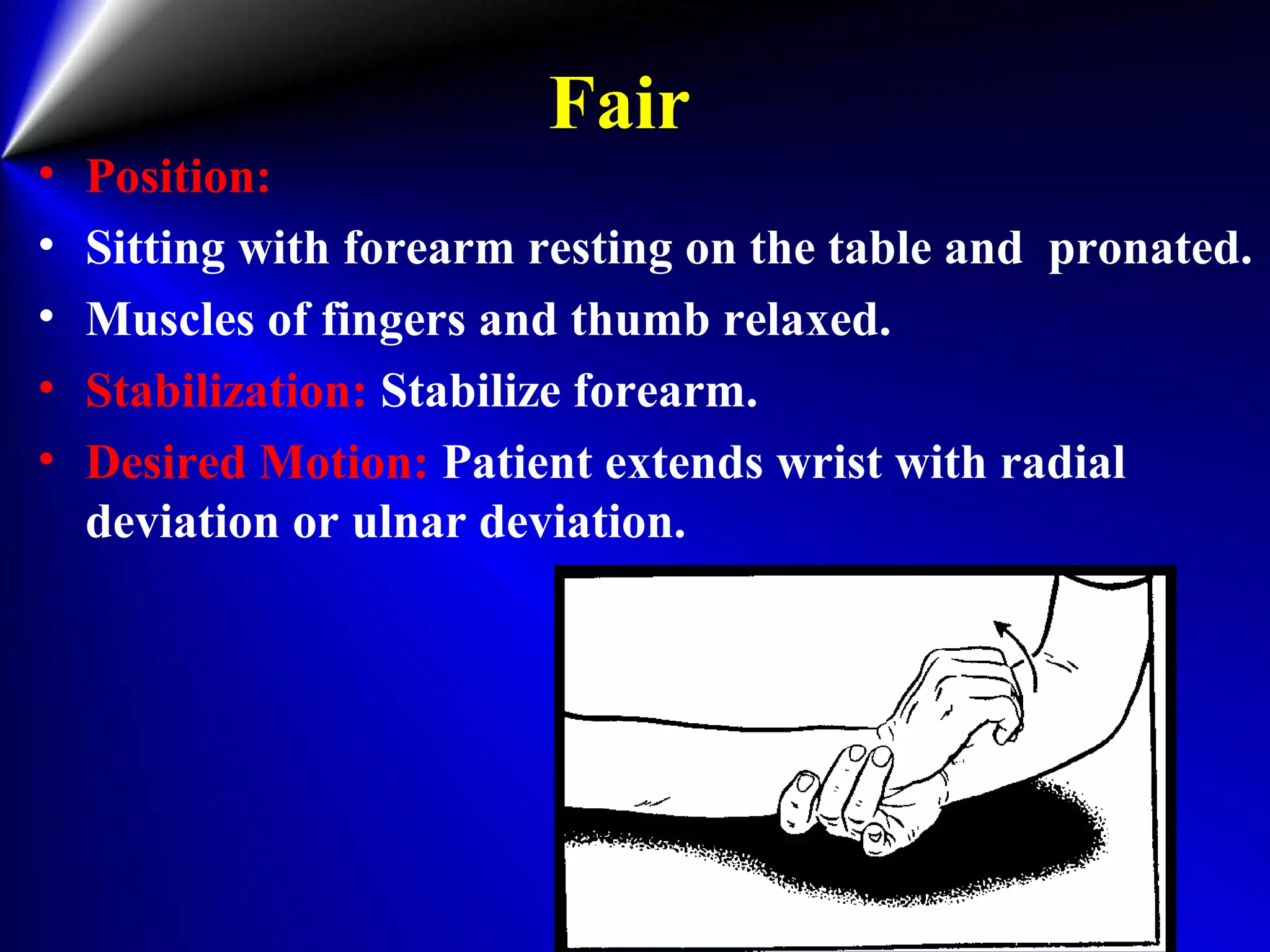
This document provides instructions for testing range of motion and muscle strength of the wrist and forearm. It describes positioning, stabilization, desired motion, and grading for flexion and extension of the wrist. Key muscles that contribute to wrist flexion and extension are identified. Methods of testing individual muscles like the flexor carpi radialis and extensor carpi ulnaris are outlined. Normal range of motion and factors limiting motion are also noted.