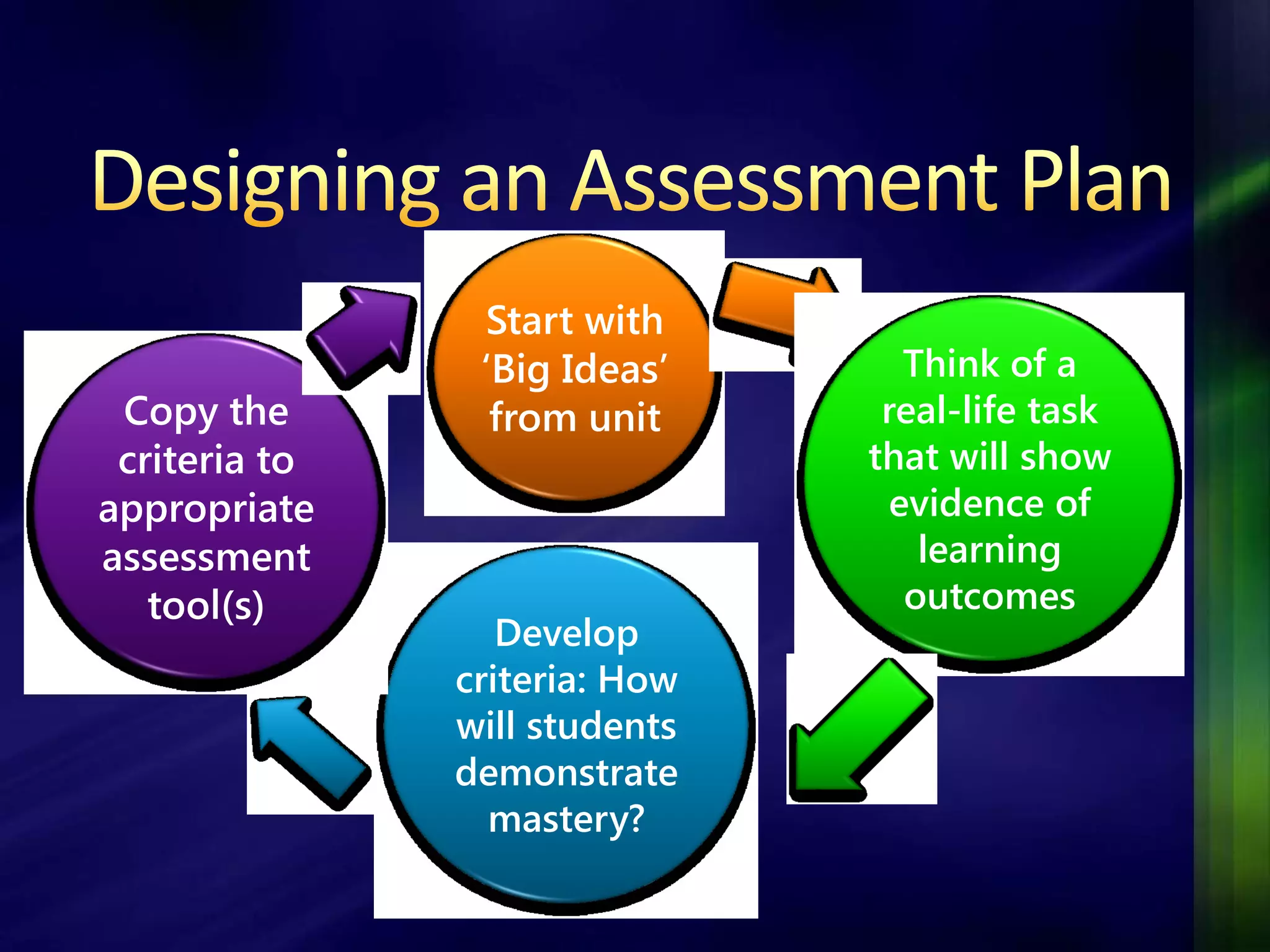
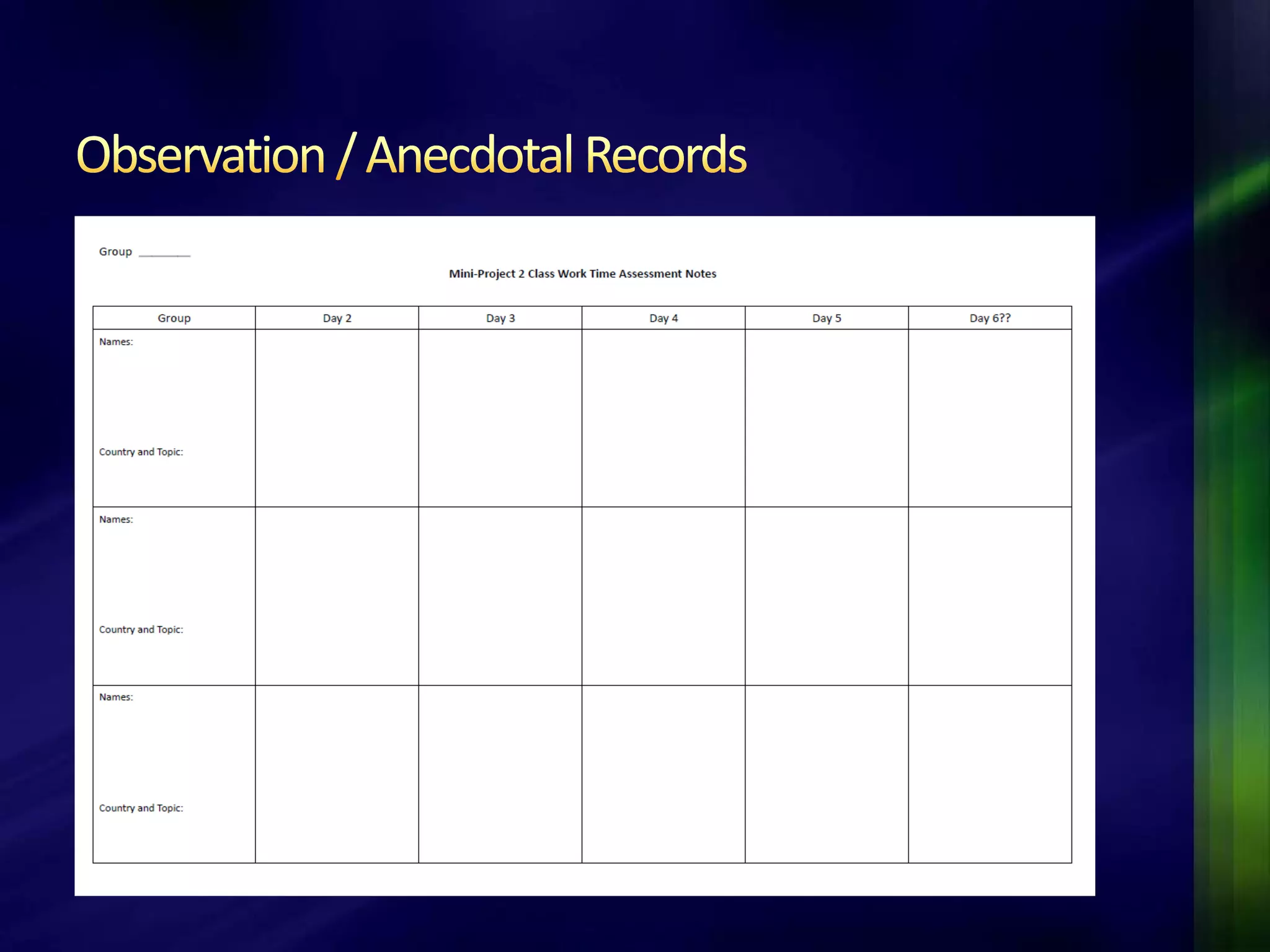
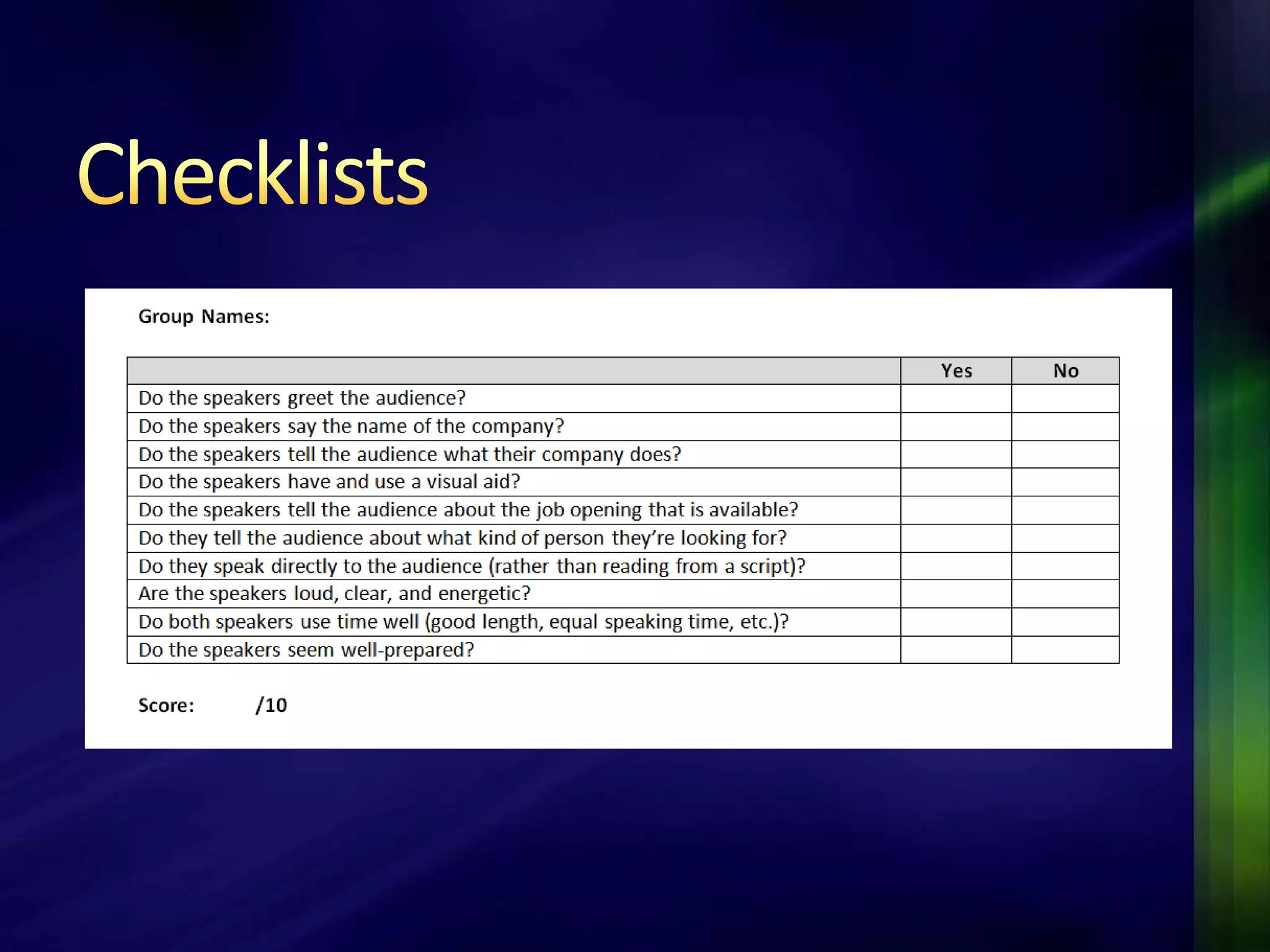
