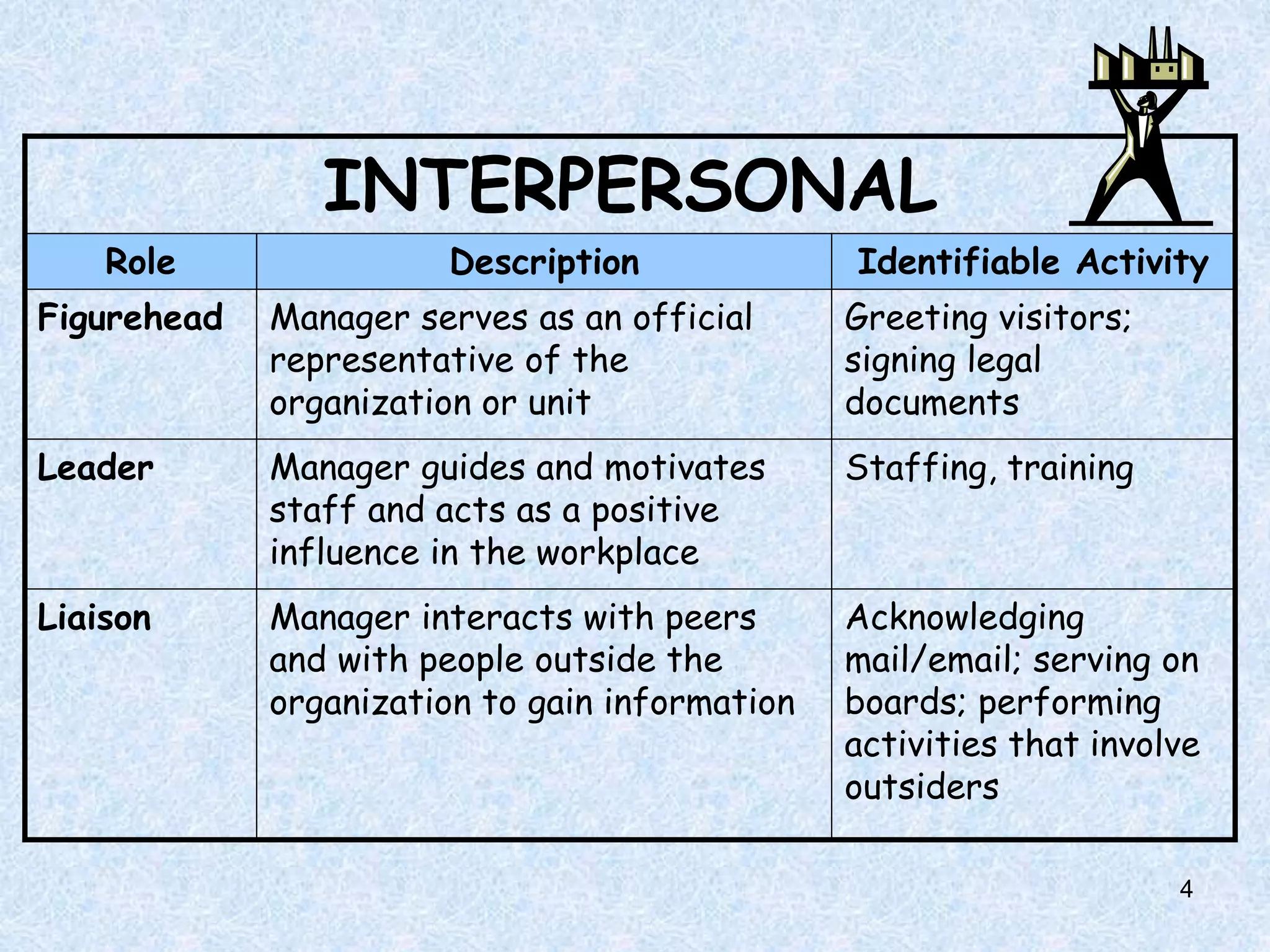
Mintzberg studied managerial roles and identified three primary categories: interpersonal, informational, and decisional. The interpersonal roles involve representing the organization as a figurehead, leading others, and interacting with outsiders. Informational roles center around monitoring the environment, disseminating information within the organization, and acting as a spokesperson. Decisional roles pertain to initiating change, resolving conflicts, allocating resources, and negotiating. Effective managers must also have strong conceptual, interpersonal, technical, and political skills.