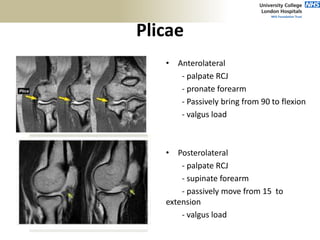
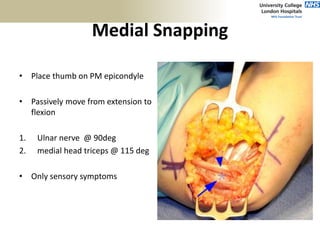
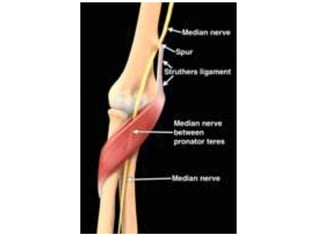
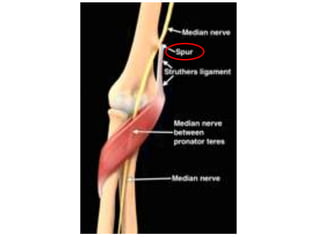
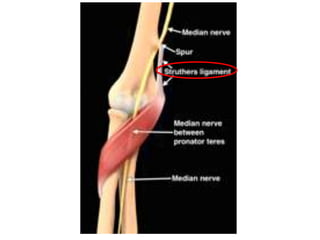
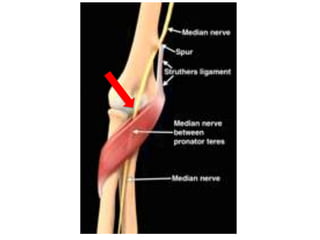
This document provides an overview of an examination of the elbow, including:
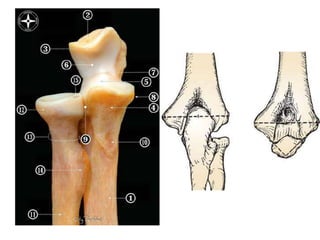
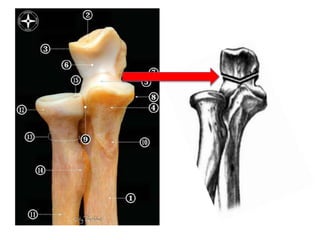
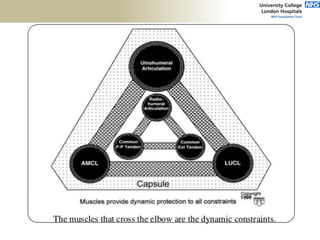
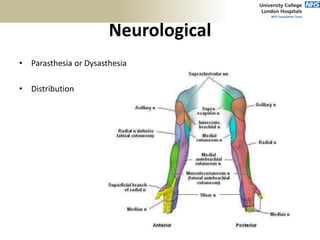
1. Anatomical structures are discussed such as bones, ligaments, muscles and nerves.
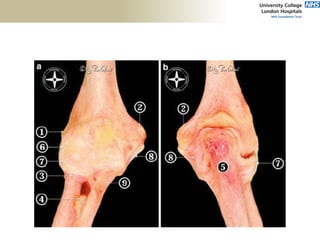
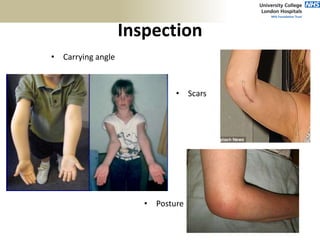
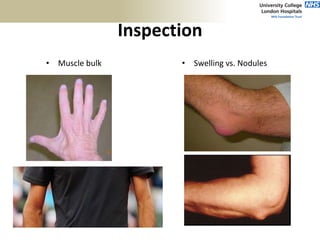
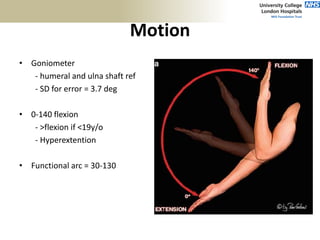
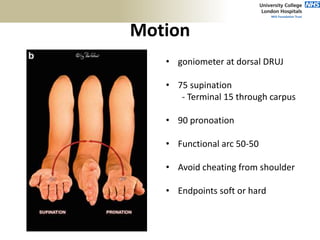
2. The ideal clinical examination is outlined including obtaining history, inspection, palpation, range of motion testing, and neurological assessment.
