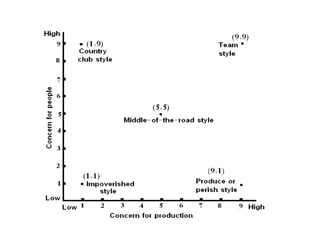
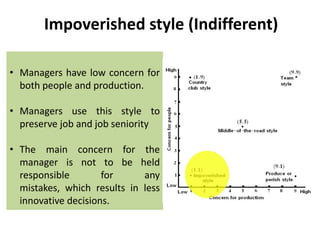
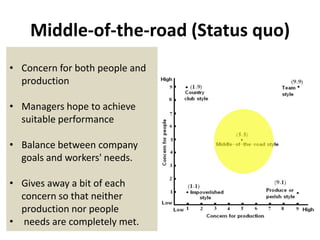
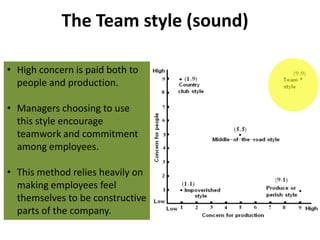
The document describes Blake and Mouton's Managerial Grid model for analyzing leadership styles. The grid plots concern for production on one axis and concern for people on the other, identifying five primary styles: impoverished, produce or perish, country club, middle of the road, and team. It also briefly mentions two additional styles - opportunistic and paternalistic. The grid is used as a tool for managers to evaluate their own leadership approach. While useful, the model does not account for all relevant situational factors and aspects of leadership.