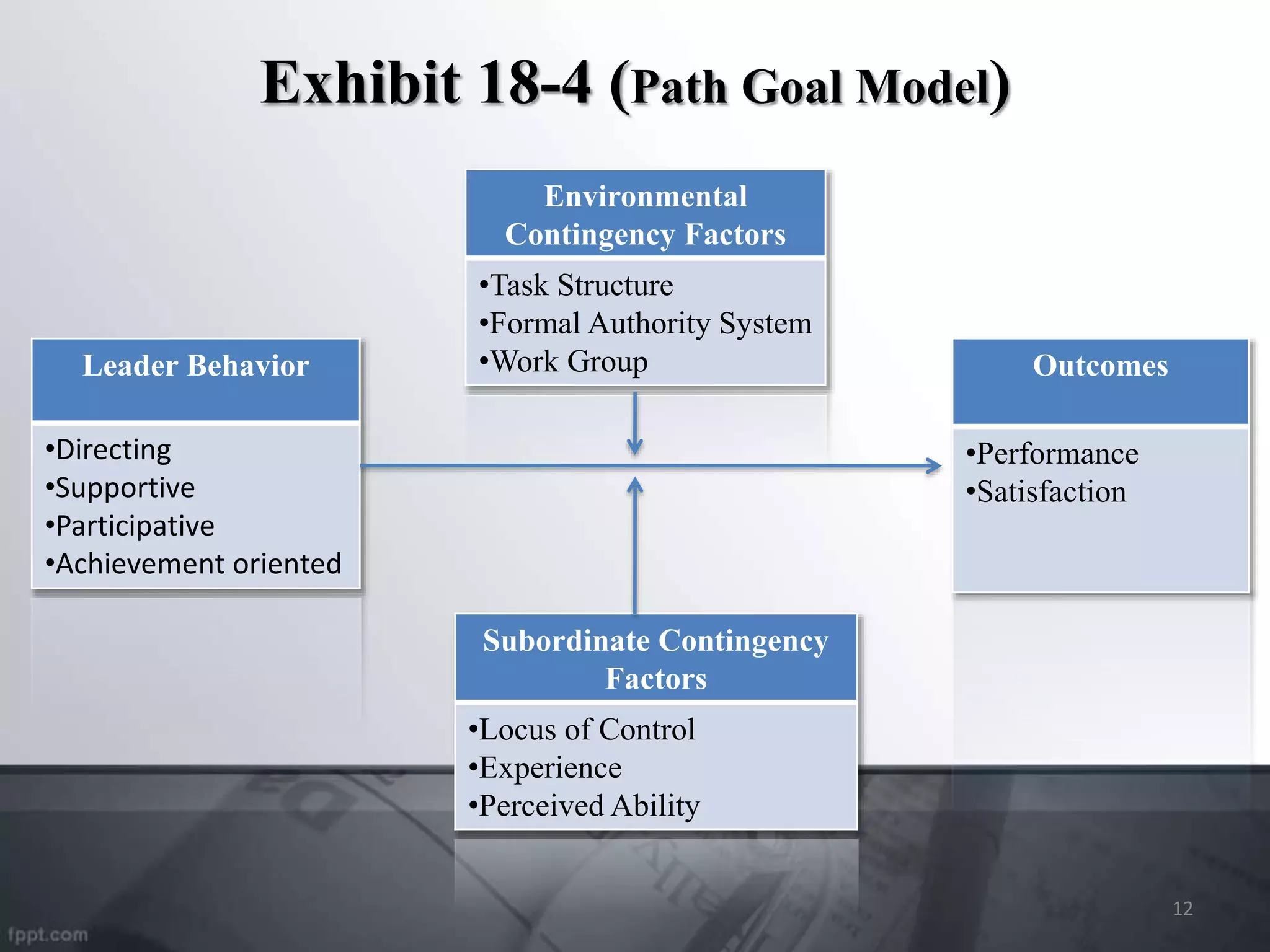
This document discusses various leadership theories from early 20th century trait theories to contemporary views. It outlines traits believed to make an effective leader such as drive and intelligence. It also describes behavioral theories that identify effective leadership behaviors and styles like democratic and autocratic. Contemporary views discussed include leader-member exchange theory, transformational-transactional leadership, and charismatic-visionary leadership.