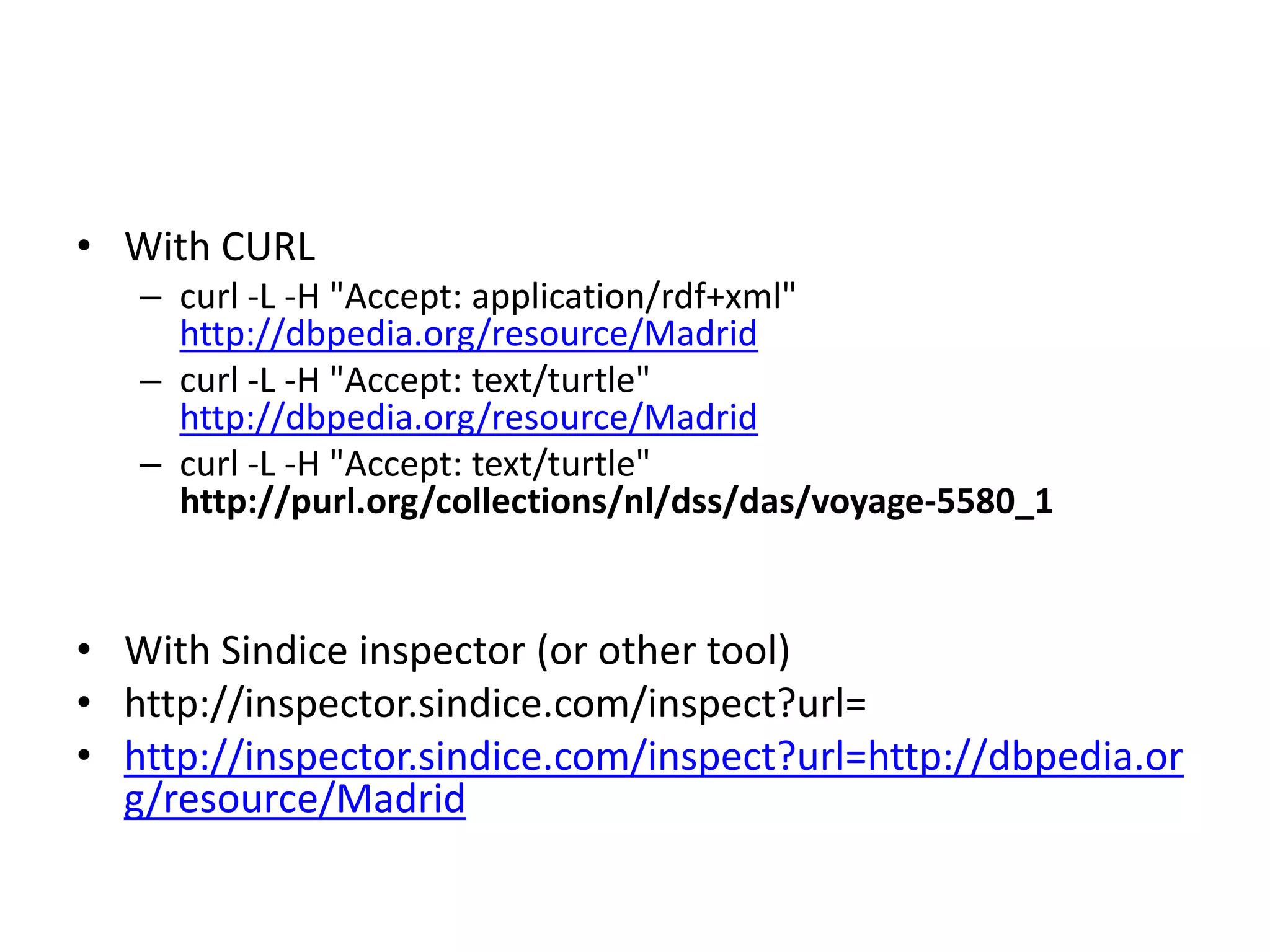
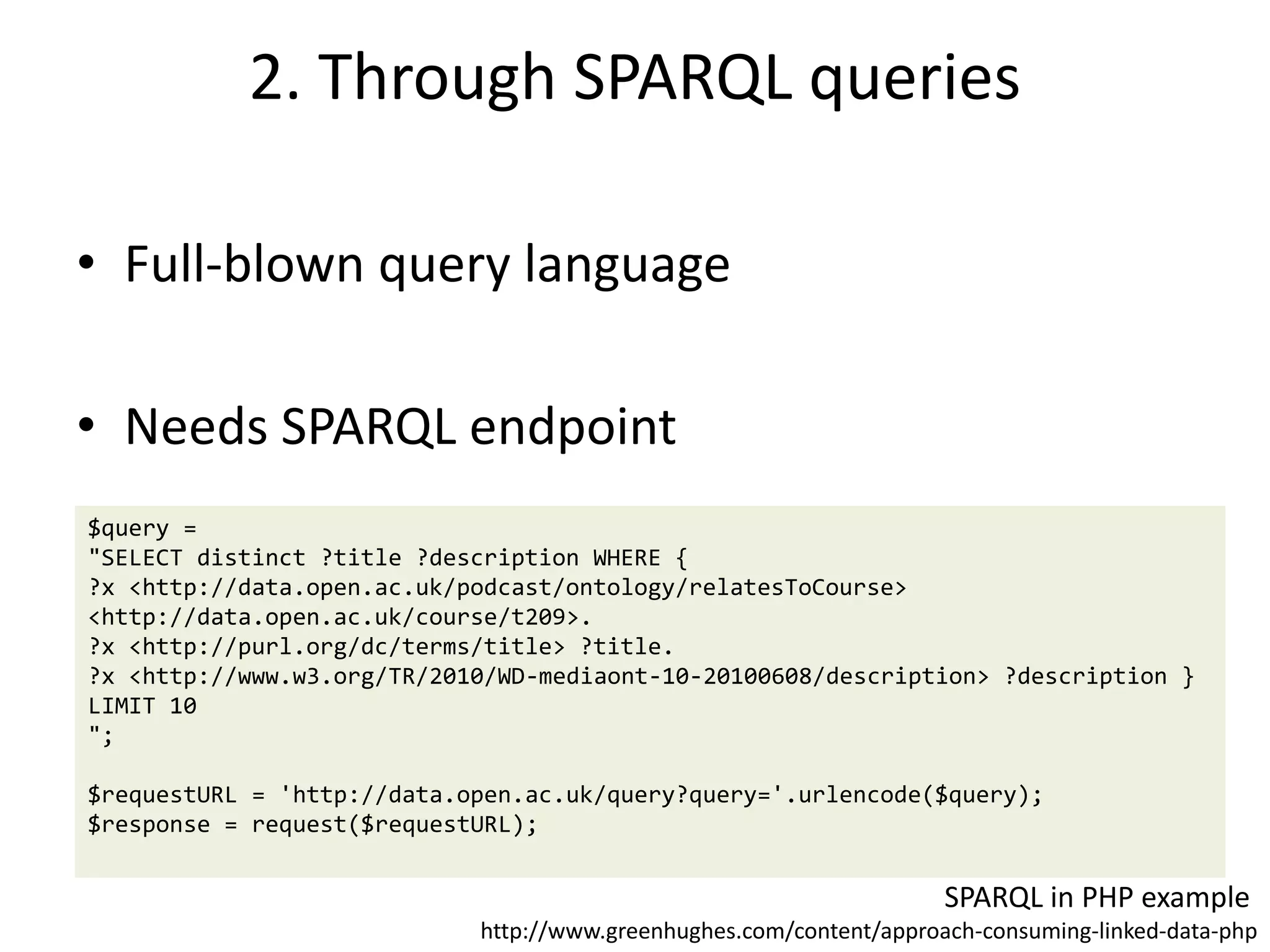
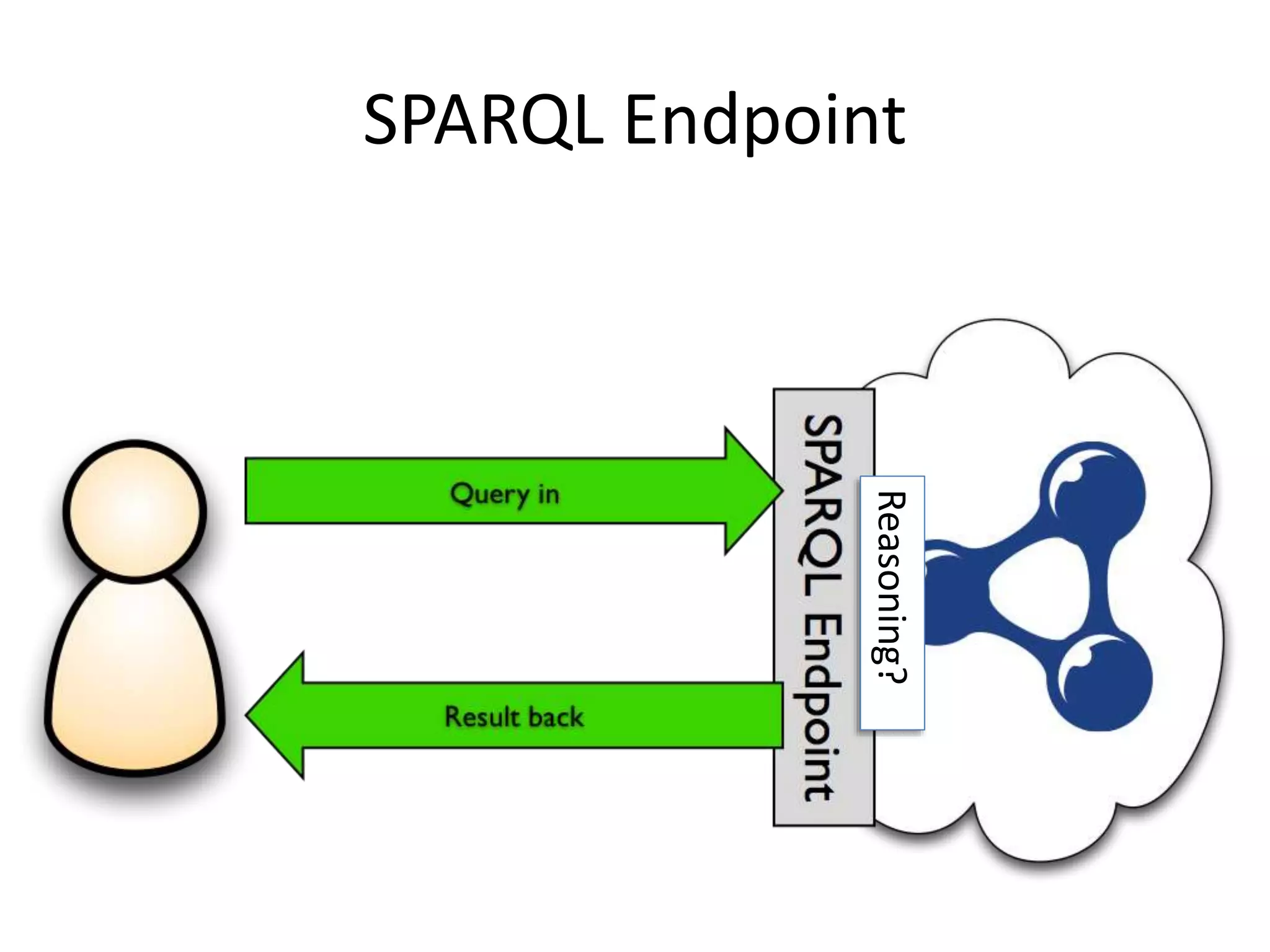
