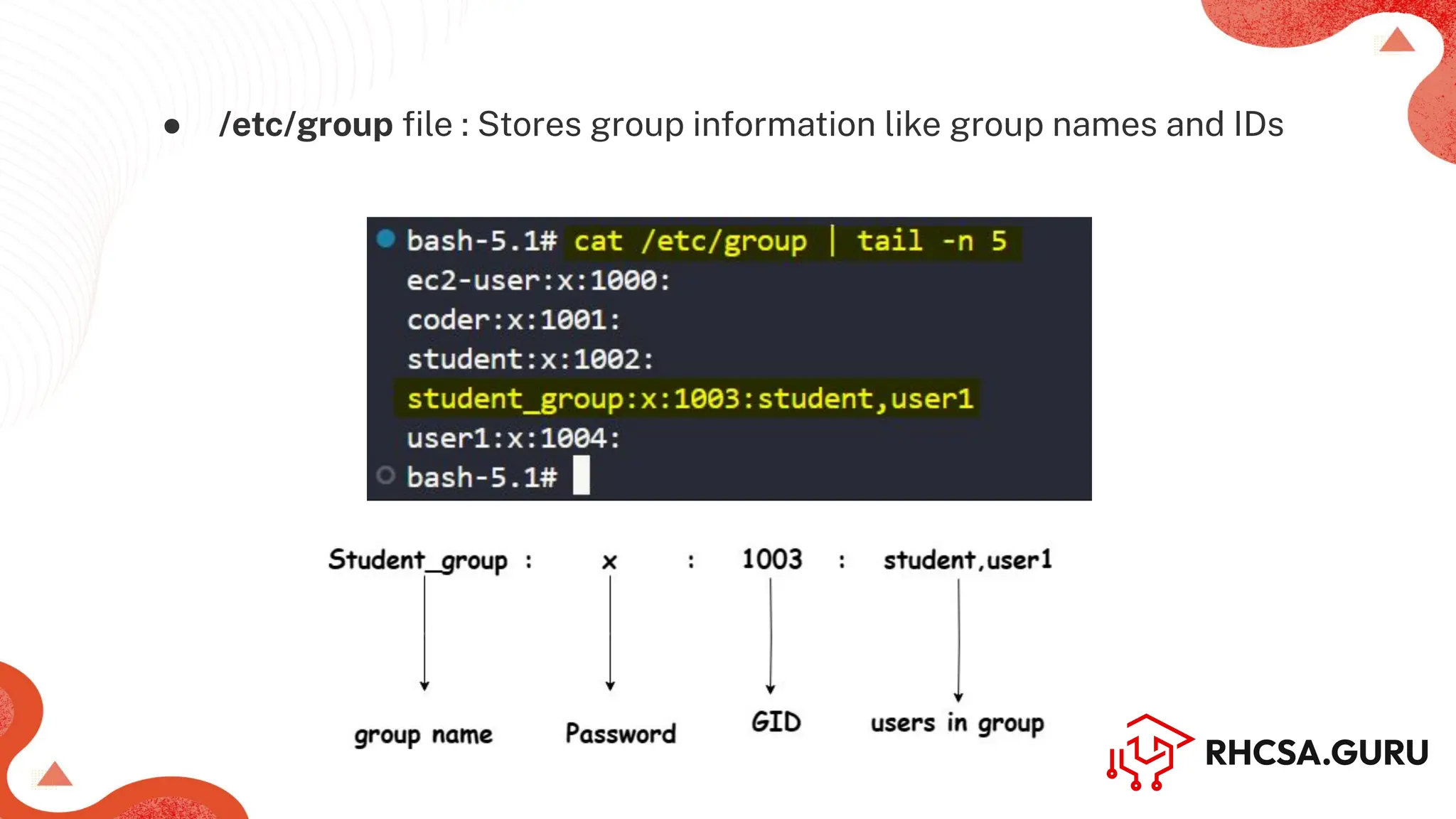
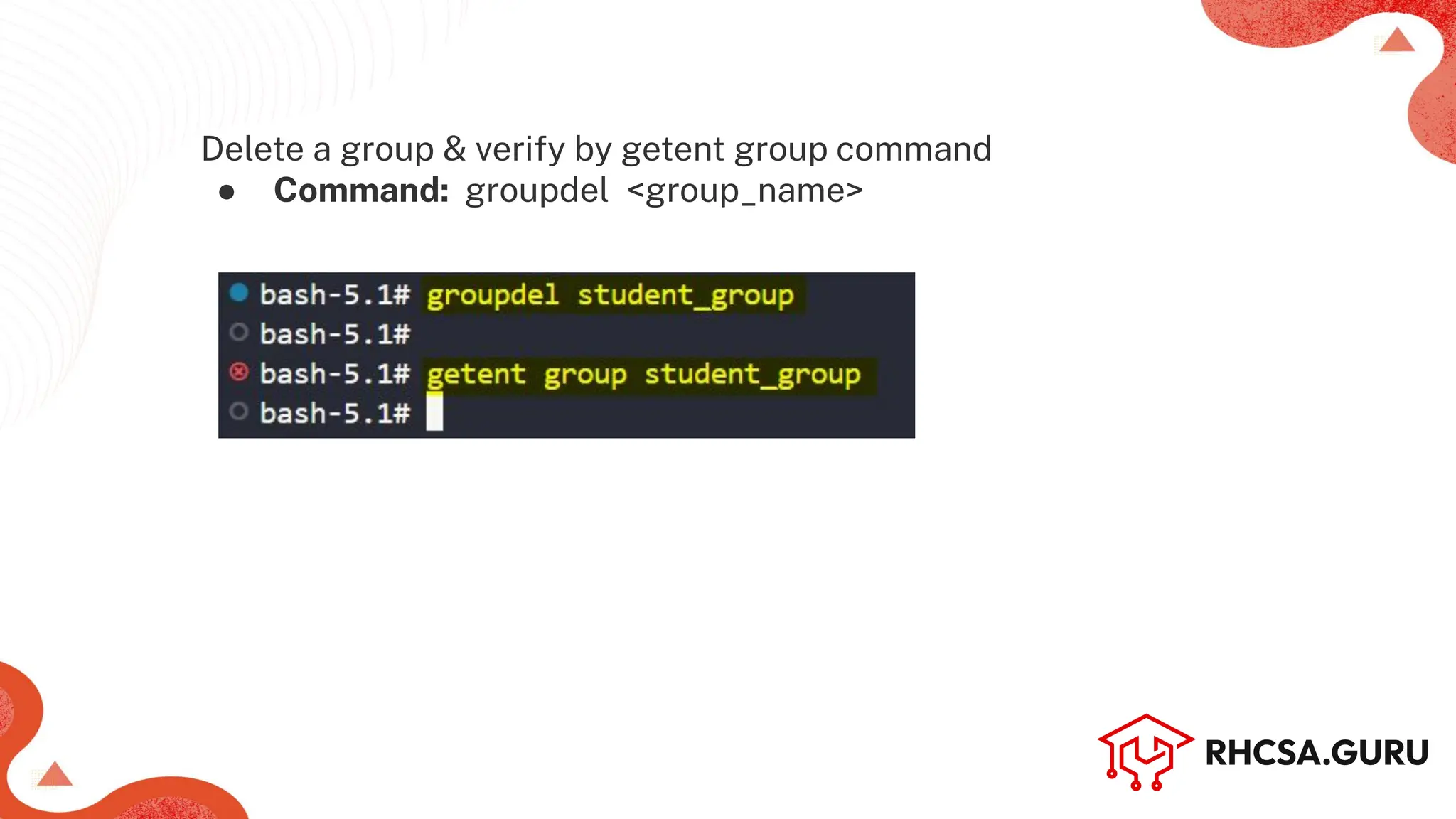
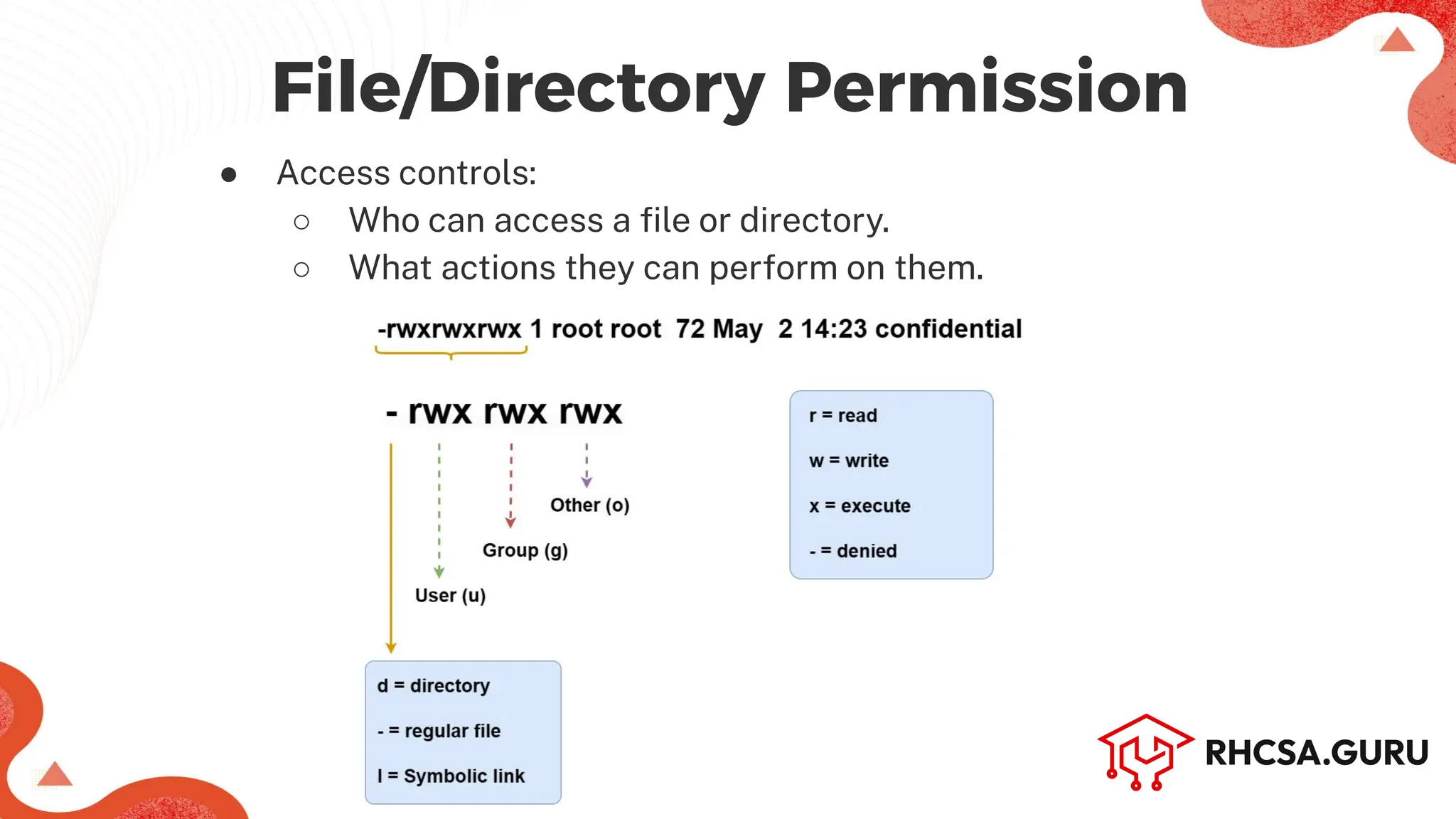
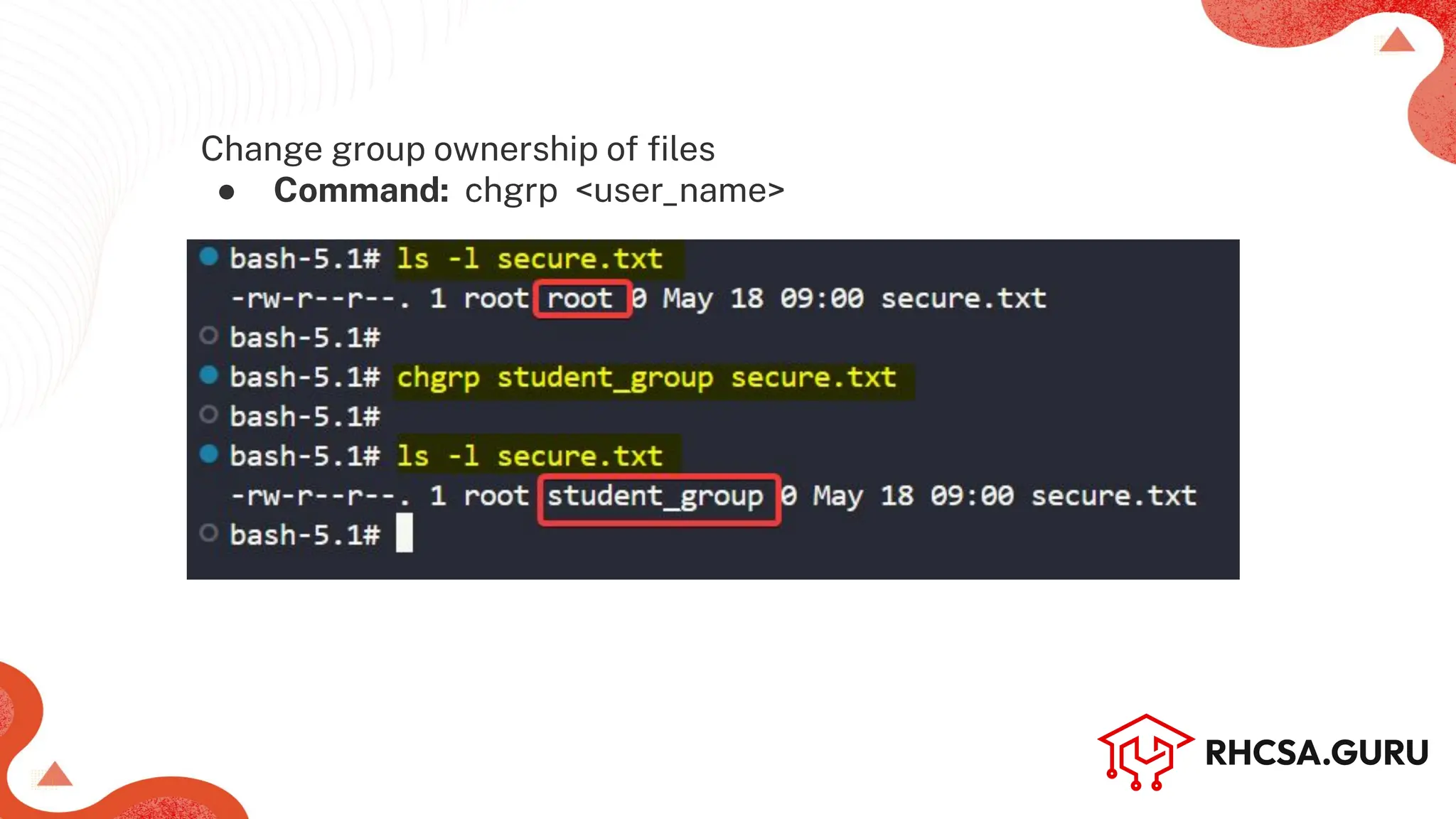
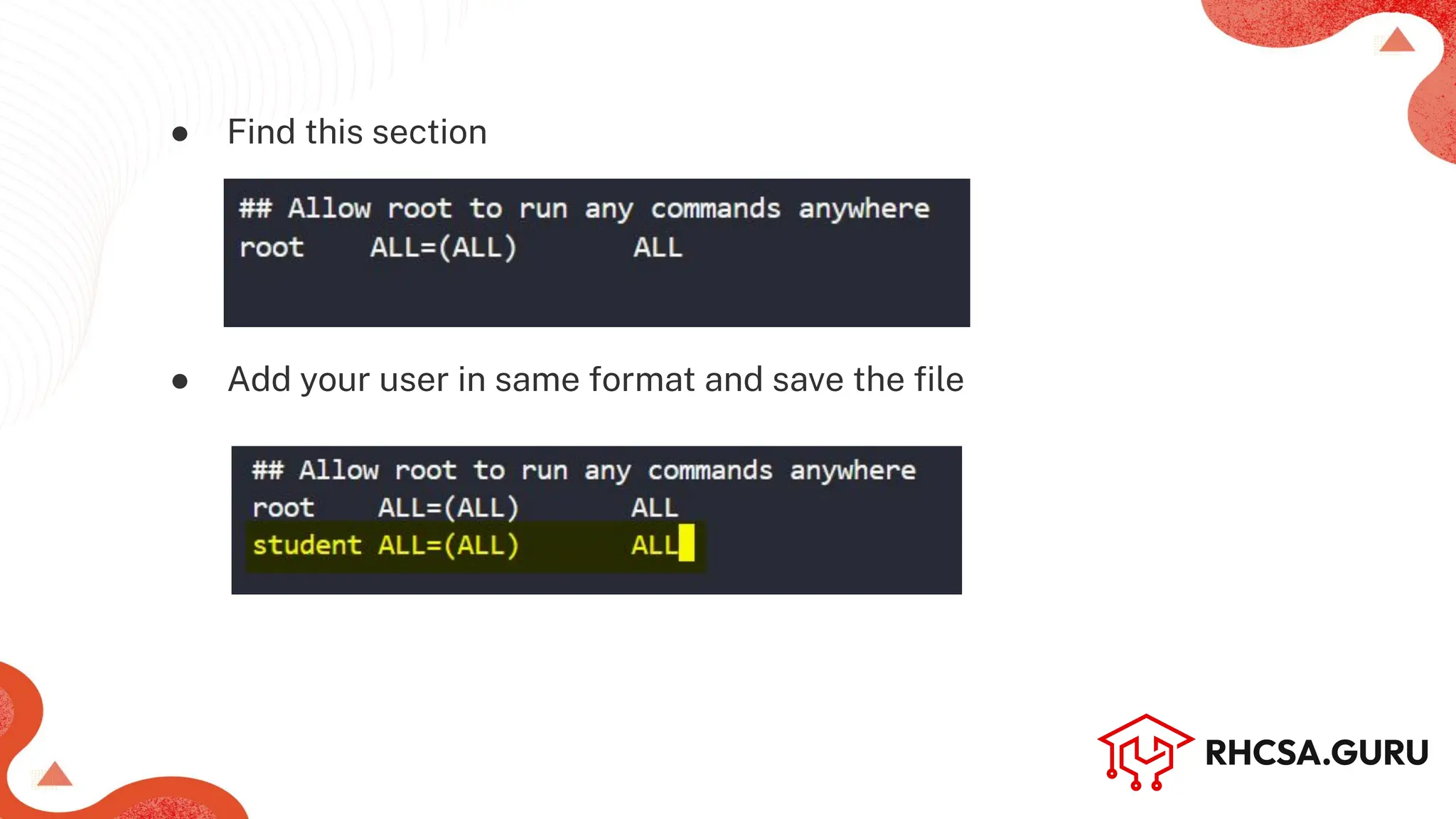
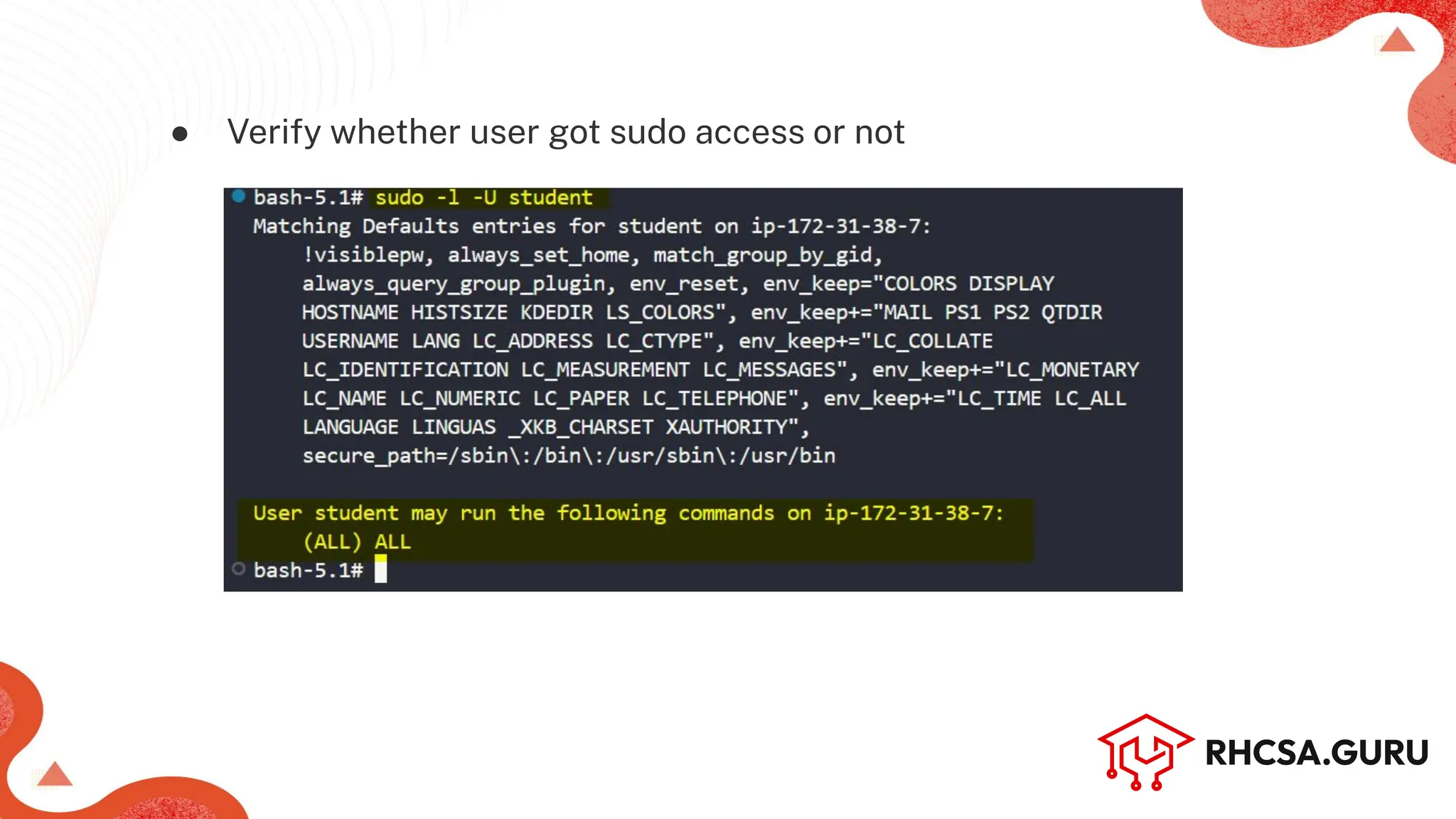
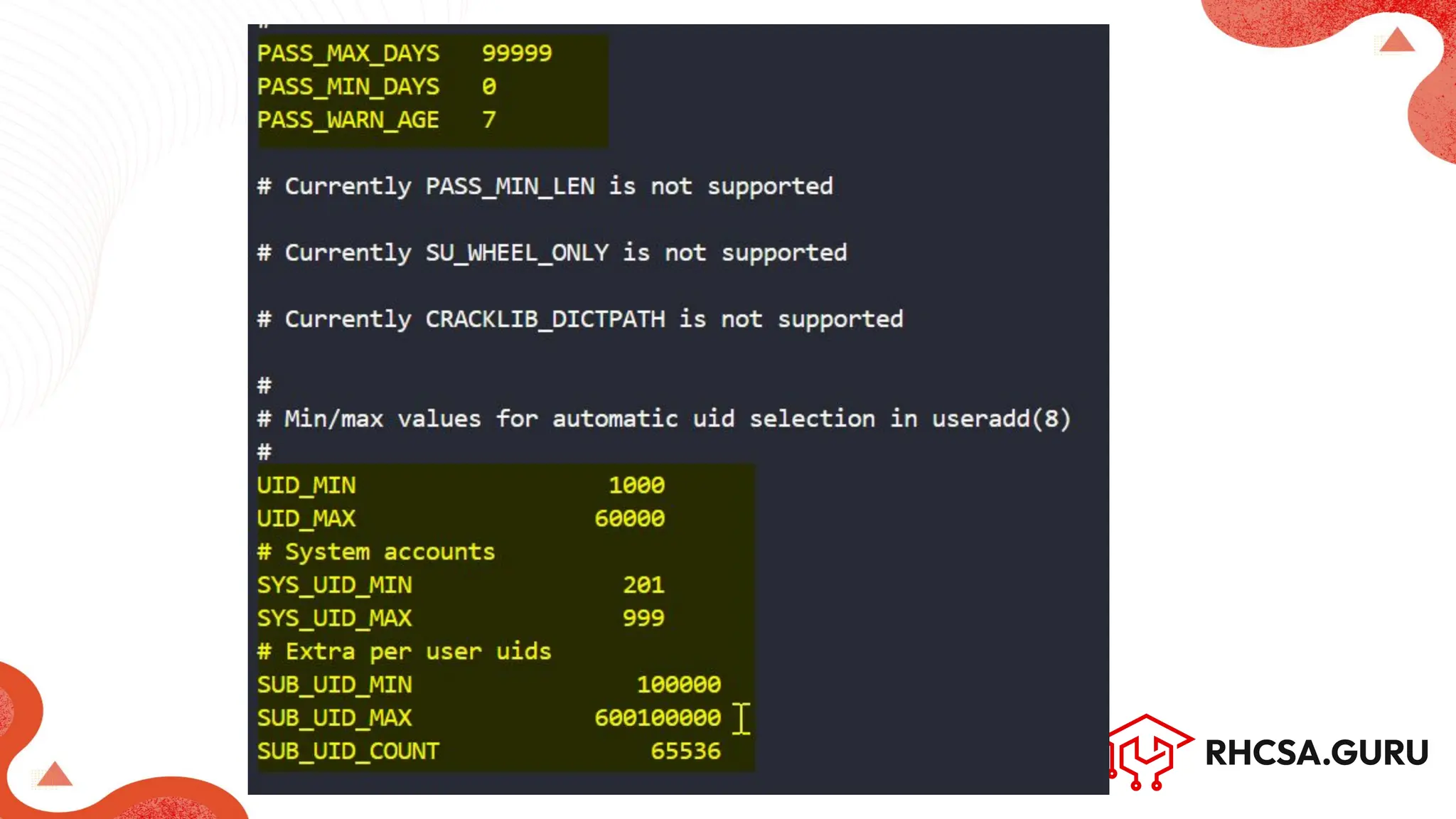
