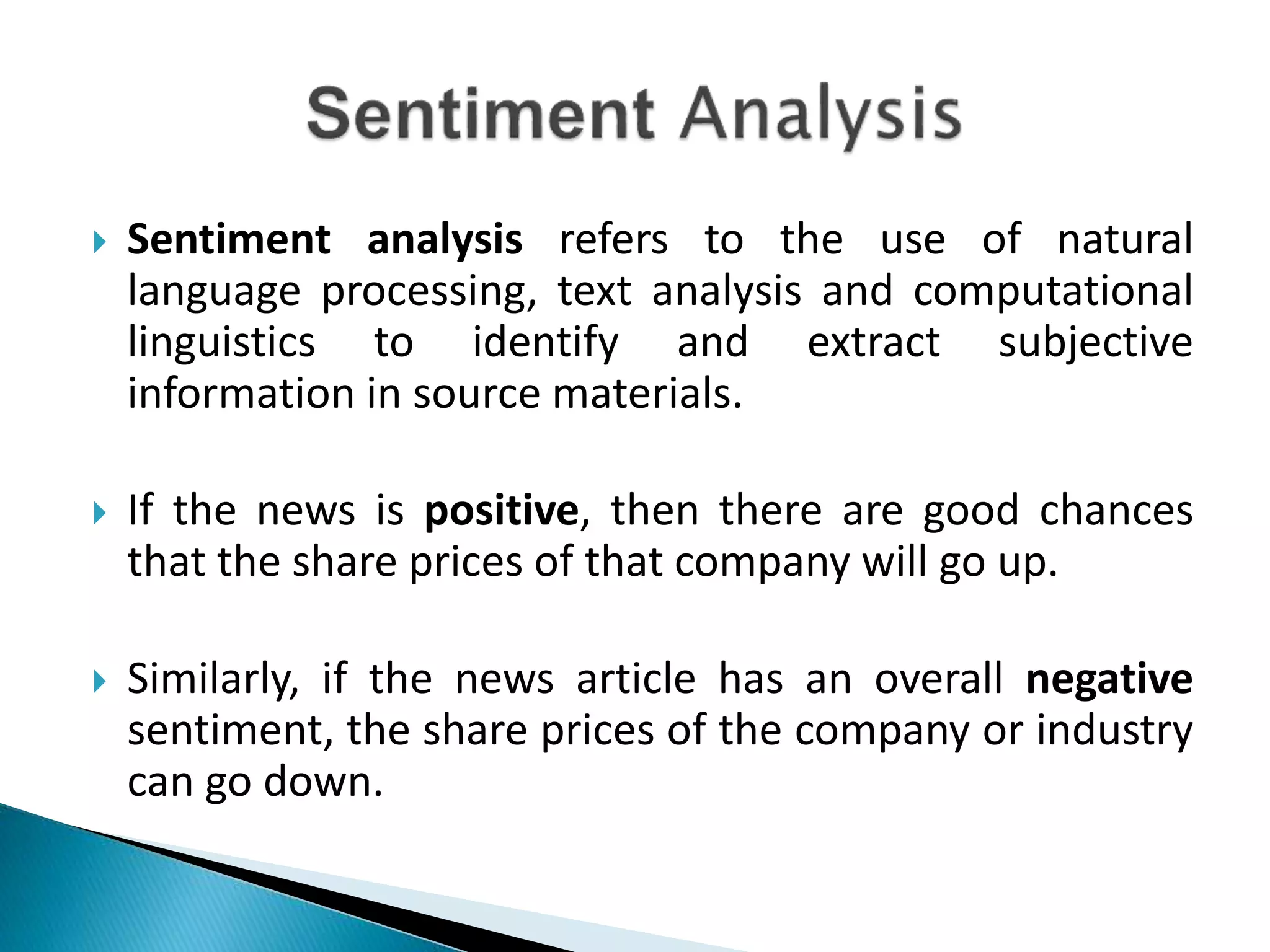