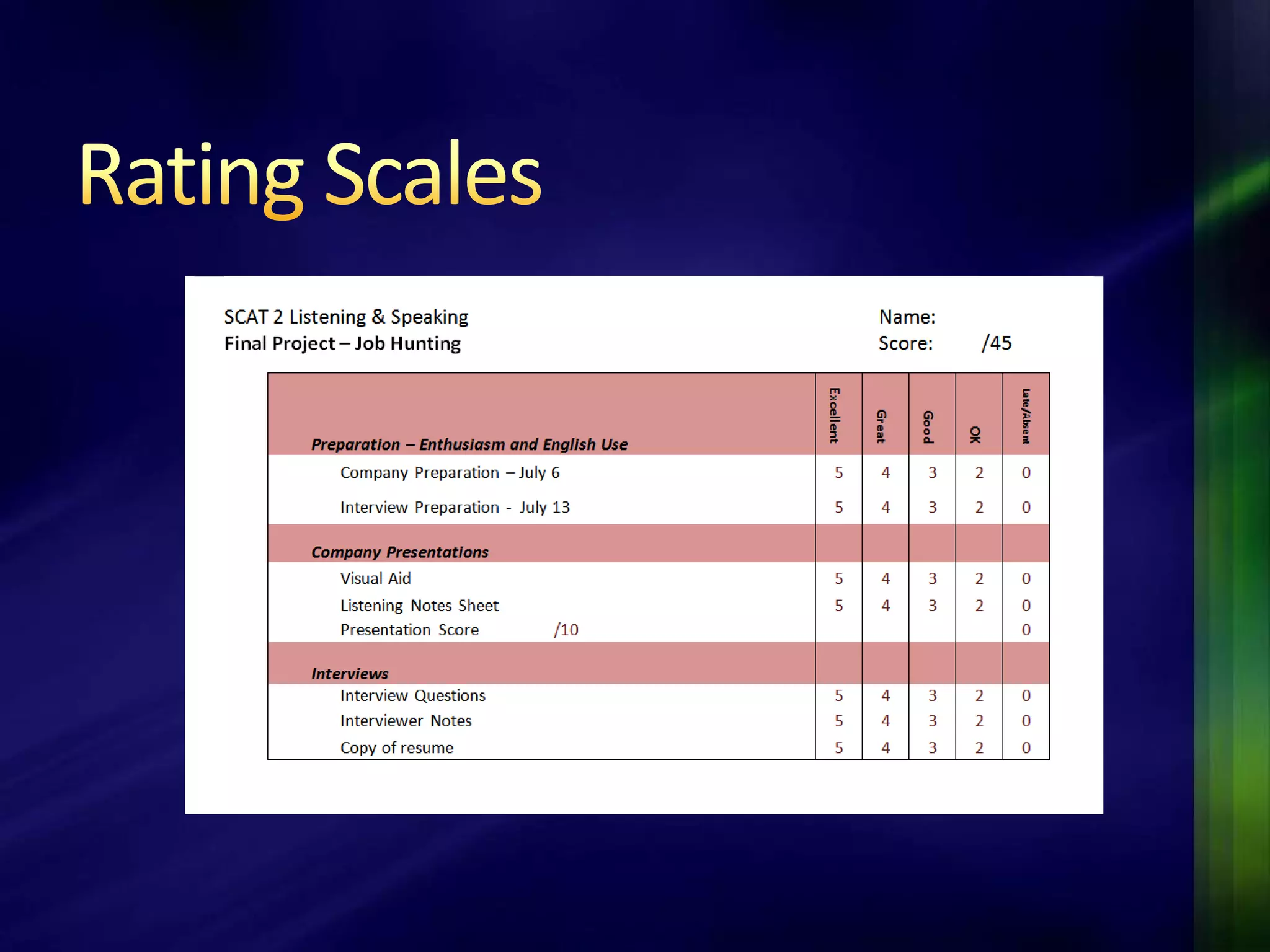
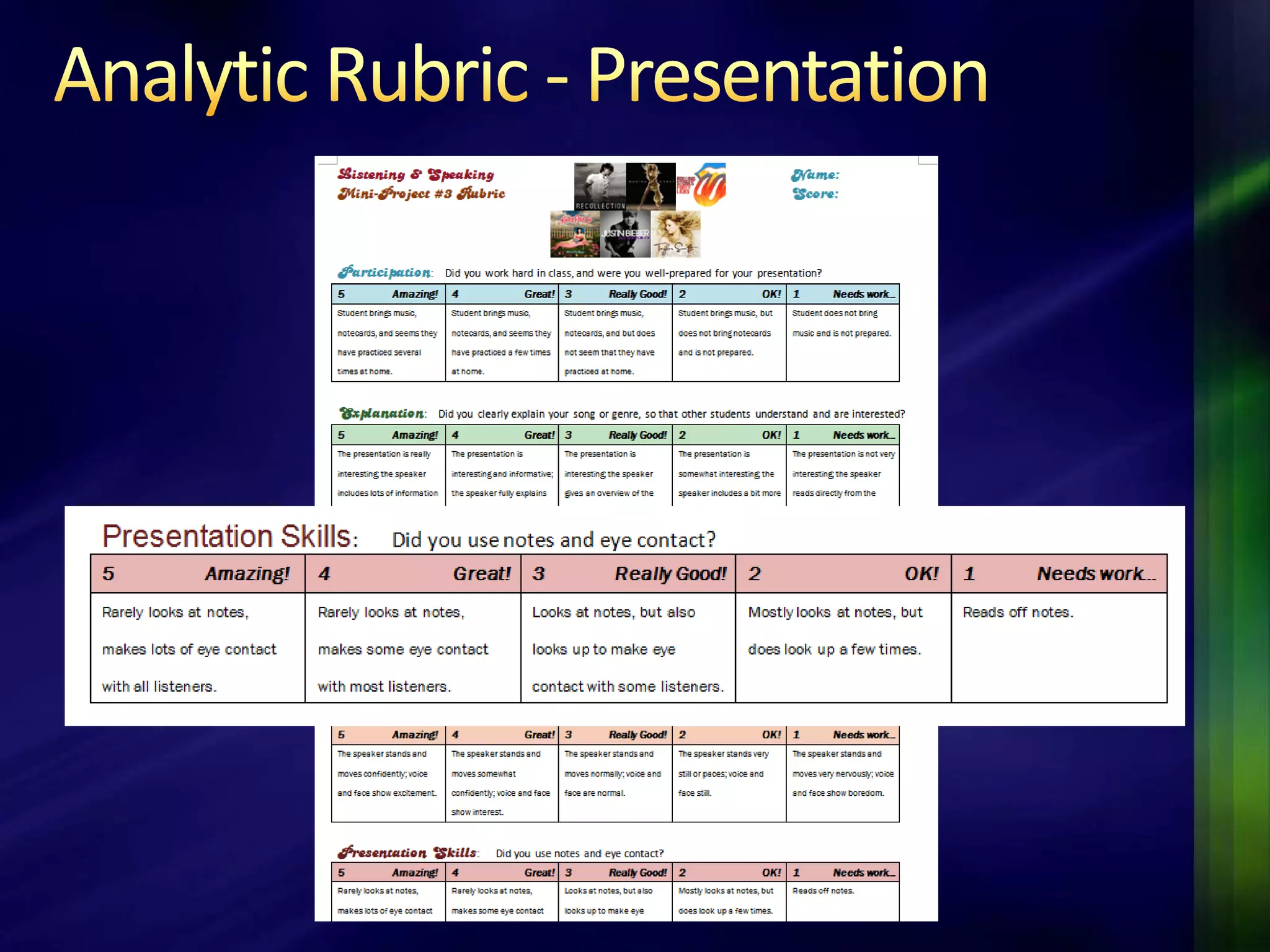
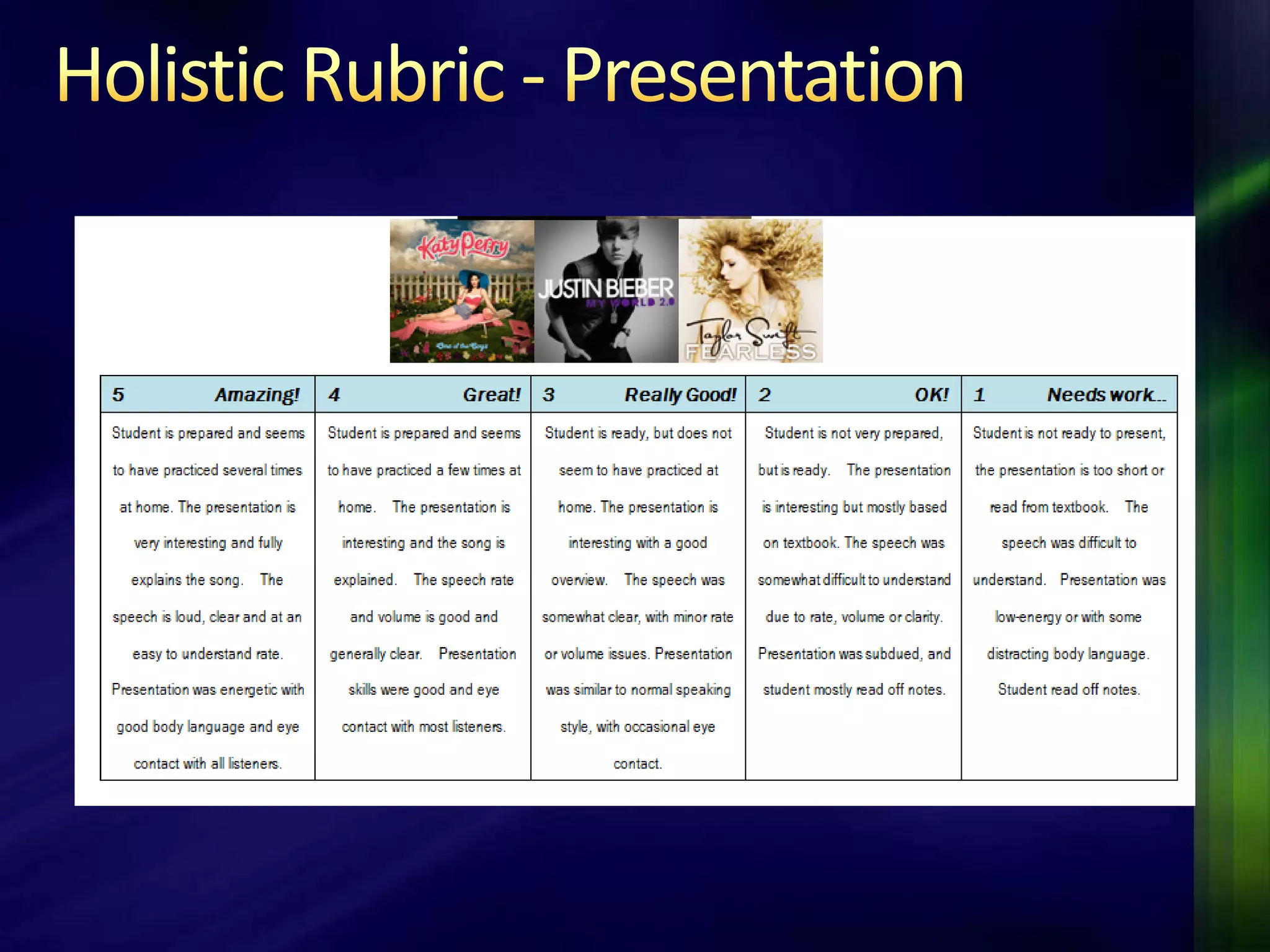