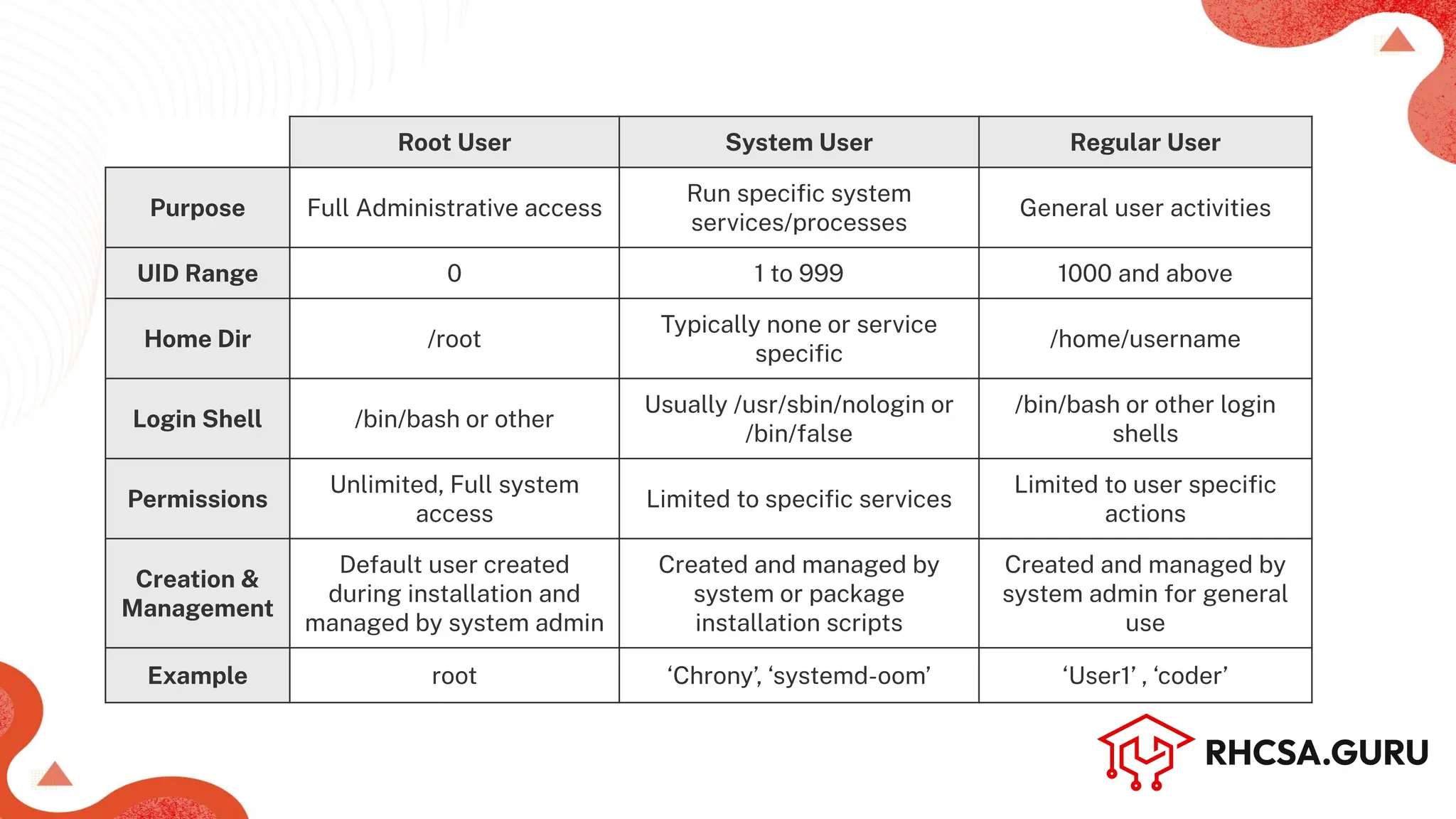
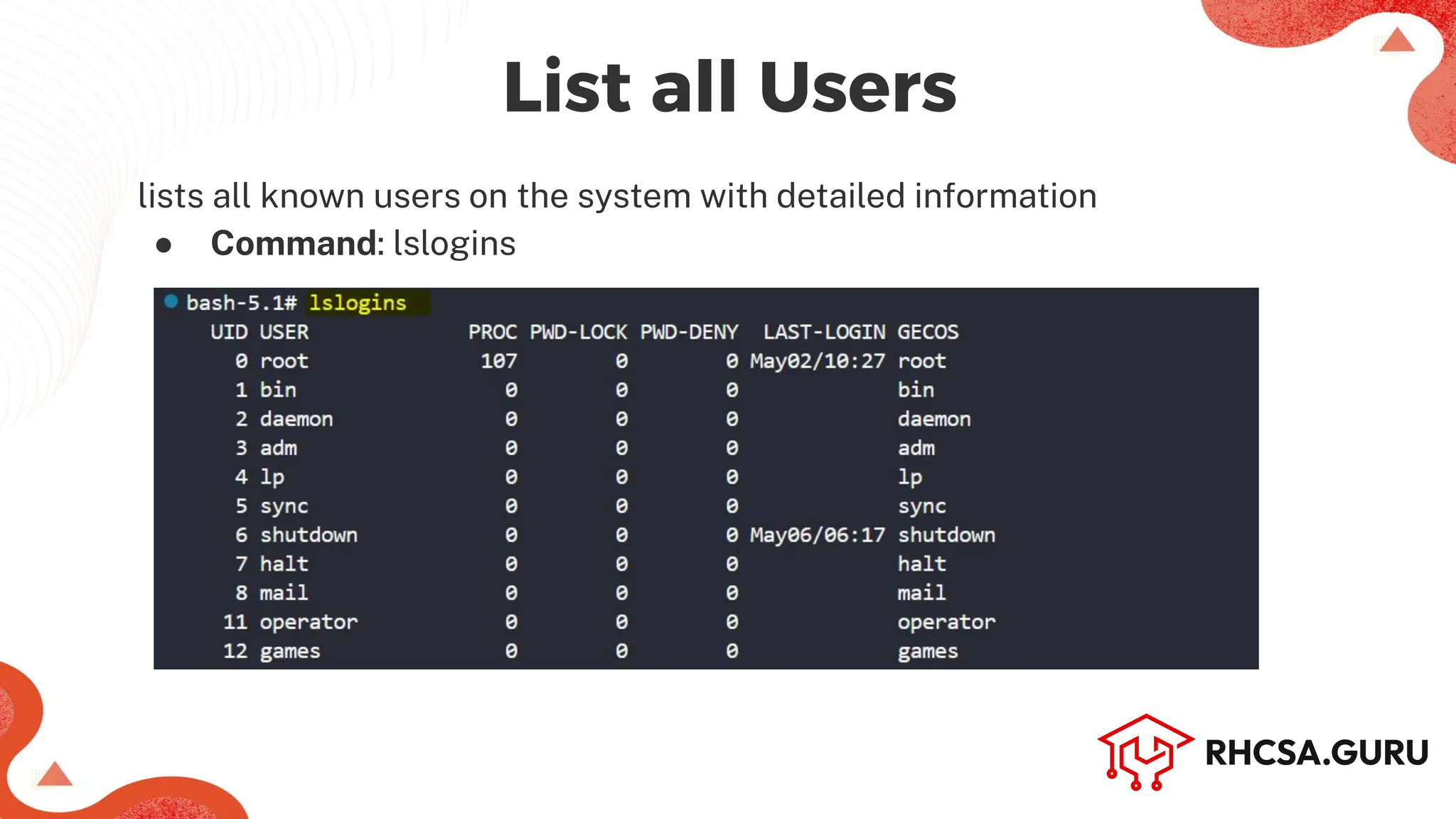
The document covers user and group management in a system, detailing the different types of users, their permissions, and account management commands. It includes instructions on creating, modifying, and deleting