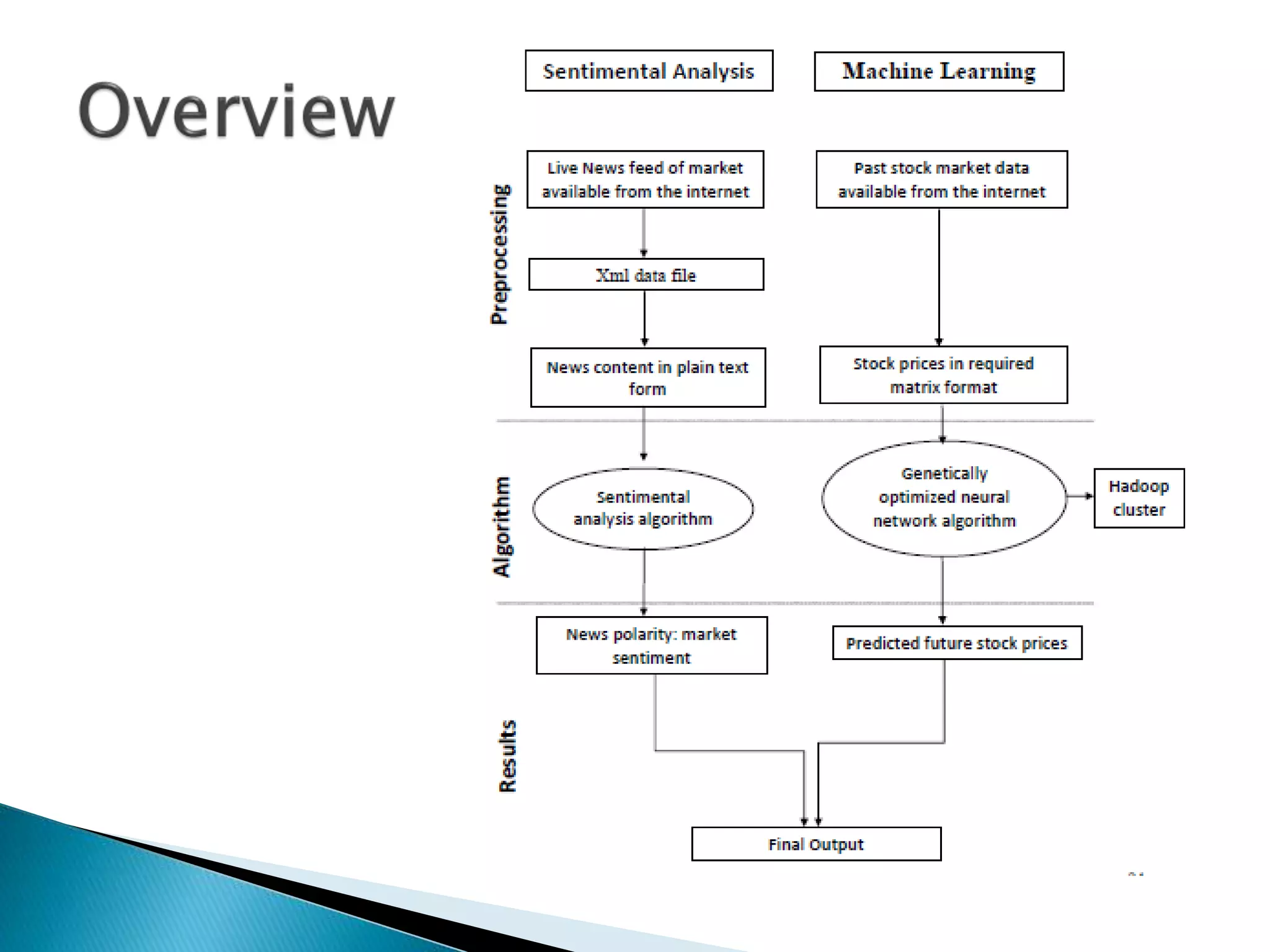