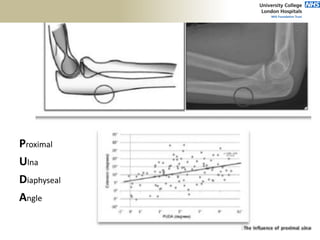
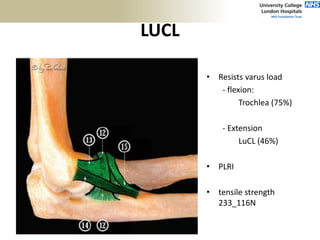
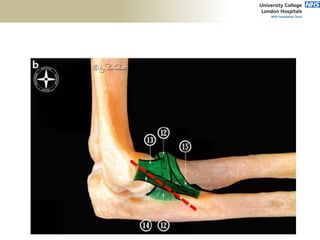
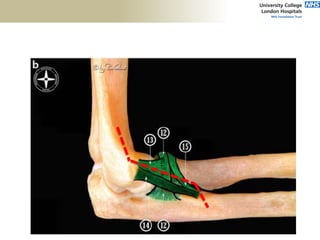
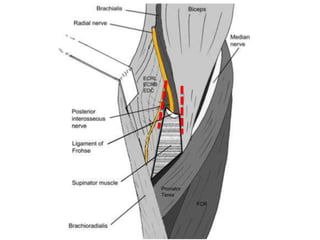
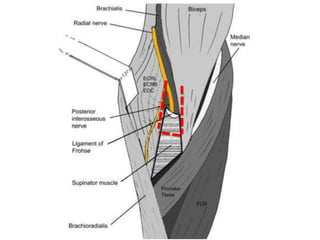
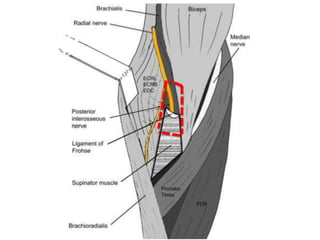
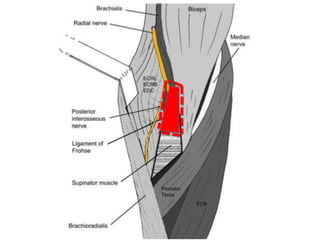
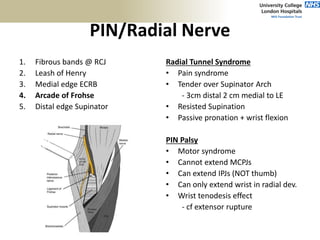
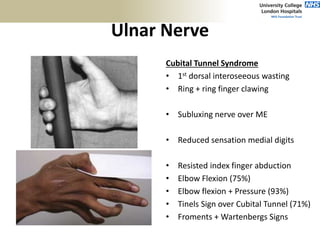
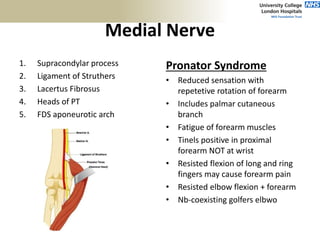
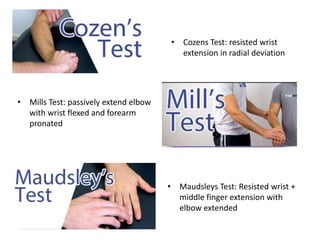
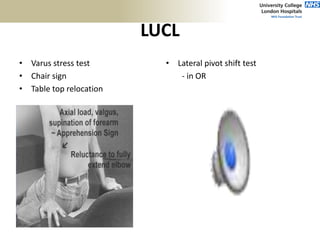
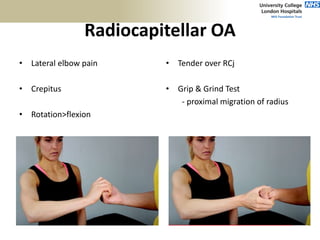
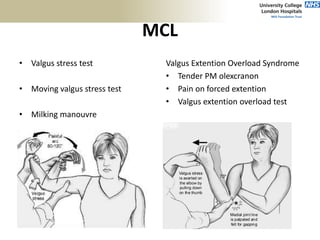
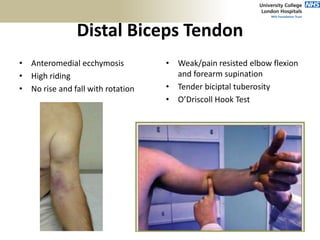
3. Specific tests and maneuvers are described to evaluate various conditions like tennis elbow, ulnar nerve entrapment, and ligament injuries.