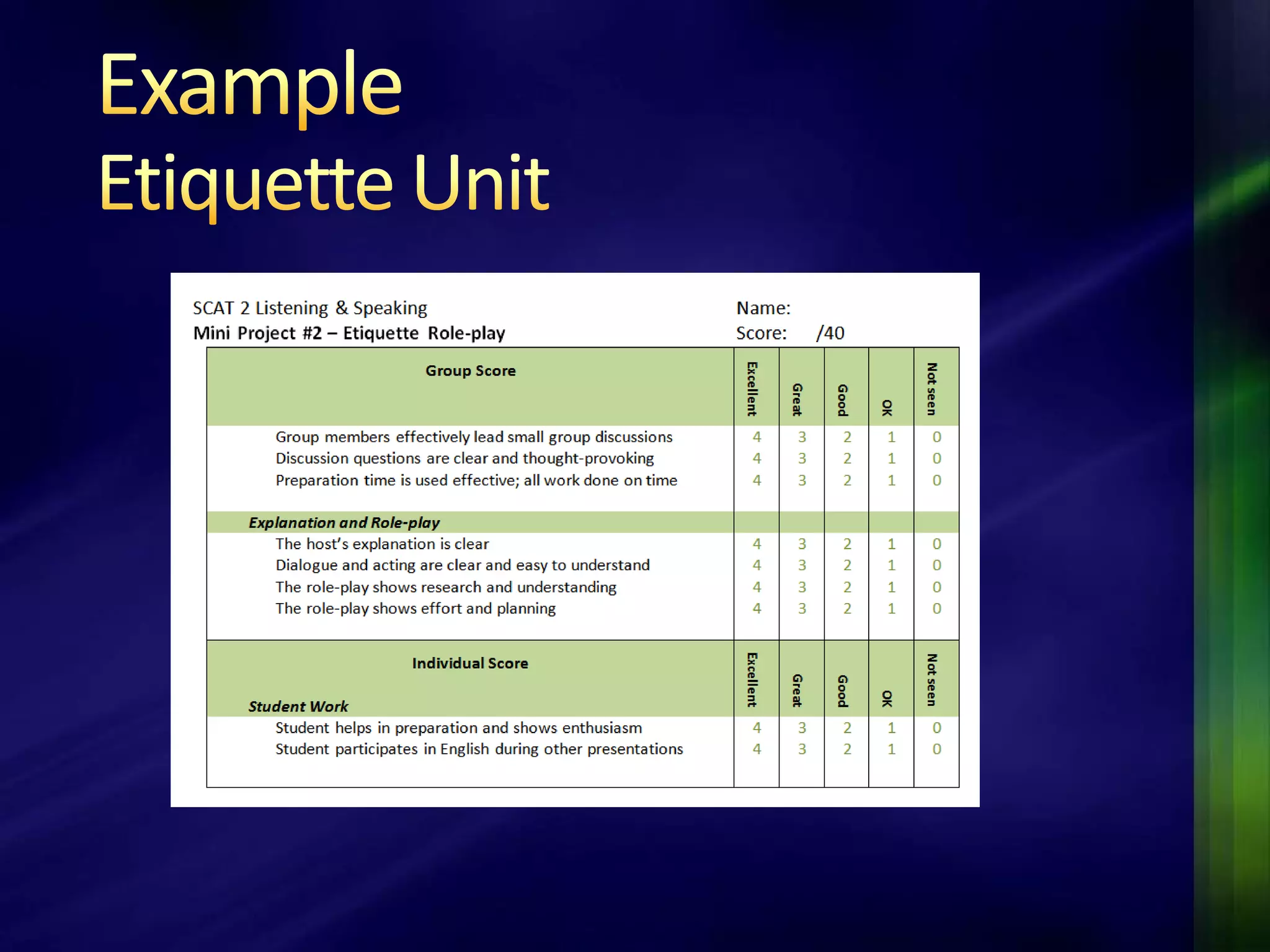
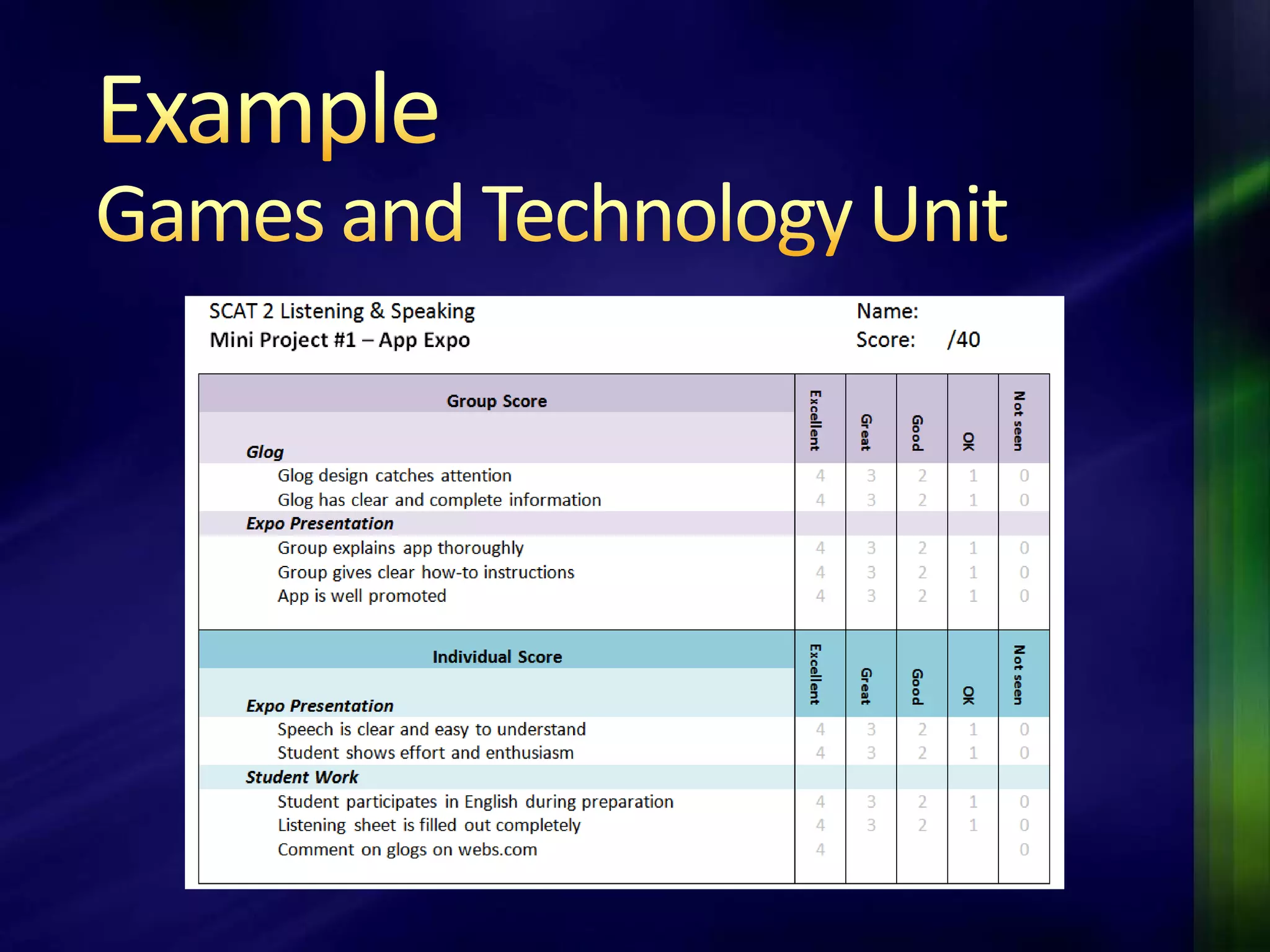
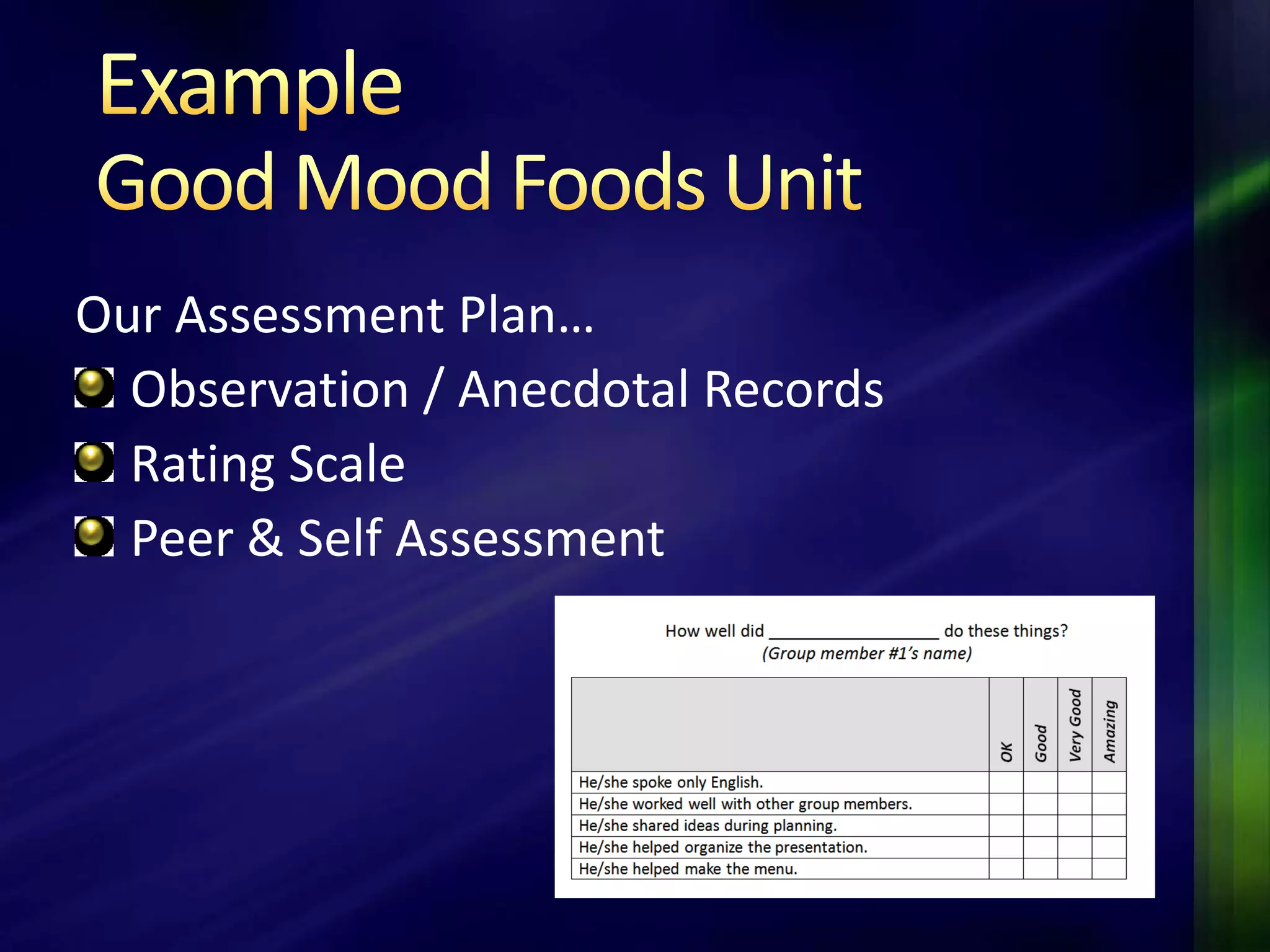