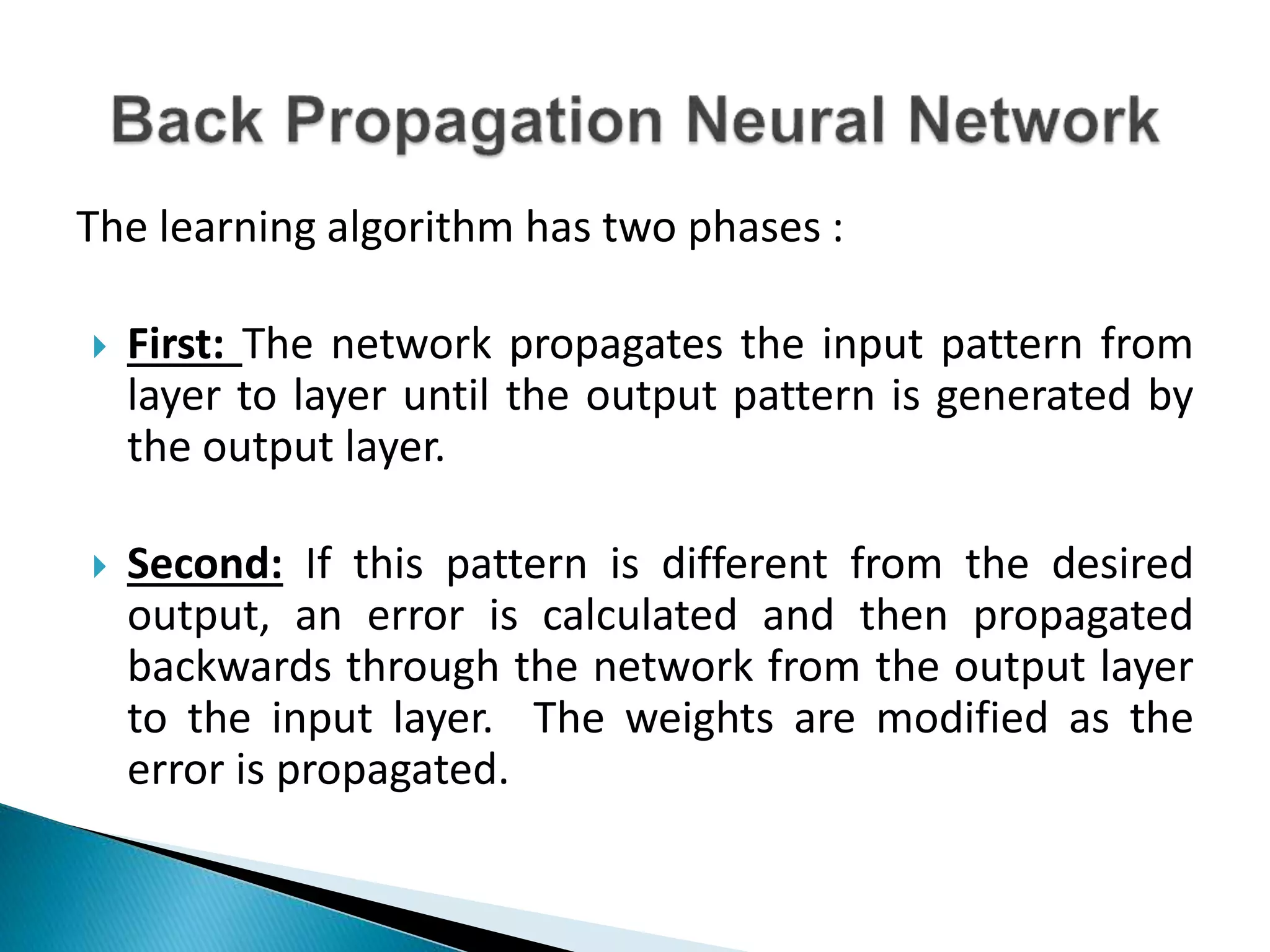
