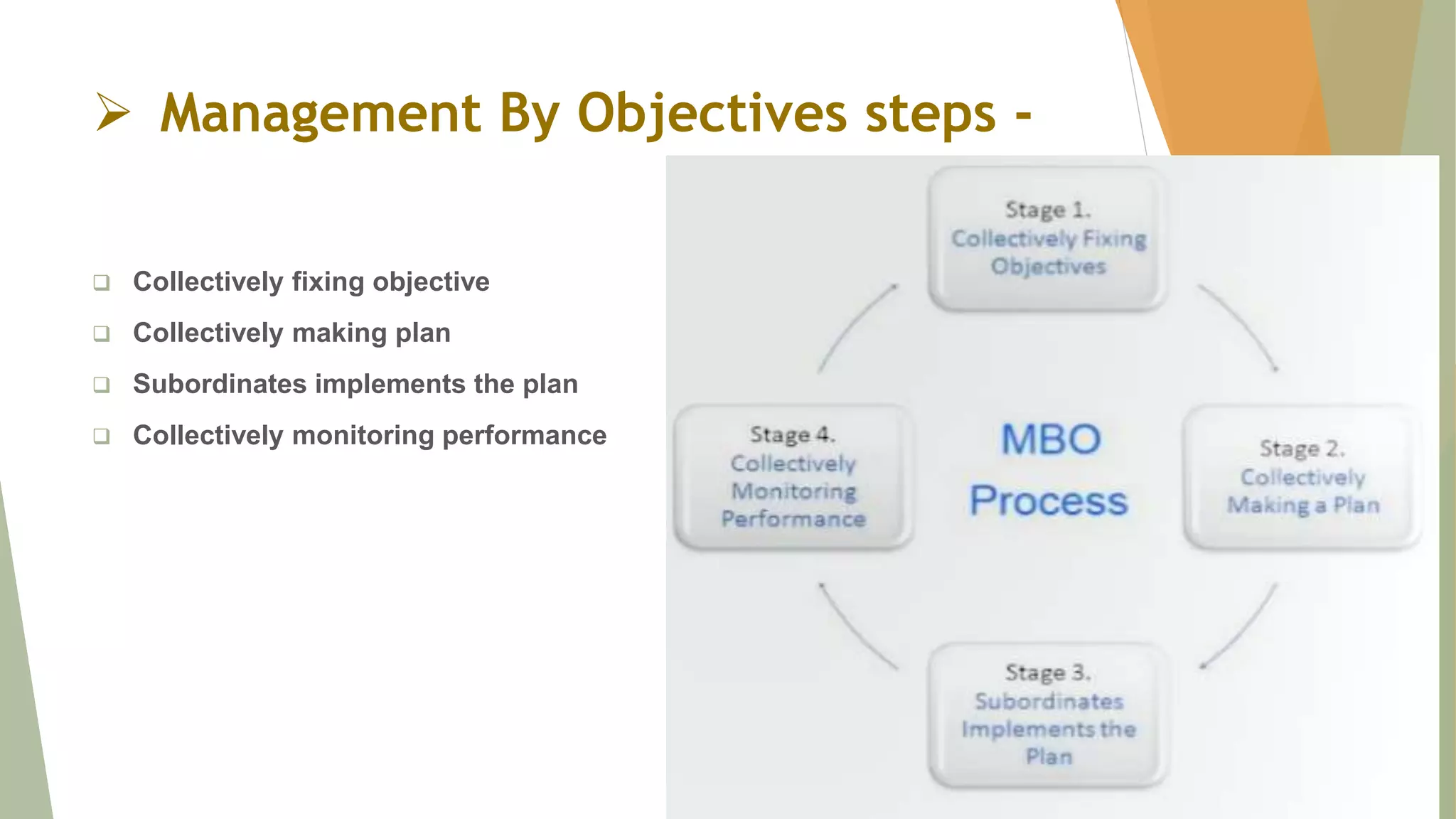
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a performance management approach where employees and organizations jointly set goals and objectives. It is based on the principle that goal alignment between employees and the organization will lead to more successful work performance. MBO involves managers and subordinates together defining common goals, individual responsibilities, expected results, and using these measures to guide work and assess contributions. Key aspects of MBO include cascading goals through the organization, setting specific objectives for each member, participative decision making, explicit time periods, and providing performance feedback.