Embed presentation
Download to read offline
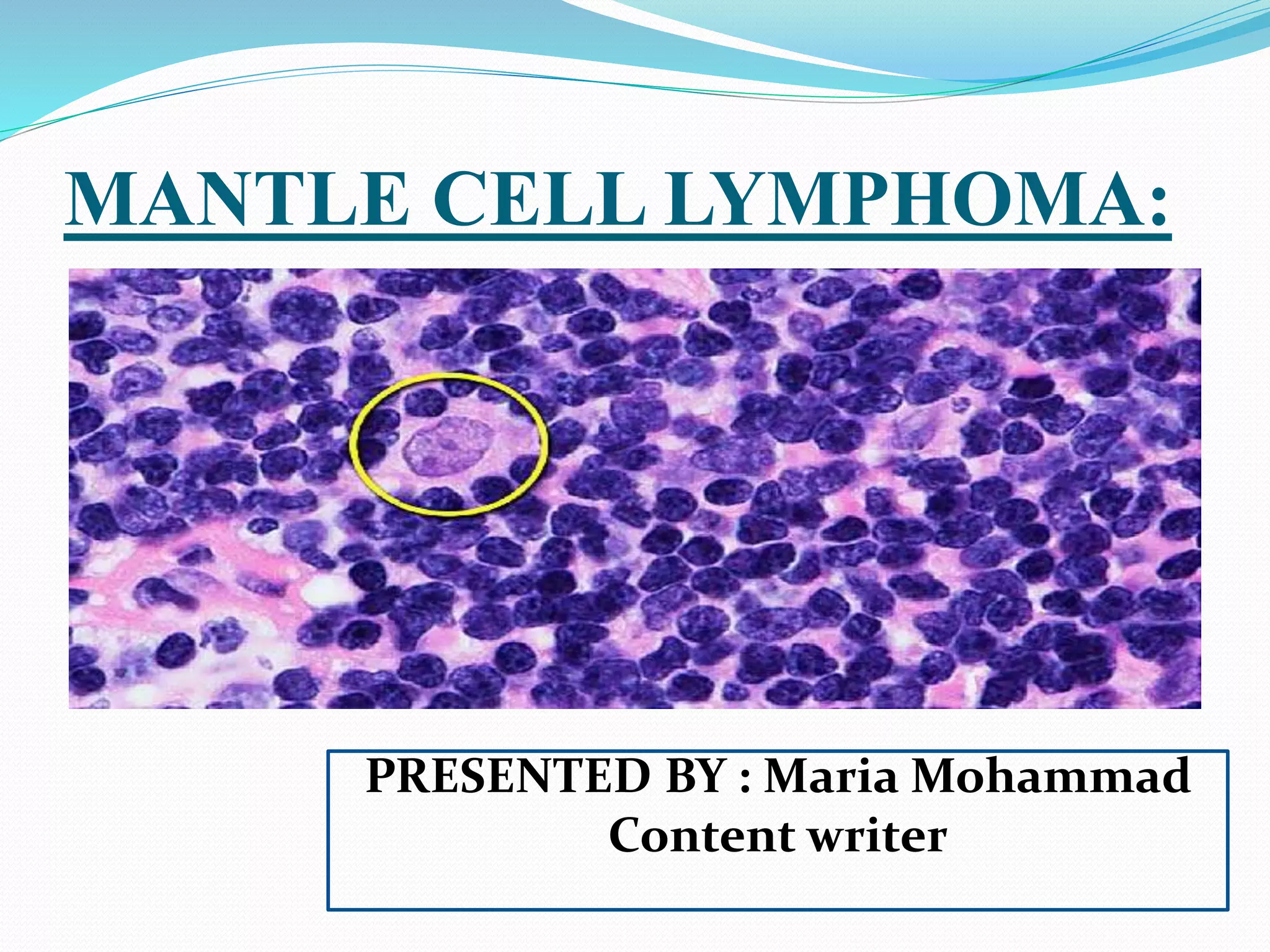

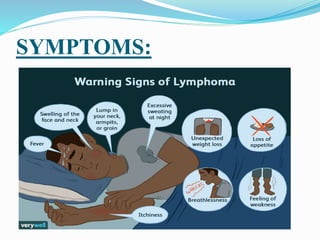


Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma caused by abnormal B-cells that generally accumulate in lymph nodes and can impact other body parts. Diagnosis involves blood tests, biopsies, imaging scans, and bone marrow samples, while treatment options include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, and stem cell transplantation, though no cure exists for advanced cases. Various agents such as proteasome inhibitors and biological agents like temsirolimus are also considered in managing the disease.