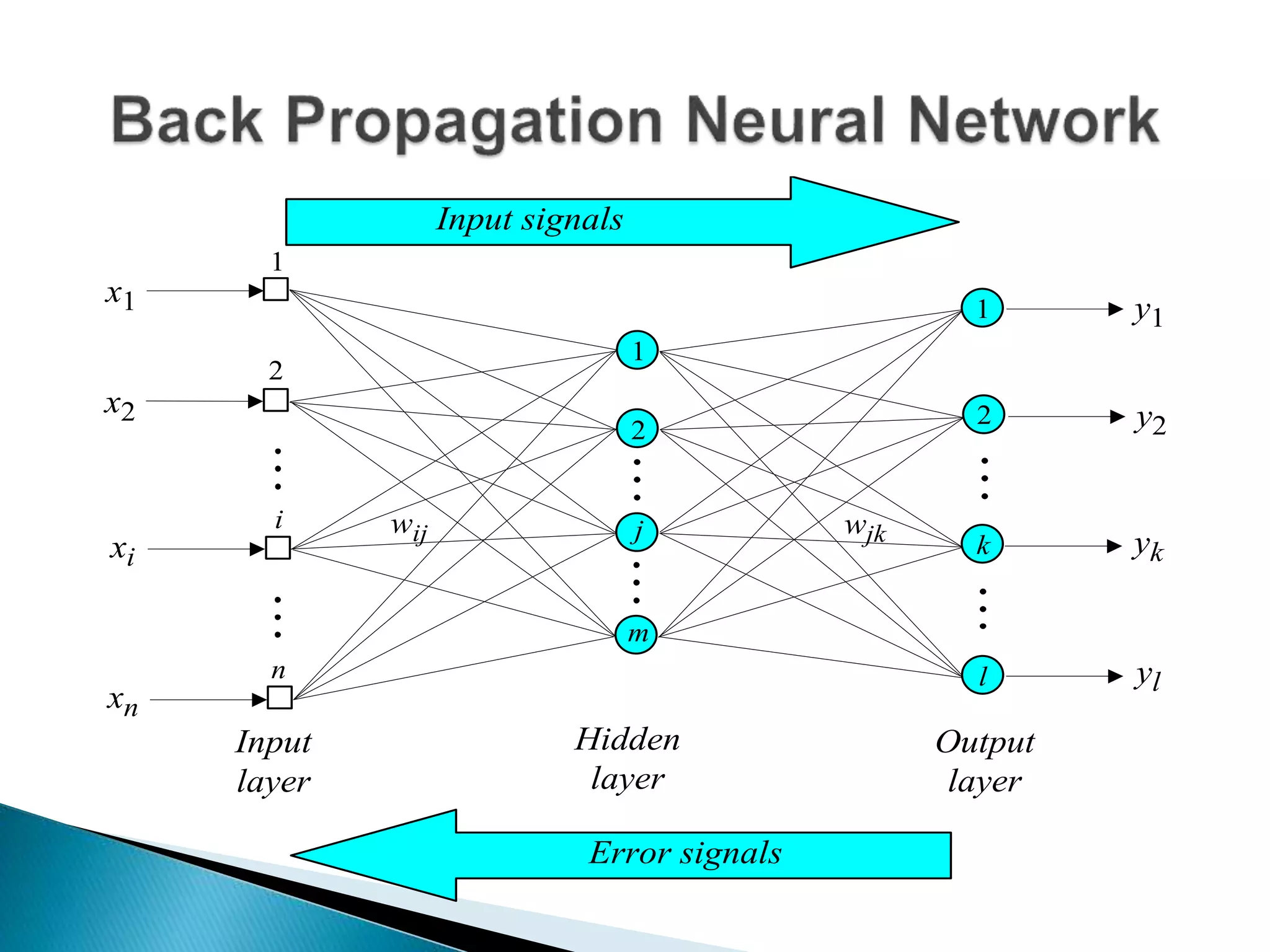