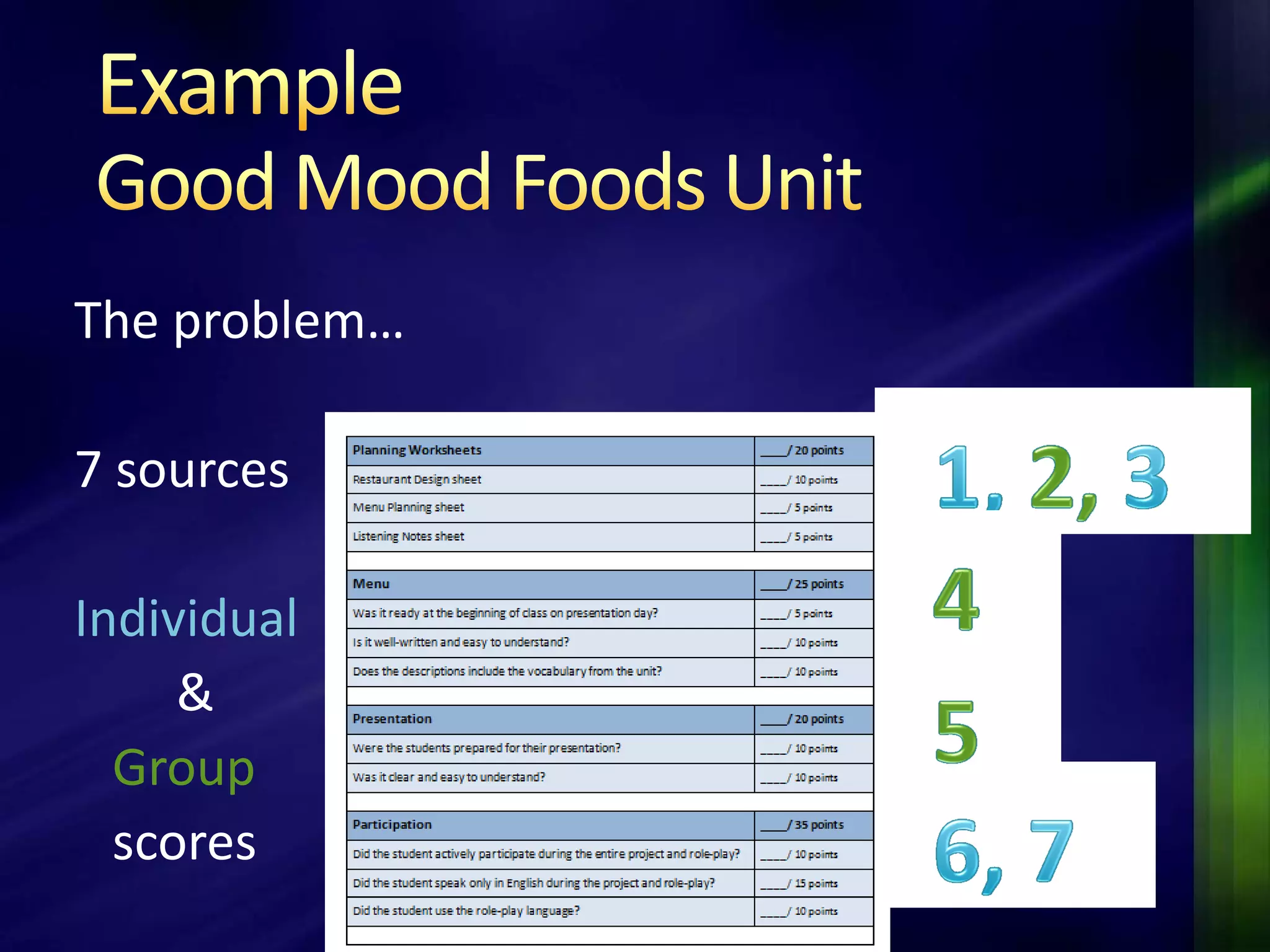
The document outlines a project-based assessment approach implemented in an English as a Foreign Language (EFL) program at Toyo University, focusing on tasks like role-playing and creating menus in a restaurant context. It discusses goals such as increasing study abroad participation and improving English competence, while highlighting the benefits of project-based assessments, including motivation and real-life skills. The document also covers grading methods and evaluation criteria, emphasizing the need for effective feedback and fair grading practices.