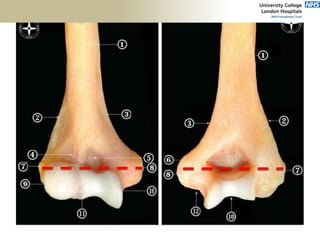
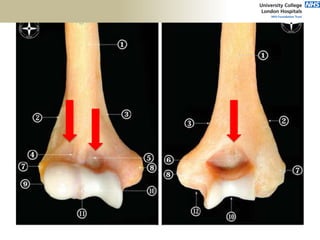
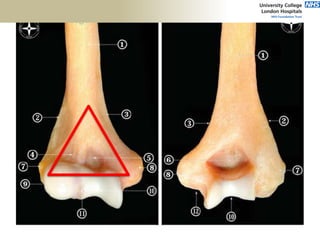
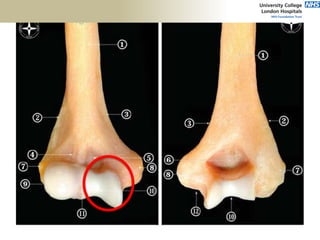
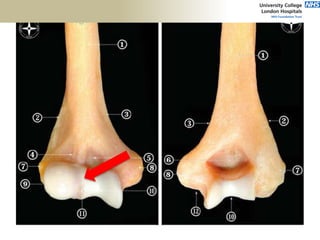
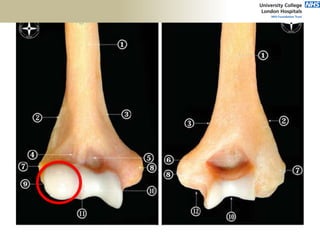
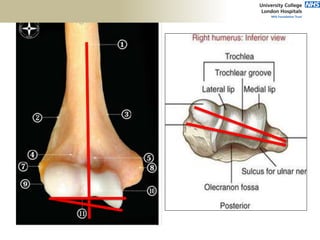
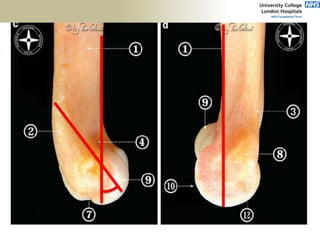

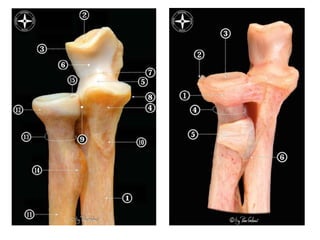
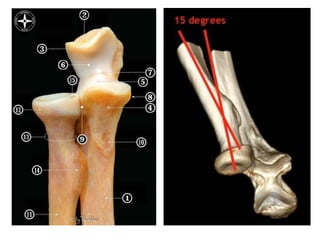
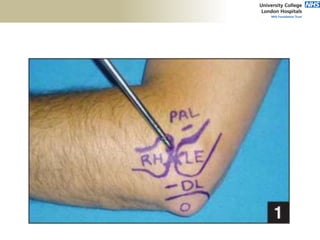
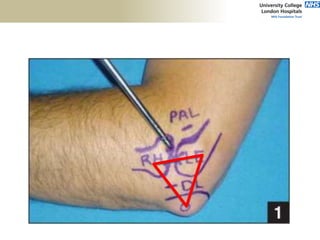
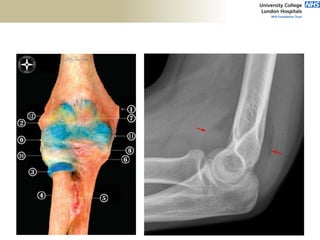
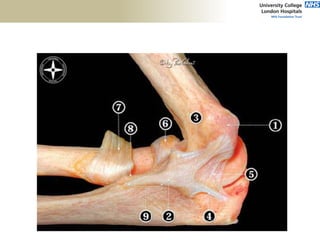
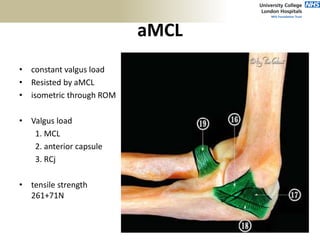
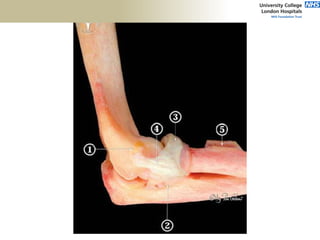
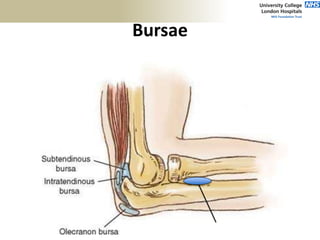
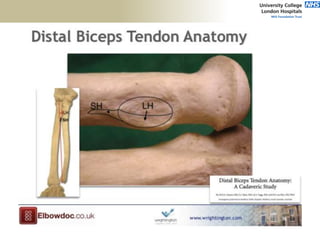
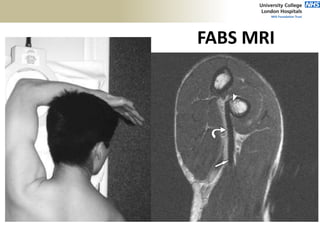
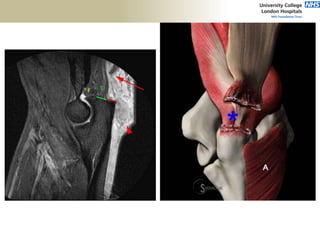
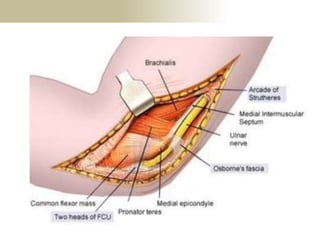
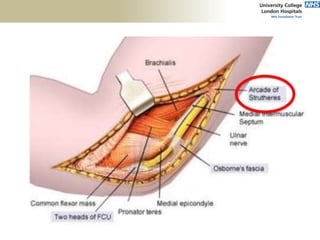
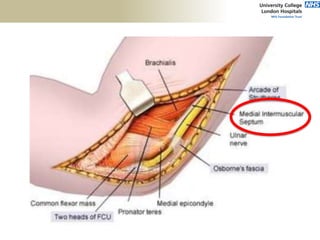
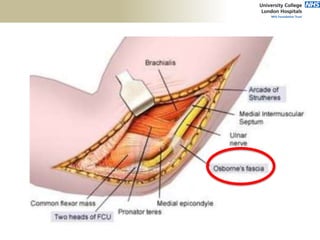