users and groups, as well as managing passwords and permissions. Additionally, it discusses the configuration of elevated privileges through the sudoers file and user authentication logging.


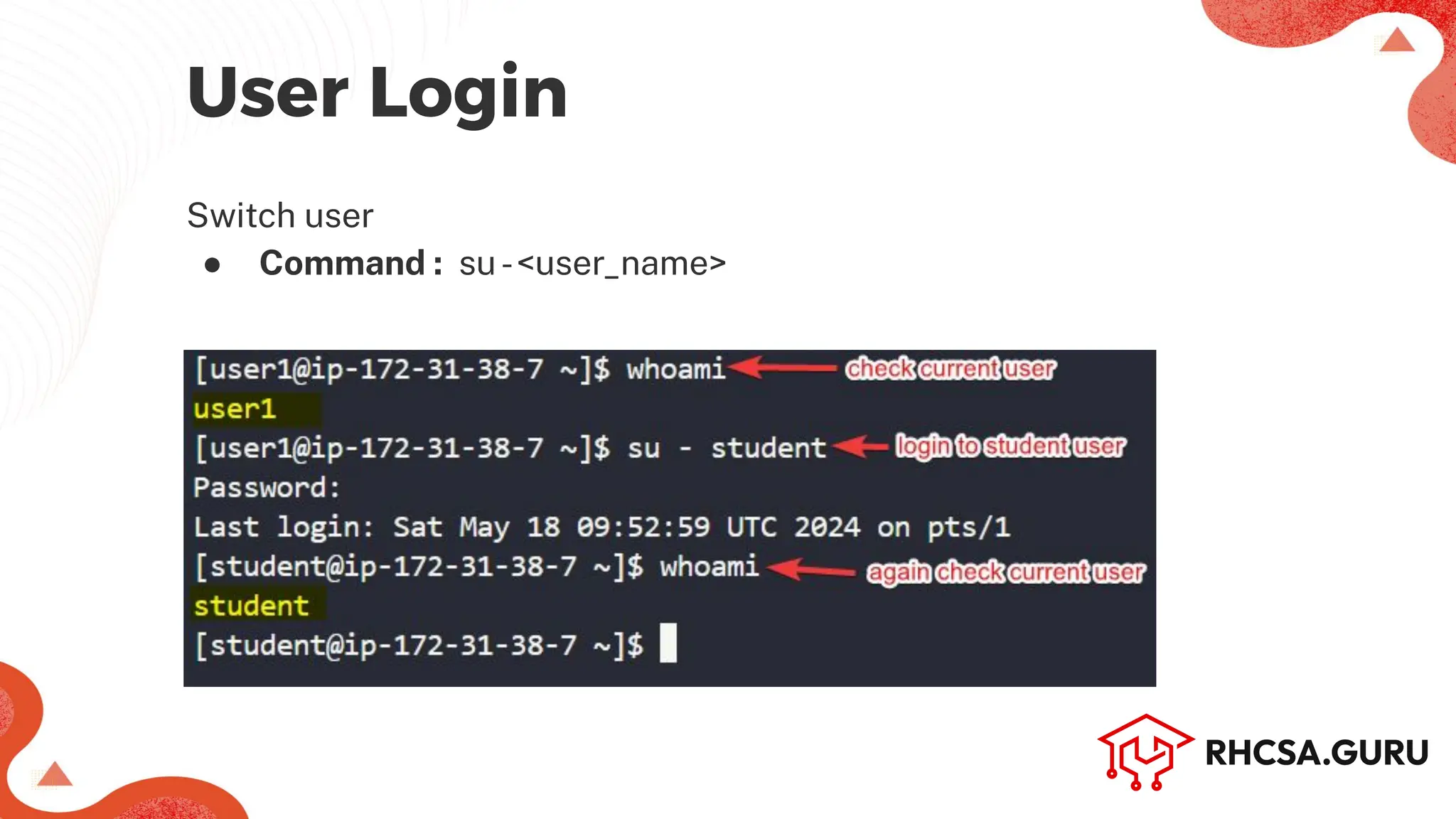
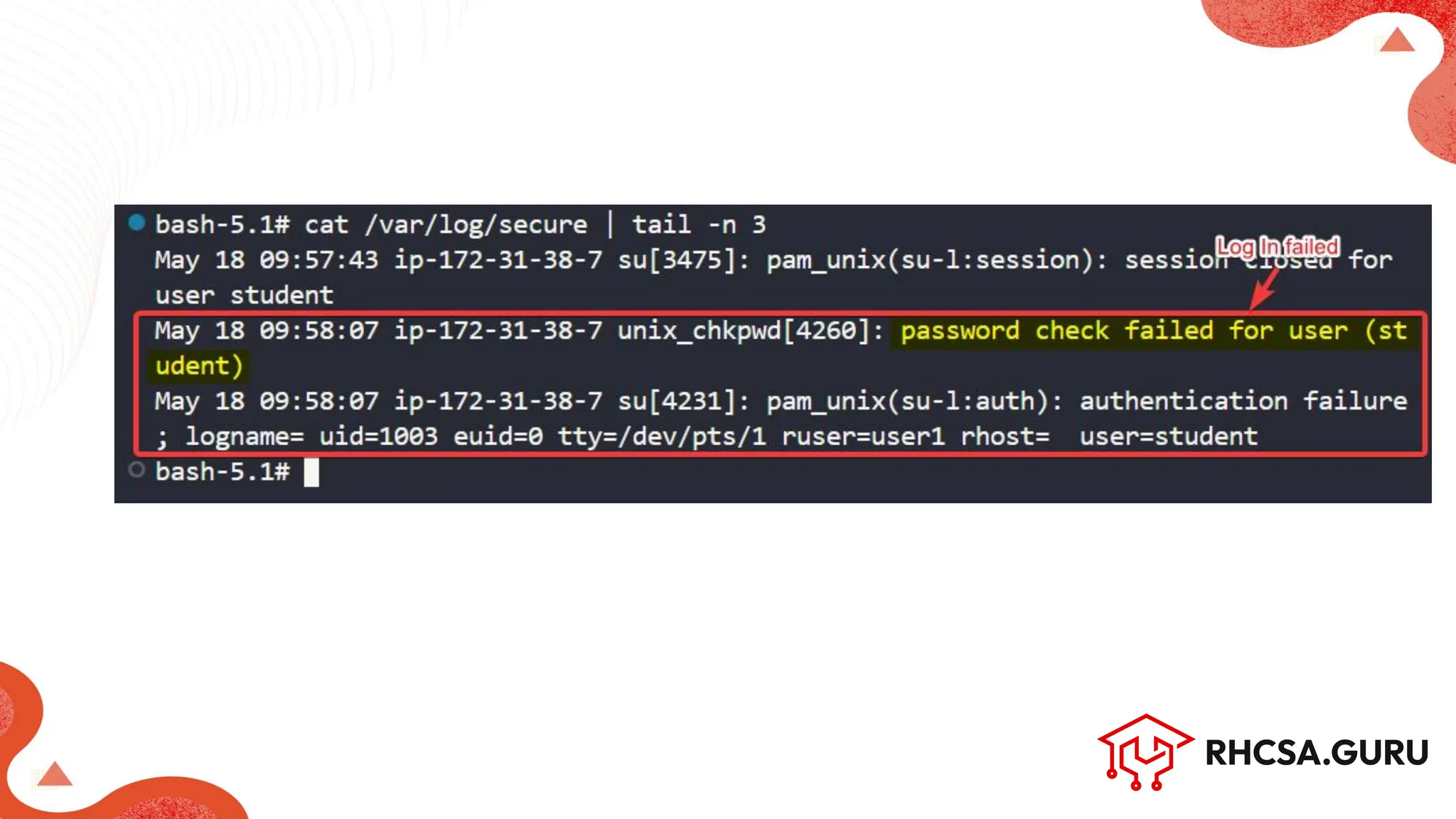
