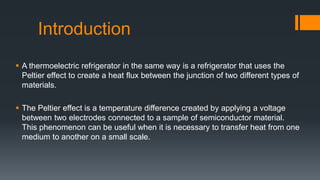
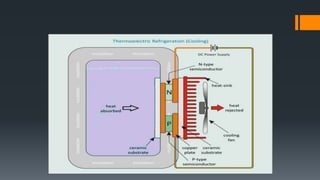
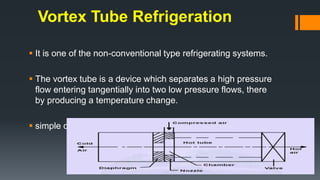
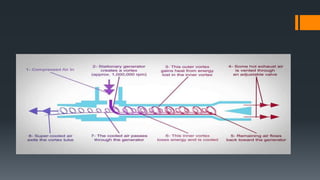
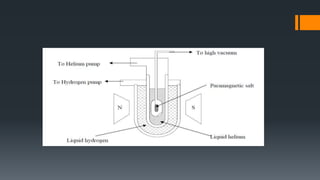
This document discusses three methods of refrigeration: thermoelectric refrigeration using the Peltier effect, vortex tube refrigeration using compressed air, and cooling by adiabatic demagnetization. Thermoelectric refrigeration uses the temperature difference created when applying a voltage to semiconductor materials to pump heat. Vortex tube refrigeration separates compressed air flows to produce hot and cold air without moving parts. Cooling by adiabatic demagnetization exploits the magnetocaloric effect where exposing magnetic materials to changing magnetic fields causes temperature changes, allowing cooling below absolute zero temporarily. Examples of each method and their advantages/disadvantages are provided.