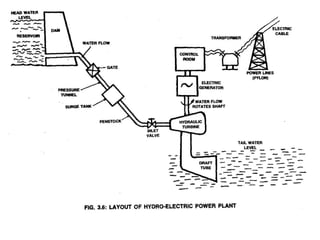
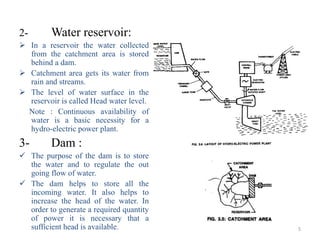
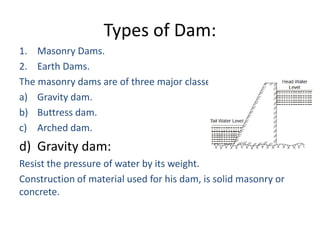
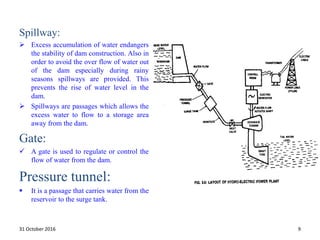
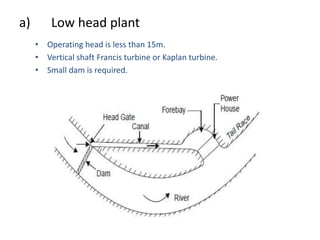
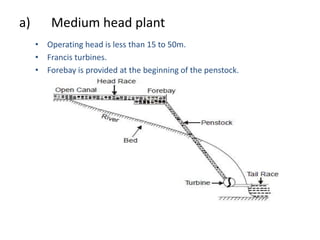
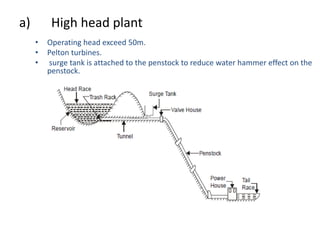
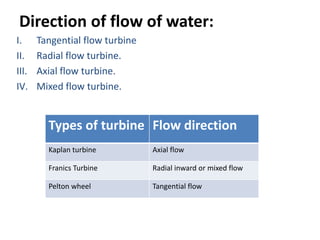
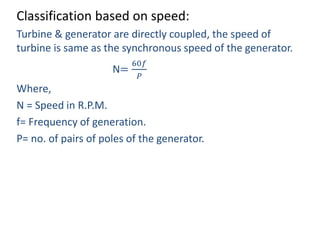
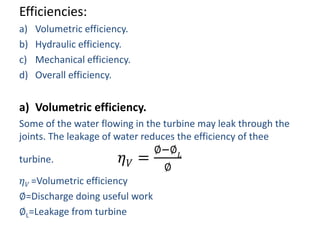
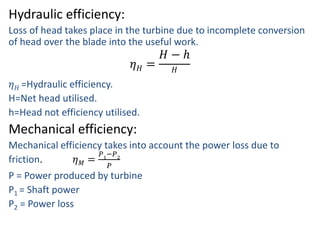
This document provides information about hydroelectric power plants. It discusses the essential components of hydroelectric plants including the catchment area, reservoir, dam, waterways, powerhouse, and tailrace. It describes the functions of these components and classifications such as type of dam. The document also discusses hydraulic turbines and components within the powerhouse such as the generator, transformer, and penstock. It provides advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric power.