![To display the username of the current user
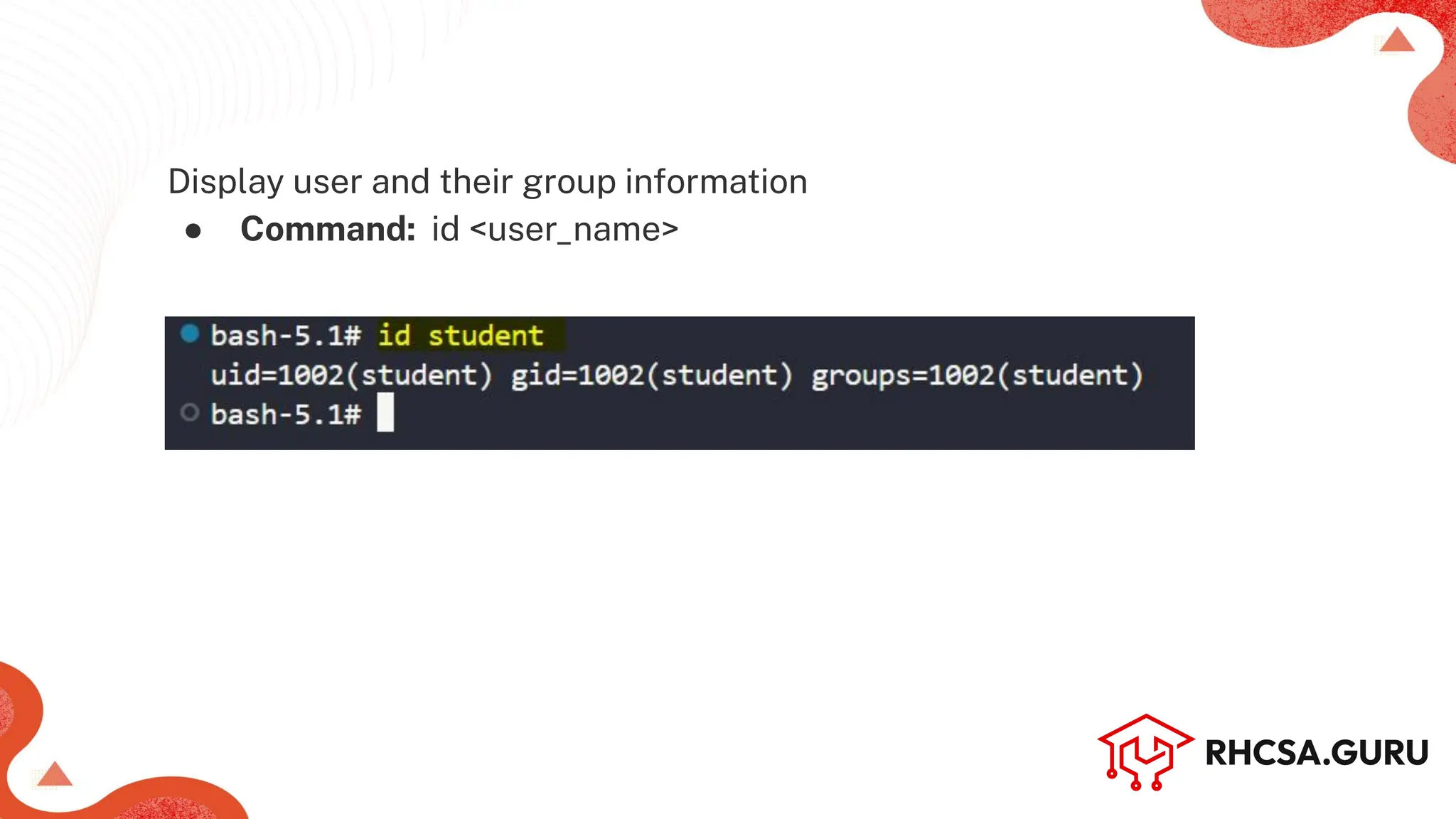
● Command: whoami
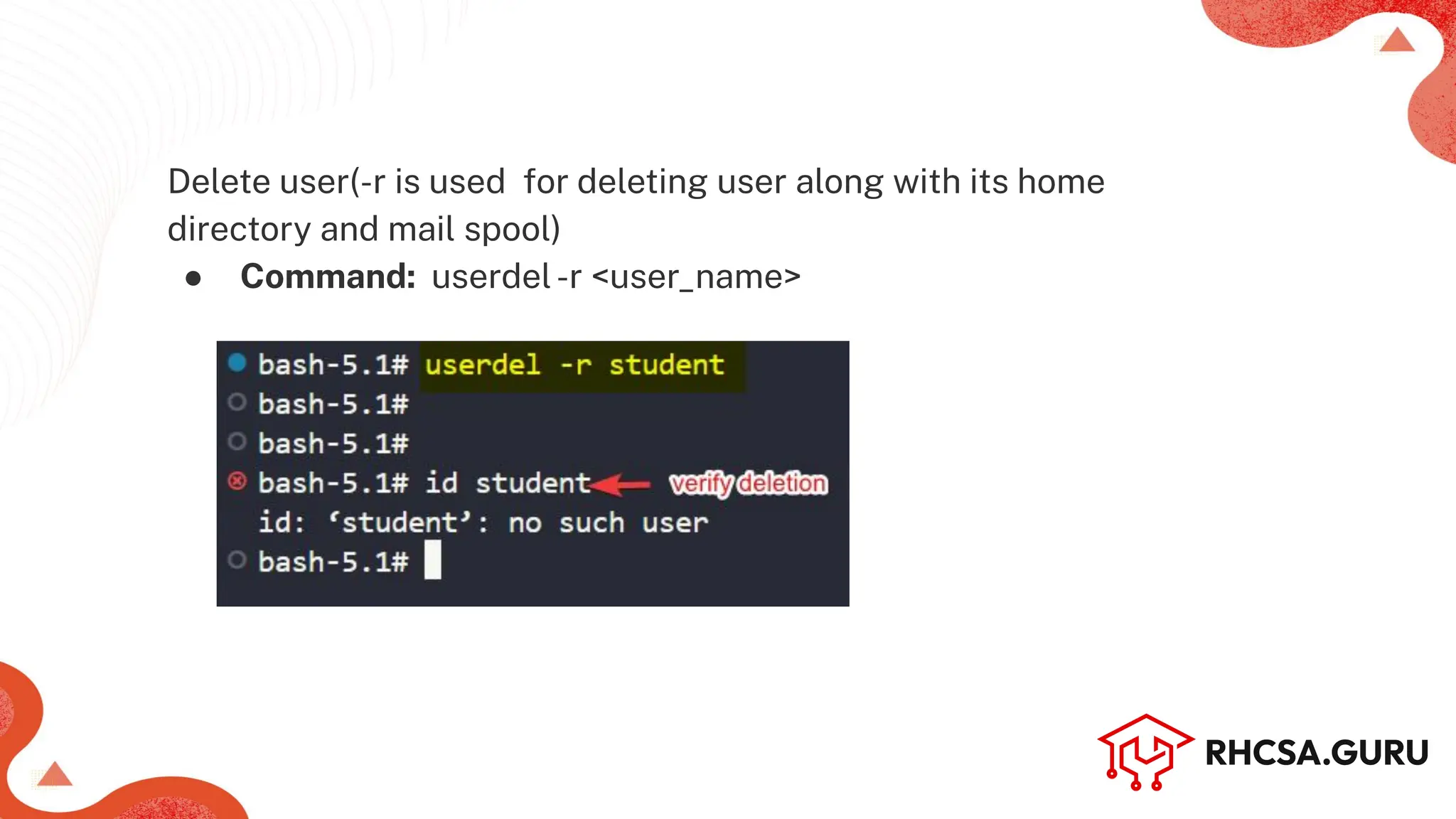
Add a new User (or Regular User account)
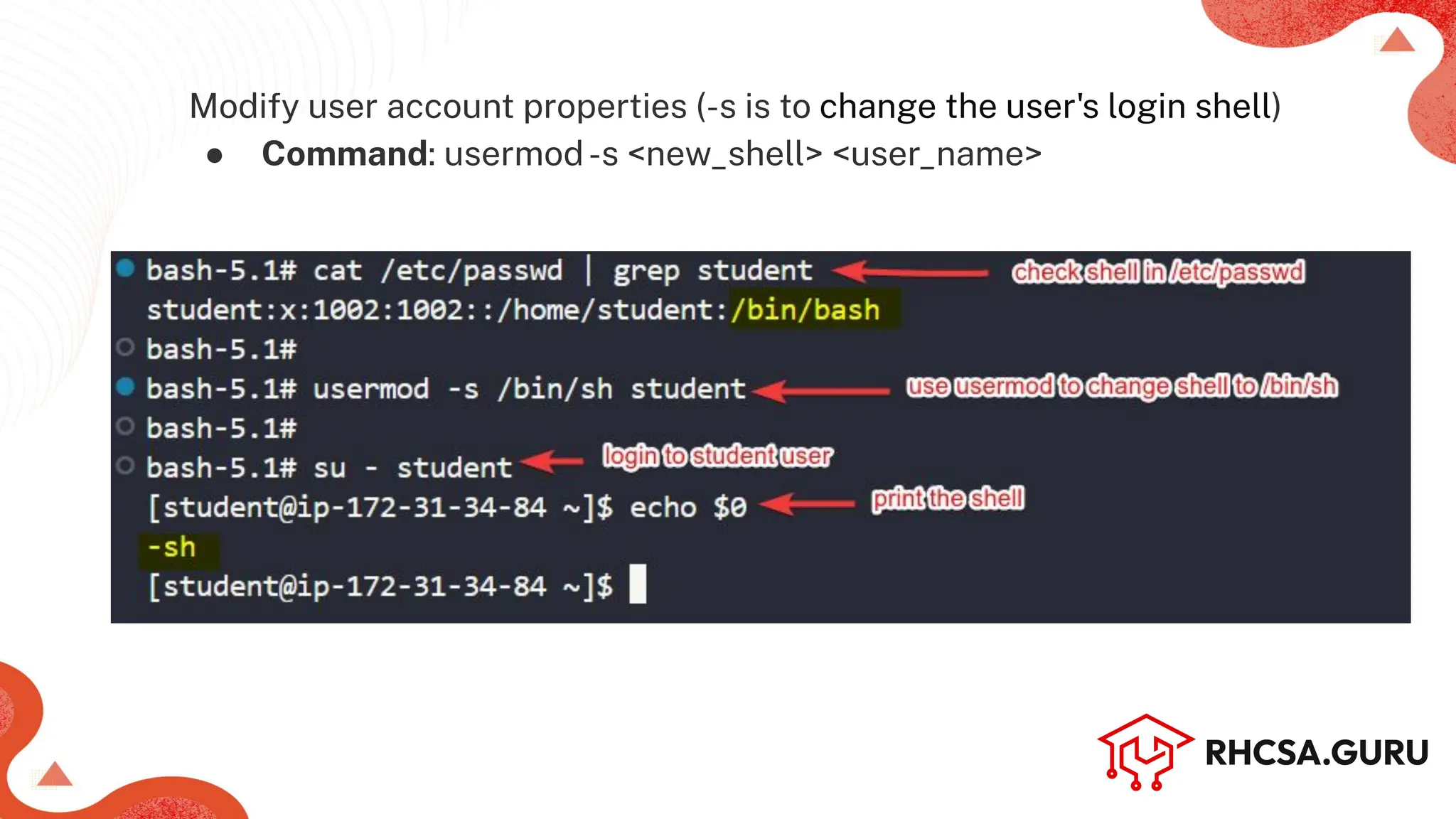
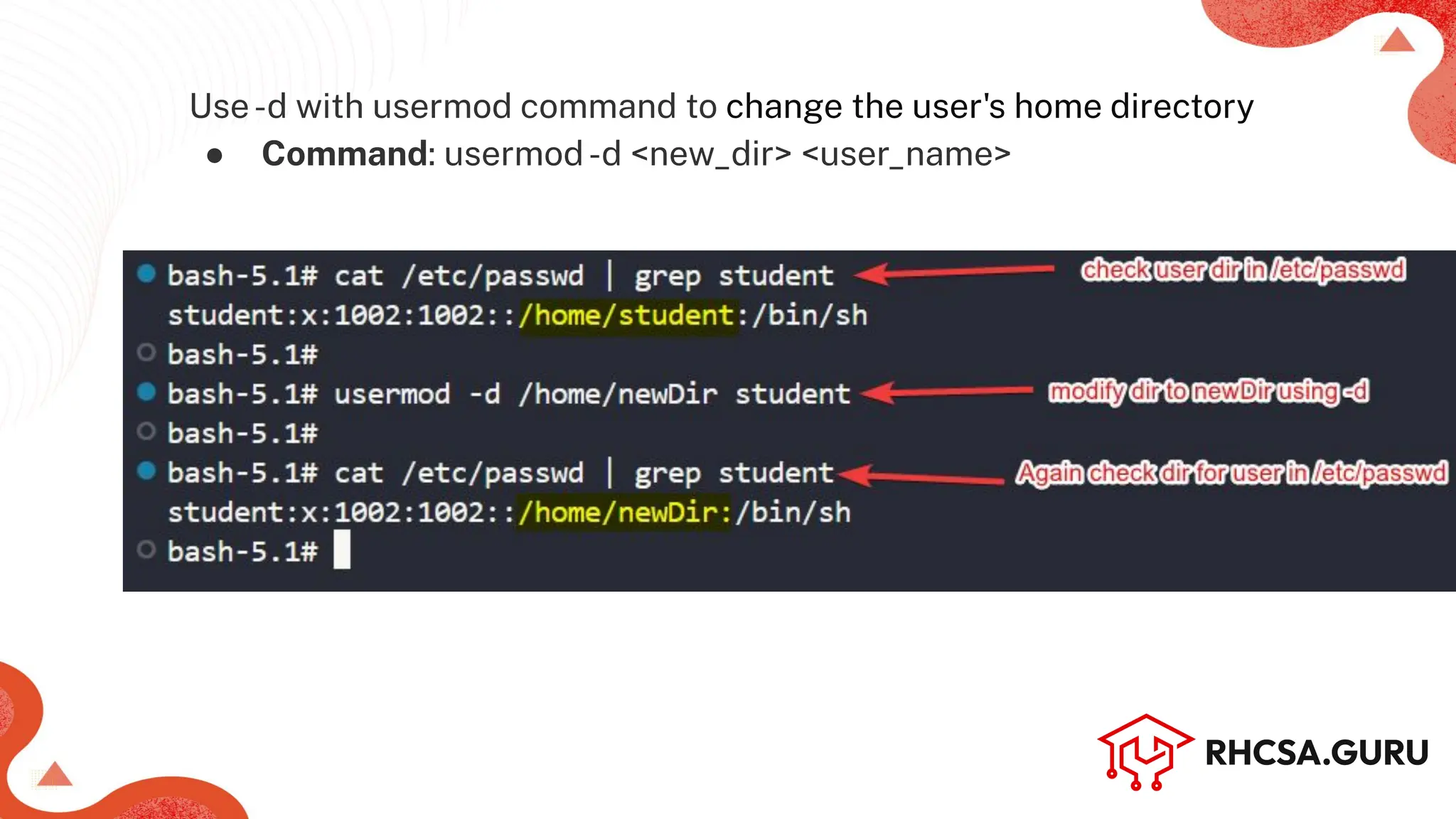
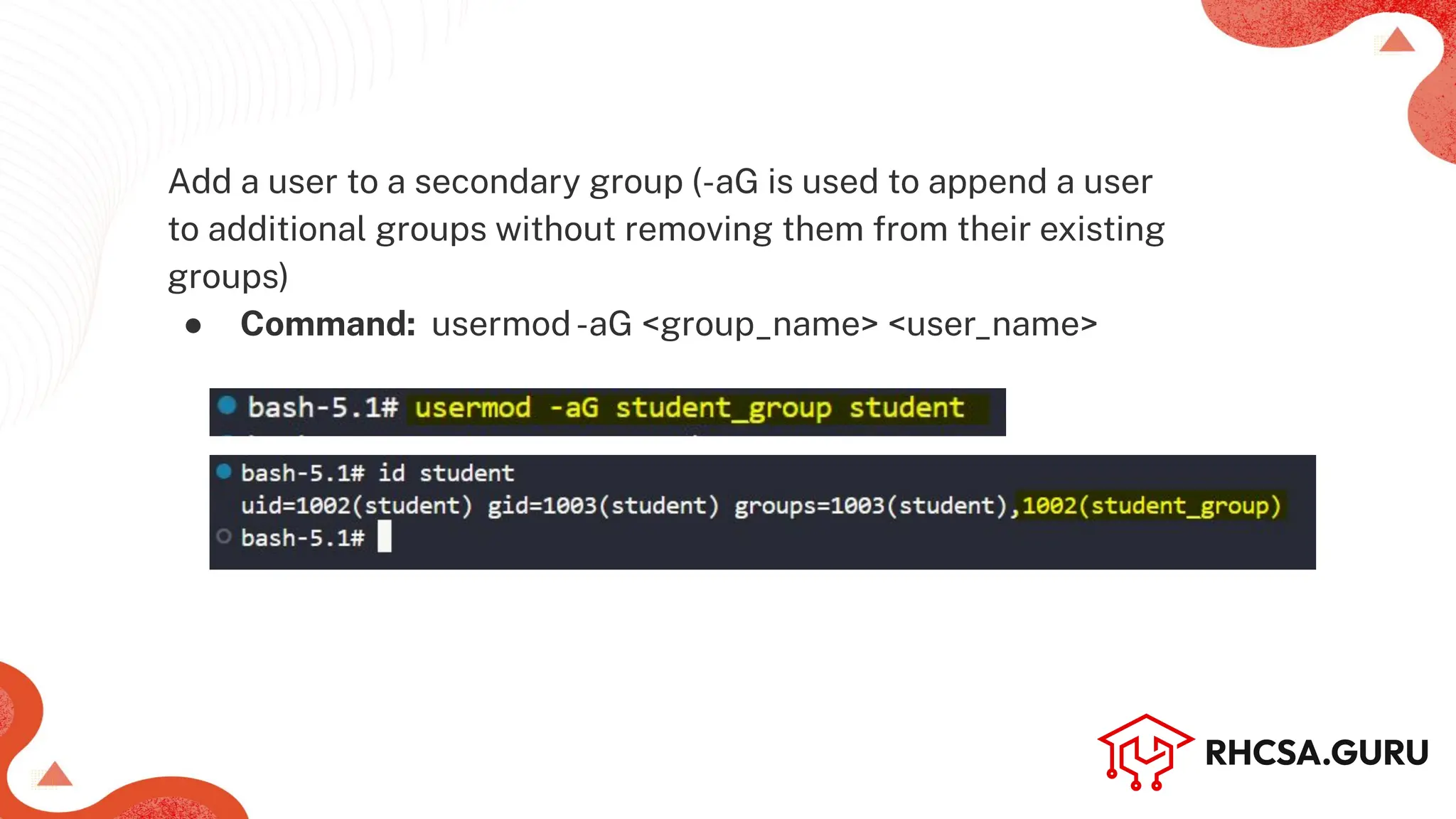