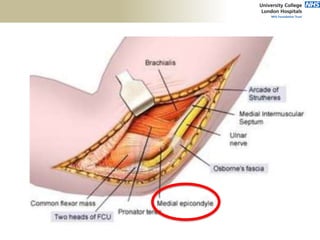
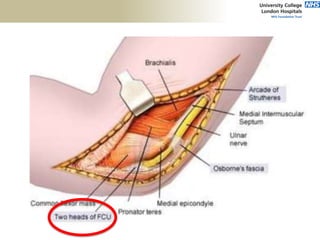
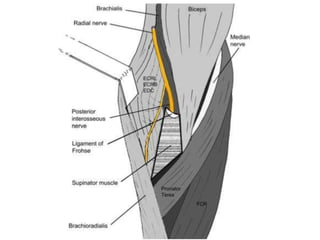
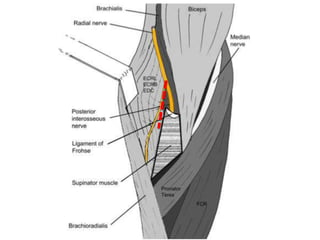




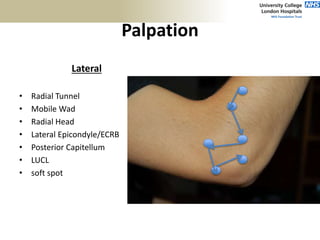
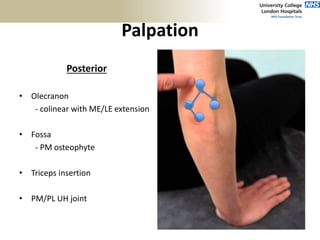
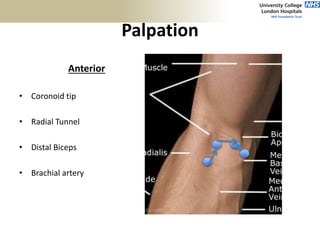
![Palpation
Medial
• ME
• CFO [under tension]
• MCL
• ulnar nerve](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elbowexamination-200302121932/85/Elbow-examination-73-320.jpg)



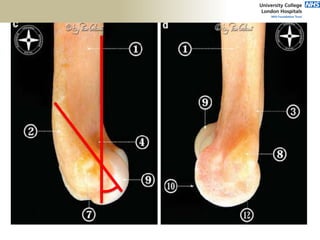
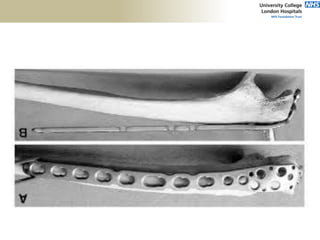
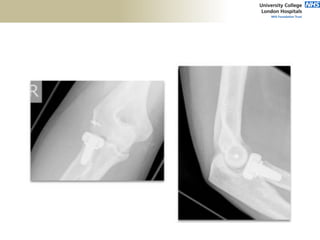
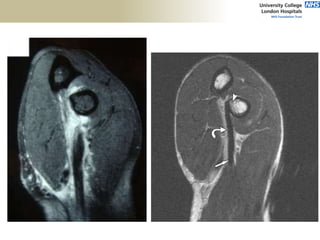
![Distal Triceps
• Pain on resisted elbow extension
• Posterior ecchymoses
• Defect proximal to olecranon tip
• No extension against gravity
• Viegas: Elbow extension when
triceps squeezed [modification of
Thompson Test].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elbowexamination-200302121932/85/Elbow-examination-88-320.jpg)