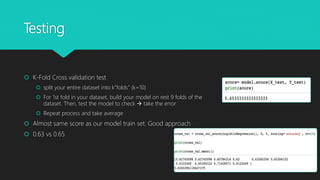
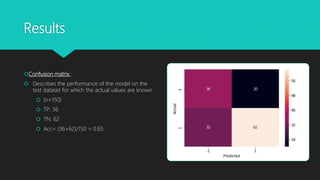
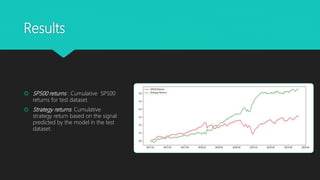
This document discusses using machine learning techniques to predict stock price movements. Specifically, it uses logistic regression on historical SP500 data to predict if the stock price will be higher or lower in the following week. Variables like open, close, volume and technical indicators are used as predictors. The model is trained on 70% of the data and tested on 30%. It achieves an accuracy of 65% on the test set, indicating the model performs well at predicting price movements. A backtest shows the strategy following the model's signals outperforms simply buying and holding the SP500. The summary concludes the approach is simple yet effective for this prediction problem.



![Model:
Logistic regression
Ability to make predictions on the dependent variable
Train dataset
Good estimator for a certain event occurring (M. Likelihood)
Predicting class probs (P) Dependent variable outcomes forced to
[-1 or 1]
Model score and coefficients
𝑝 =
ex p( 𝛽0 + 𝑖=1
𝑝
𝛽𝑖 𝑋𝑖
1 + ex p( 𝛽0 + 𝑖=1
𝑝
𝛽𝑖 𝑋𝑖](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machine-learningv3-191215135255/85/Machine-learning-Stock-Price-Prediction-5-320.jpg)
![Testing
Predict p and force to [-1 or 1]
Actual vs prediction ACCURACY
Analysis of Classification report:
Precision: number of true positives over
the number of true positives plus the
number of false positives.
Recall: number of true positives over the
number of true positives plus the number
of false negatives.
F1: weighted average of the precision and
recall F1 = 2 * (precision * recall) /
(precision + recall)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machine-learningv3-191215135255/85/Machine-learning-Stock-Price-Prediction-6-320.jpg)