● Command: useradd-c ‘<user_info’ <user_name> OR
adduser <user_name> [works in Debian based dist.]
Machine Name (Hostname)
Managing Users](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-managelocalusersandgroups-240919005605-4c23a417/75/Manage-Local-Users-and-Groups-RHCSA-RH124-8-2048.jpg)


![List or change user password expiry information (-l to list the info)
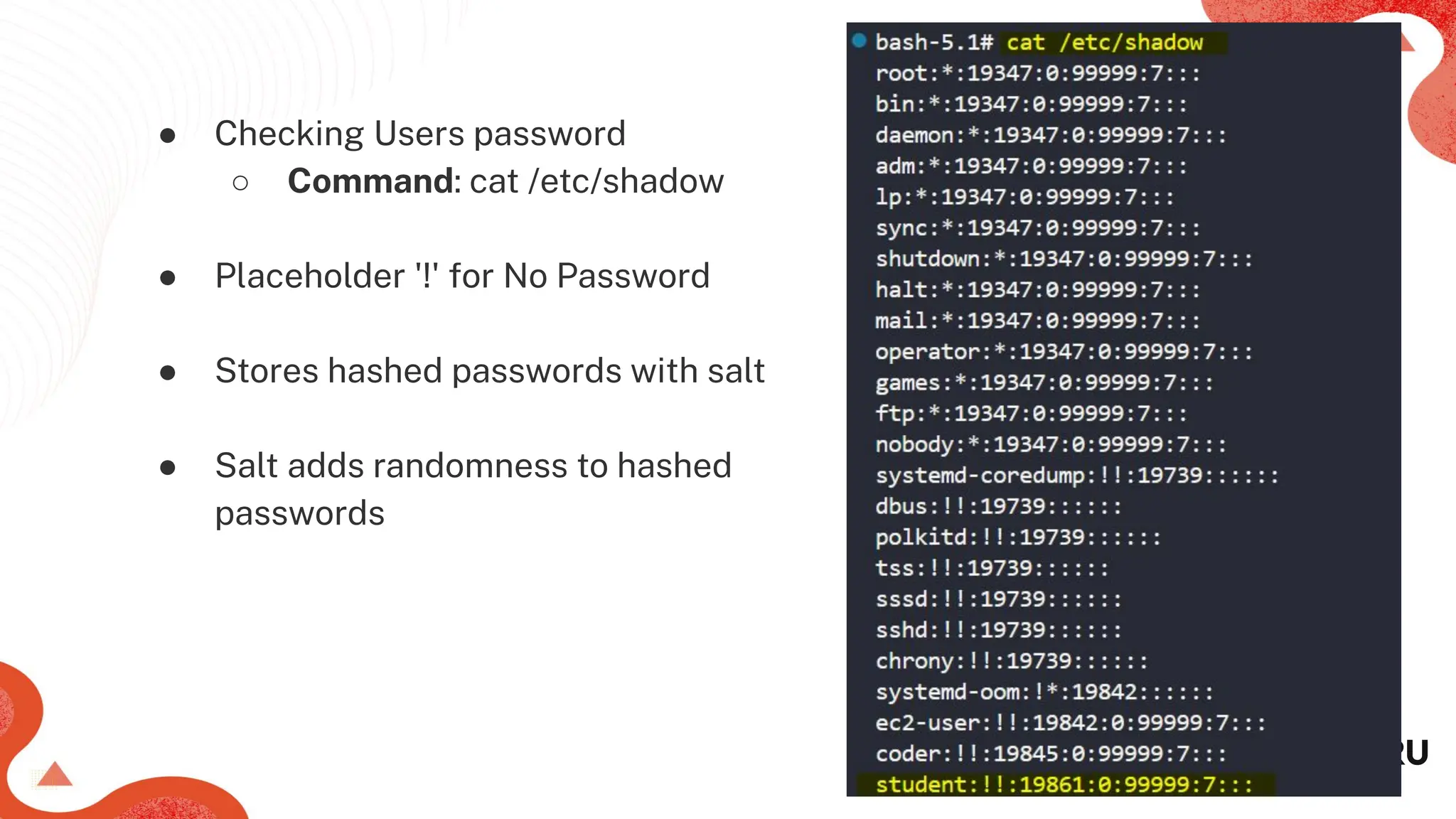
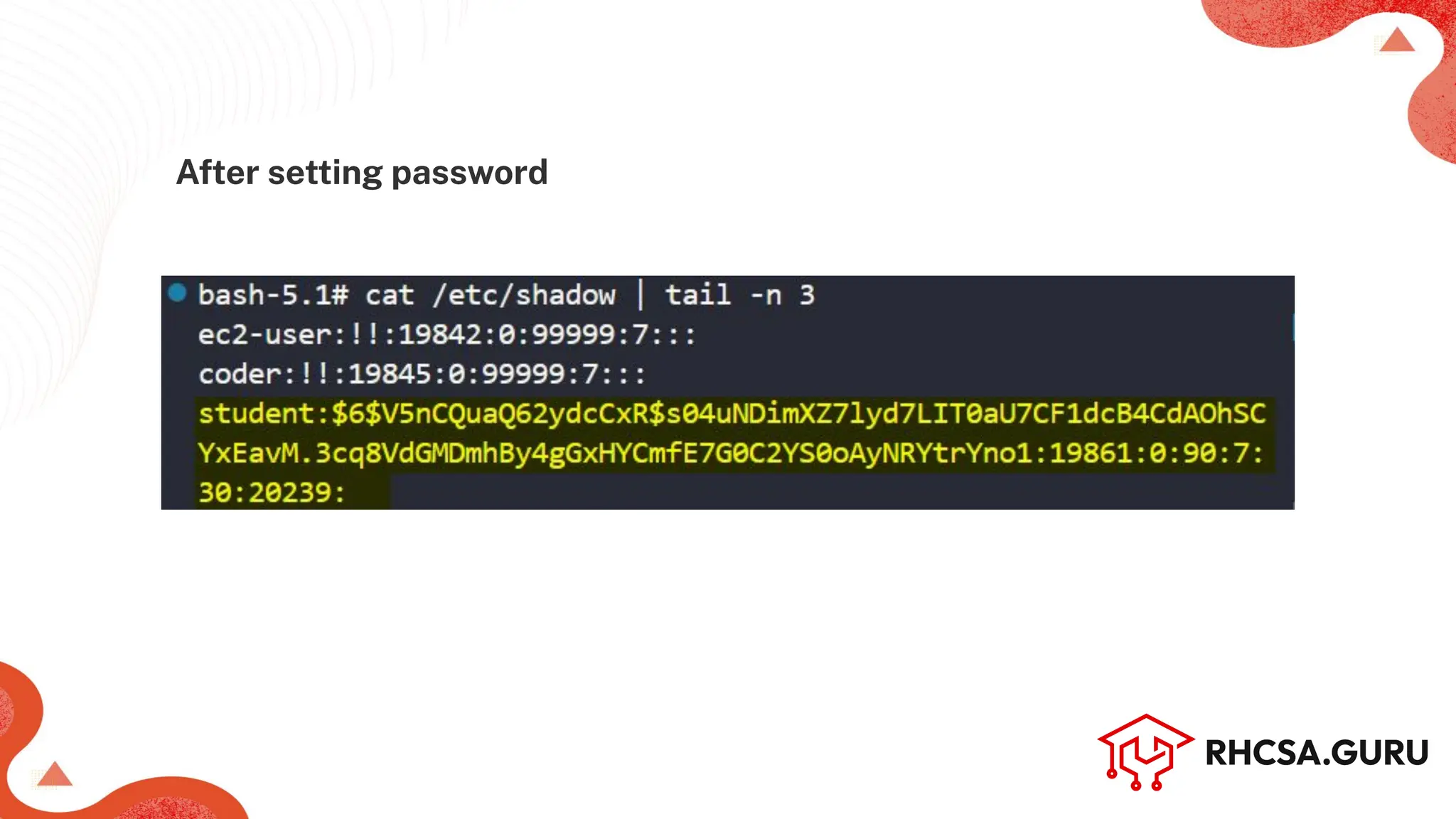
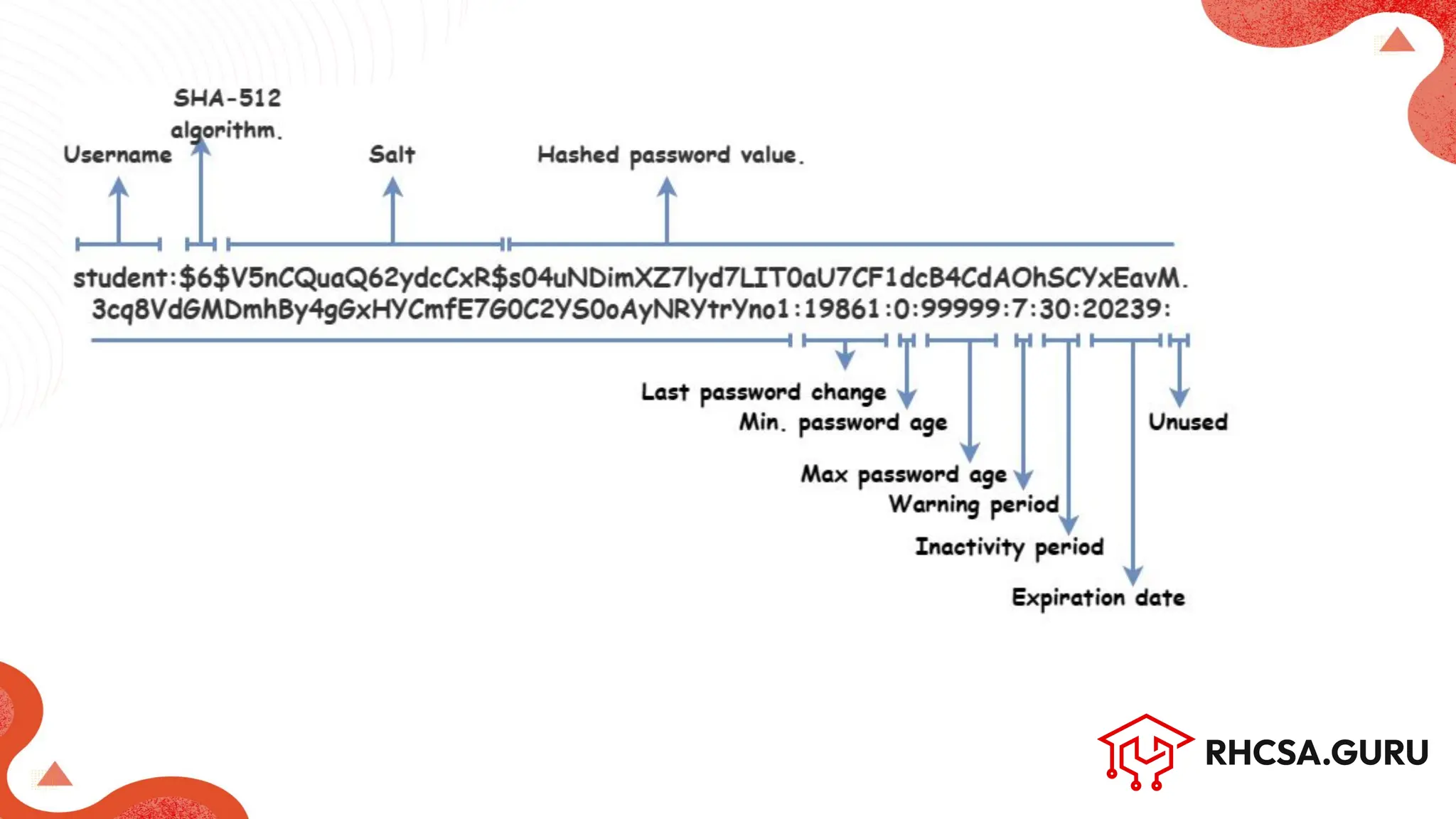
● Command: chage [options] <user_name>
