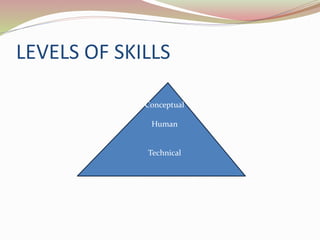
The document outlines the various types of managerial roles and skills as identified by Henry Mintzberg and Robert Katz. It categorizes managerial roles into interpersonal, informational, and decisional, and emphasizes the importance of technical, human, and conceptual skills across management levels. Each role and skill set is crucial for effective management, influencing how managers interact with subordinates, disseminate information, and make decisions.