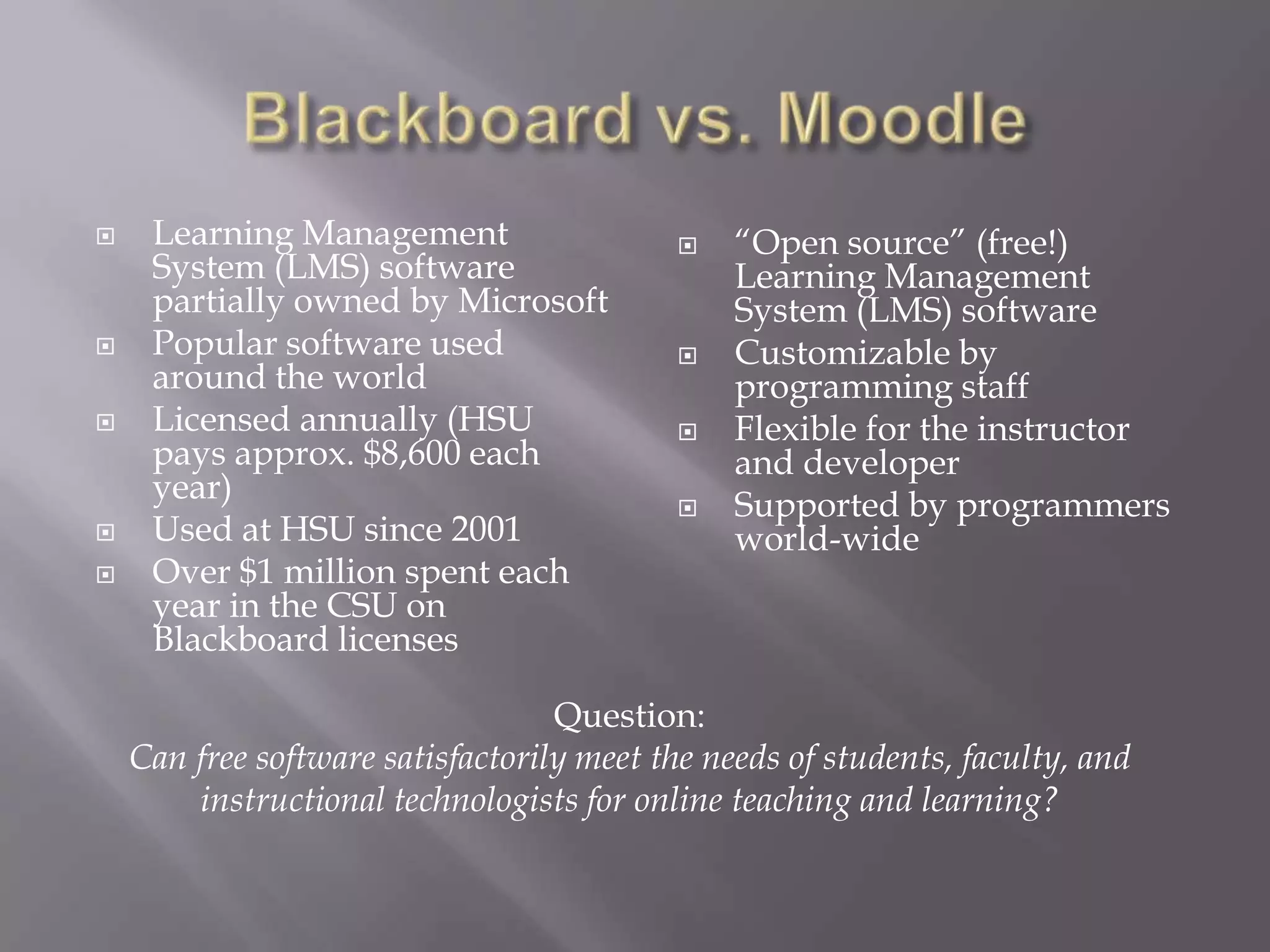
The document discusses virtual learning environments (VLEs), which are software systems designed to aid teachers in managing educational courses and facilitating e-learning. It details the features and benefits of VLEs, examples of popular systems, and explores faculty usage and perceptions through a study that gathered data from multiple institutions. The study aims to identify factors motivating faculty to use course management systems (CMS) and the barriers they encounter.