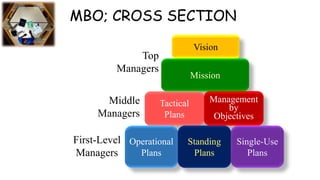
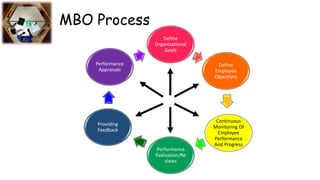
Management by Objectives (MBO), first outlined by Peter Drucker in 1954, is a systematic approach that aligns the goals of managers and employees to achieve organizational objectives through participative decision-making and performance evaluation. The MBO process emphasizes clear goal-setting, continuous monitoring, and effective communication, fostering motivation and commitment among employees. While MBO promotes organizational success, it can be time-consuming in developing objectives, potentially impacting overall productivity.