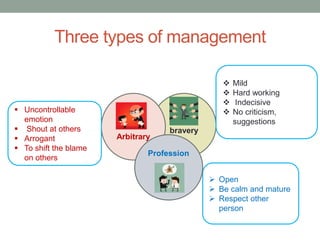
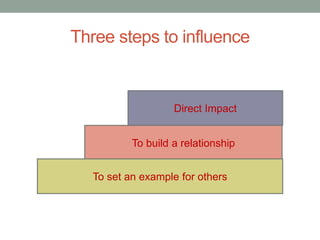
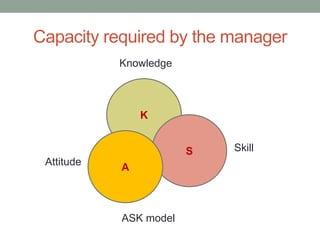
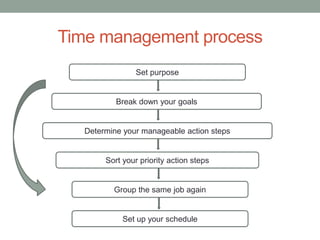
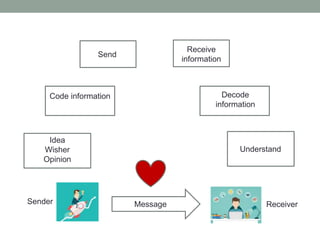
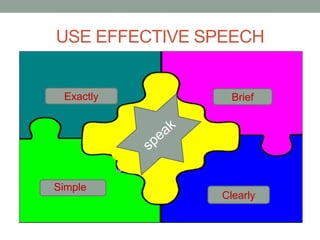
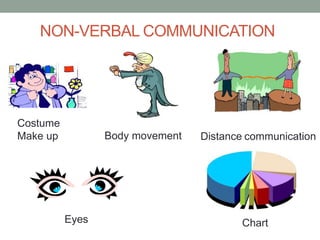
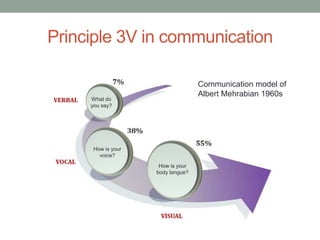
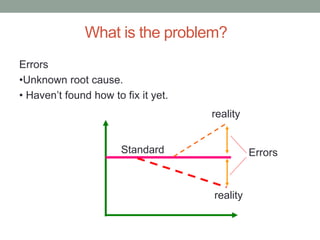
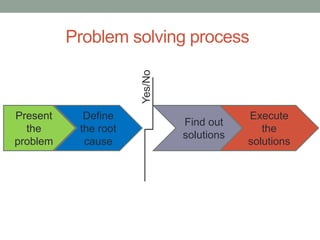
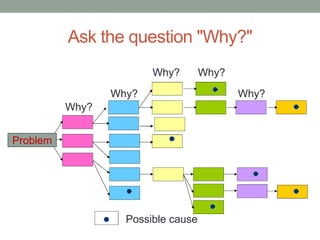
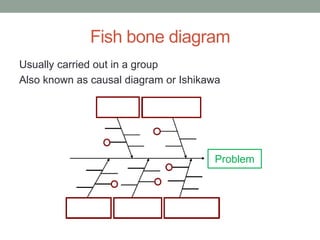
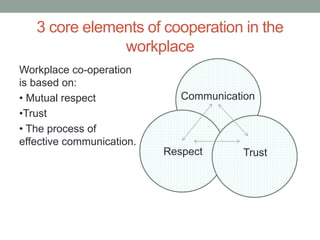
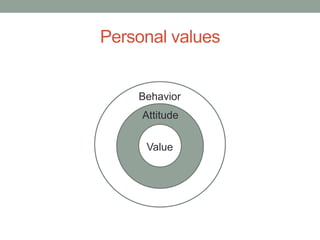
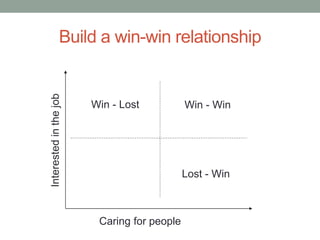
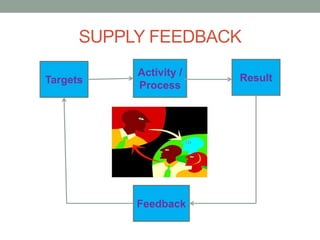
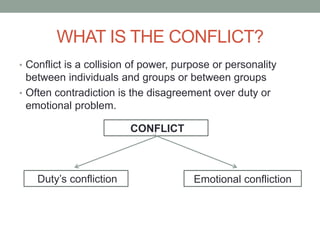
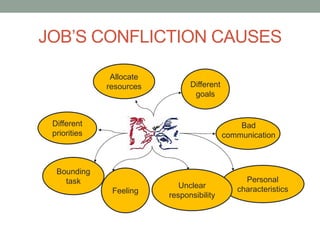
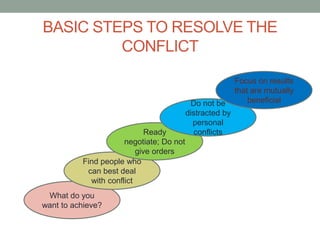
The document outlines essential management skills including roles and responsibilities, effective time management, communication, problem-solving, and conflict resolution. It emphasizes the importance of building teamwork, fostering a positive environment, and understanding the dynamics of managing people. Key points include the need for mutual respect, trust, and effective communication in the workplace to resolve conflicts and enhance cooperation.