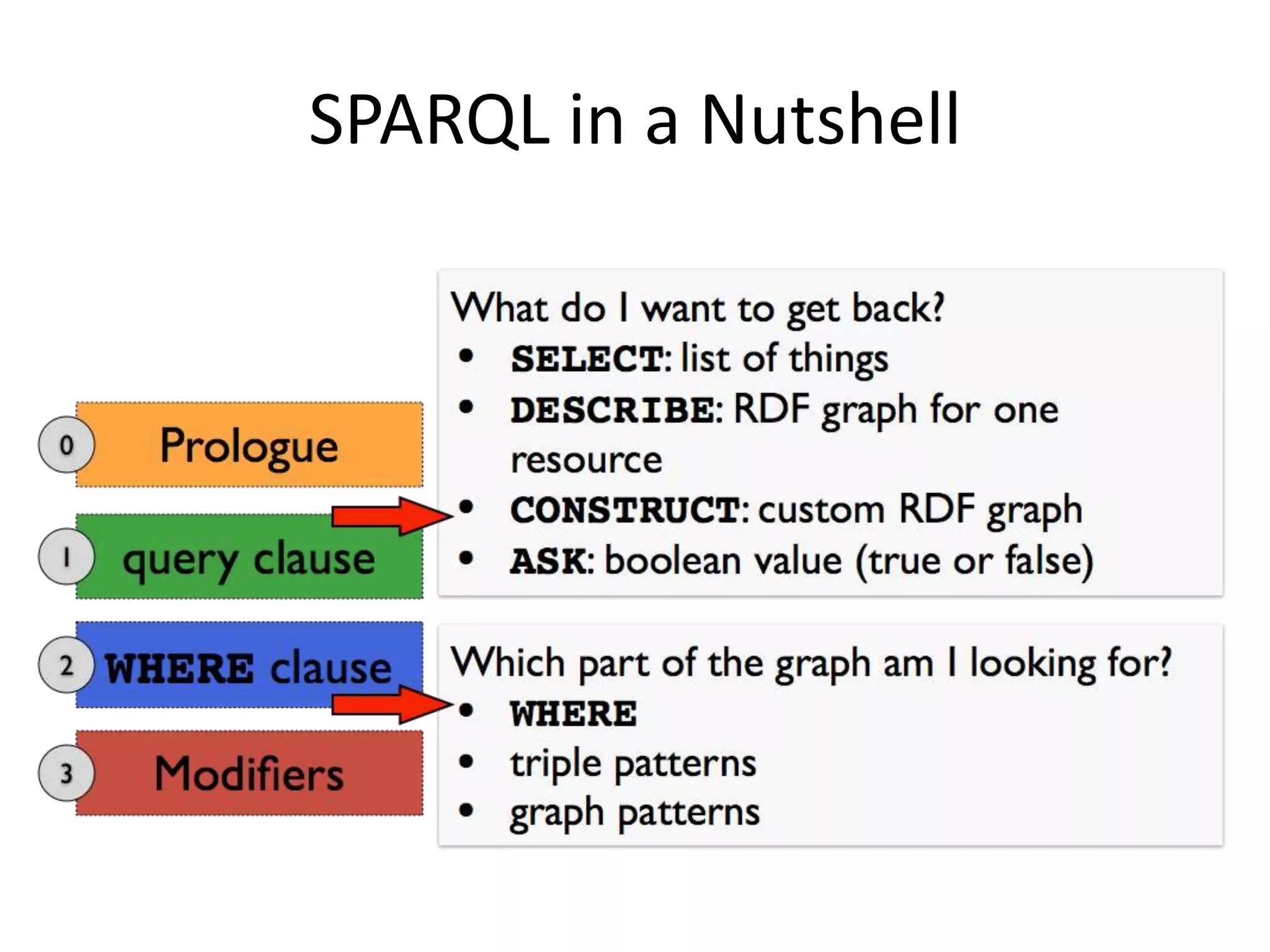
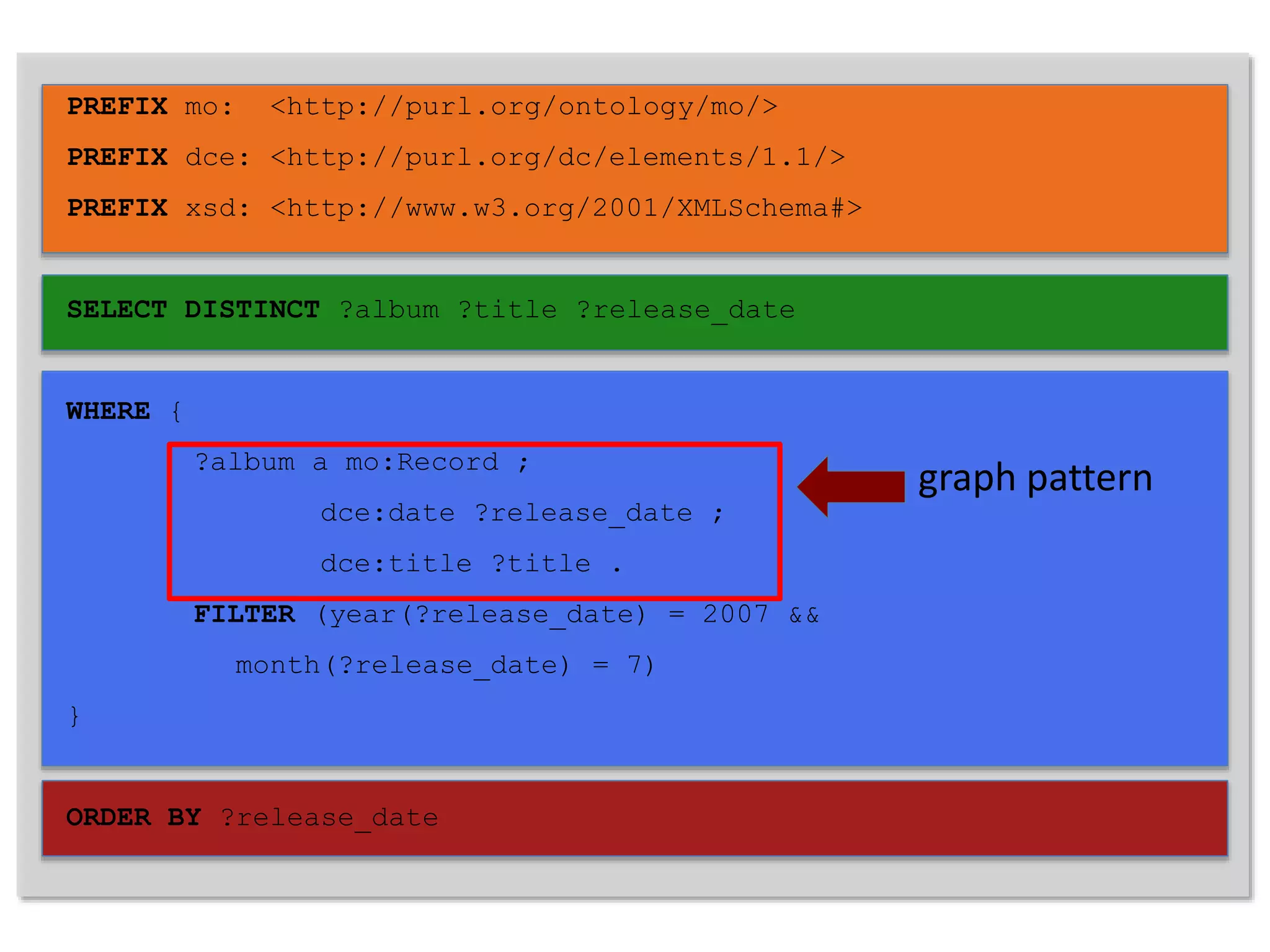
This document discusses three main ways to access remote Linked Data: 1) making HTTP requests to resource URIs, 2) using SPARQL queries, and 3) getting a local copy of a dataset. It then provides more details on each method, including making HTTP requests to retrieve RDF data, examples of SPARQL queries to endpoints, and getting local copies through SPARQL constructs, crawling, or direct downloads. The document also lists several RDF libraries and provides a hands-on example of a SPARQL query.