Machine Name (Hostname)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-managelocalusersandgroups-240919005605-4c23a417/75/Manage-Local-Users-and-Groups-RHCSA-RH124-21-2048.jpg)


![Modify group properties (add user1,student using-U in student_group)
● Command: groupmod [options] <group_name>
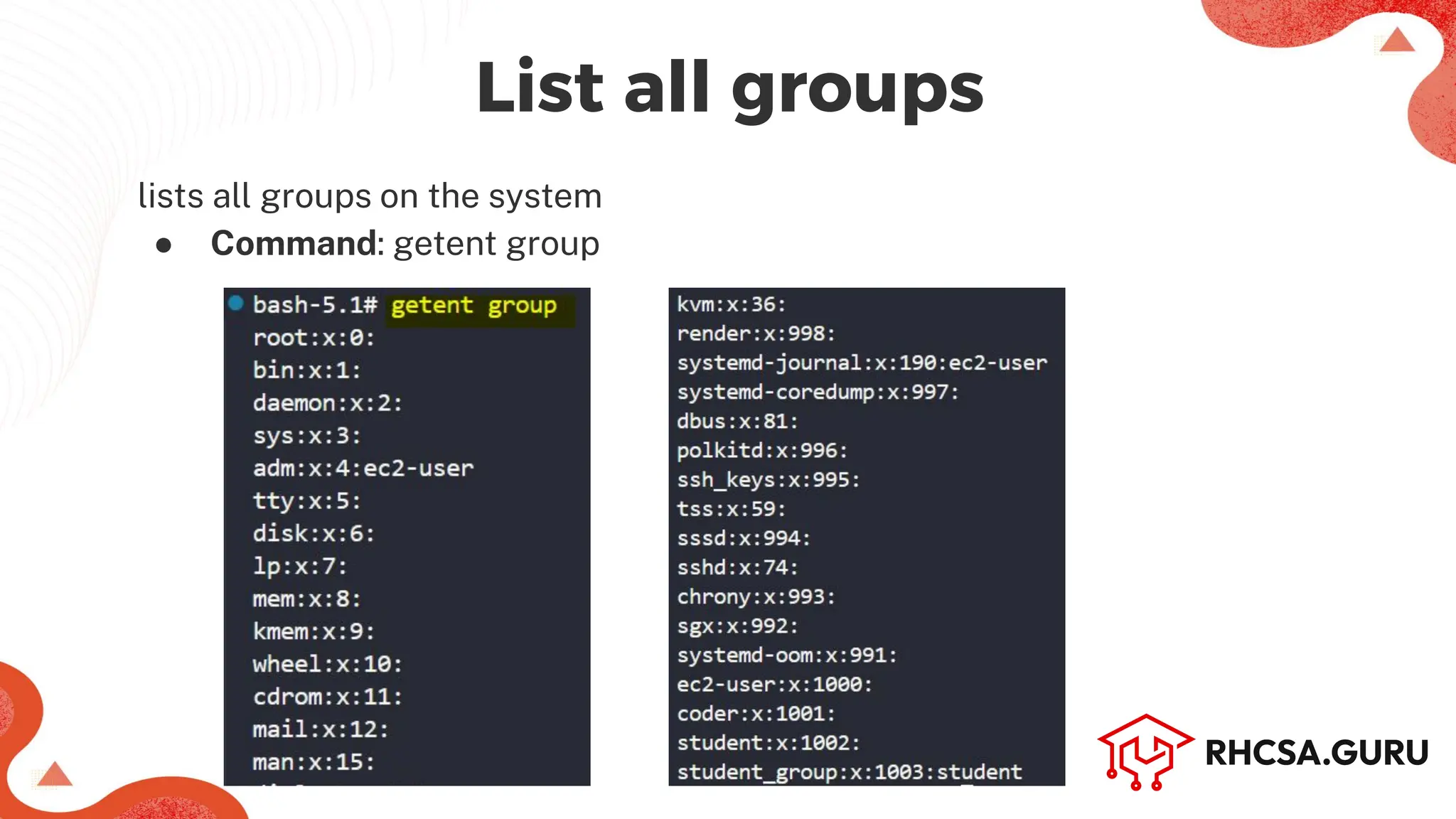
Verify by getent group command whether users added or not
● Command: getent group <group_name>
Machine Name (Hostname)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-managelocalusersandgroups-240919005605-4c23a417/75/Manage-Local-Users-and-Groups-RHCSA-RH124-26-2048.jpg)