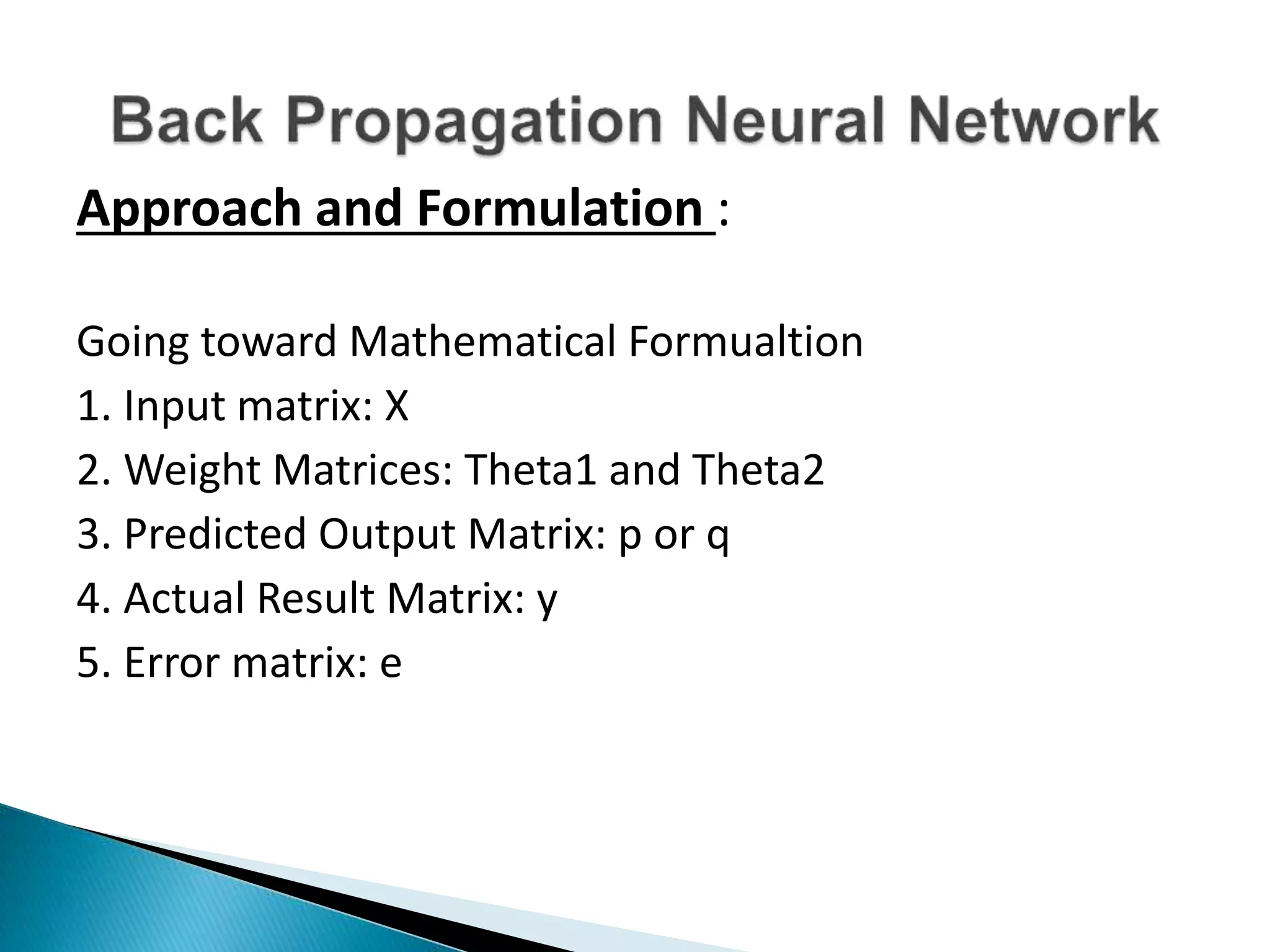
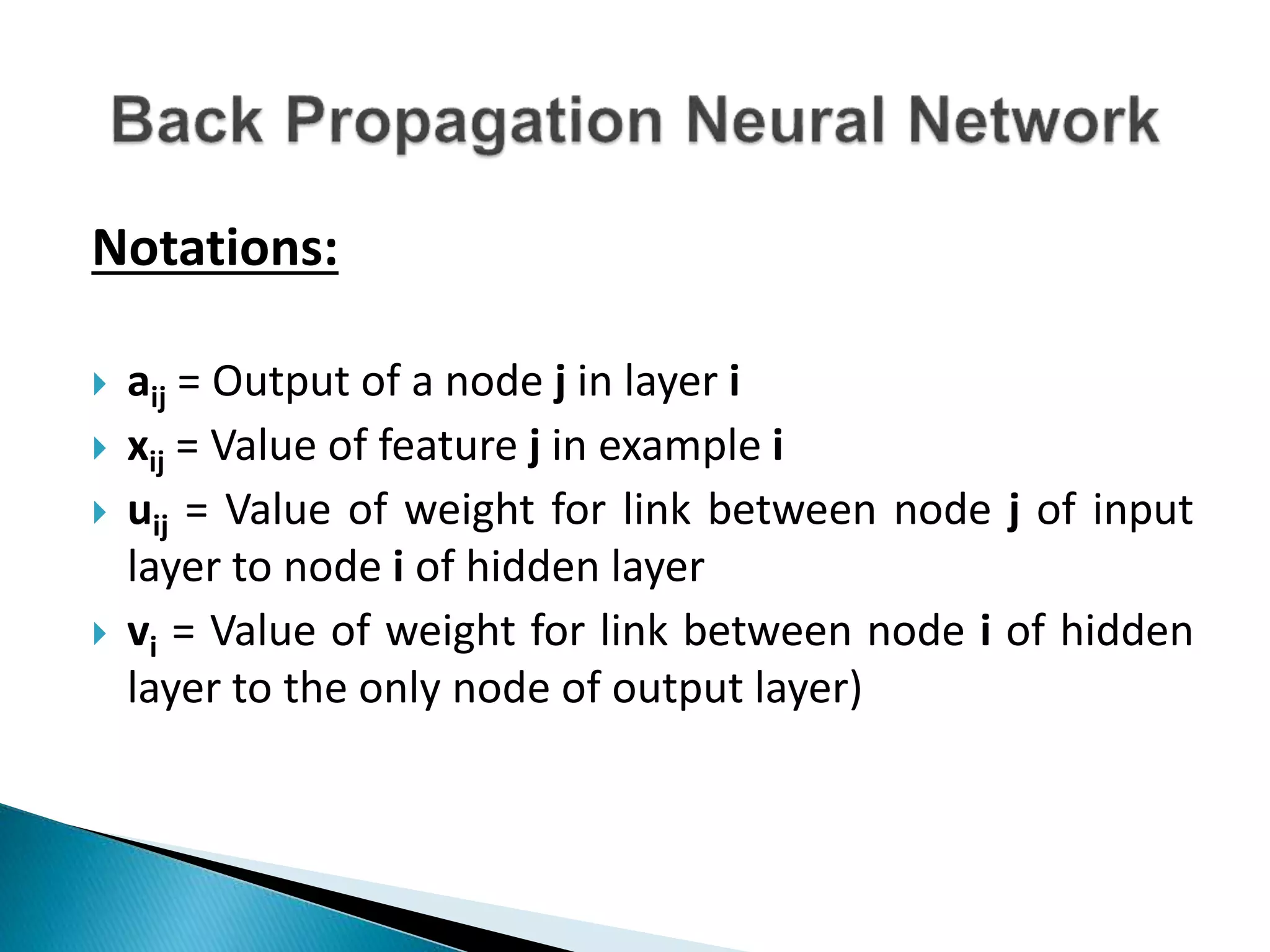
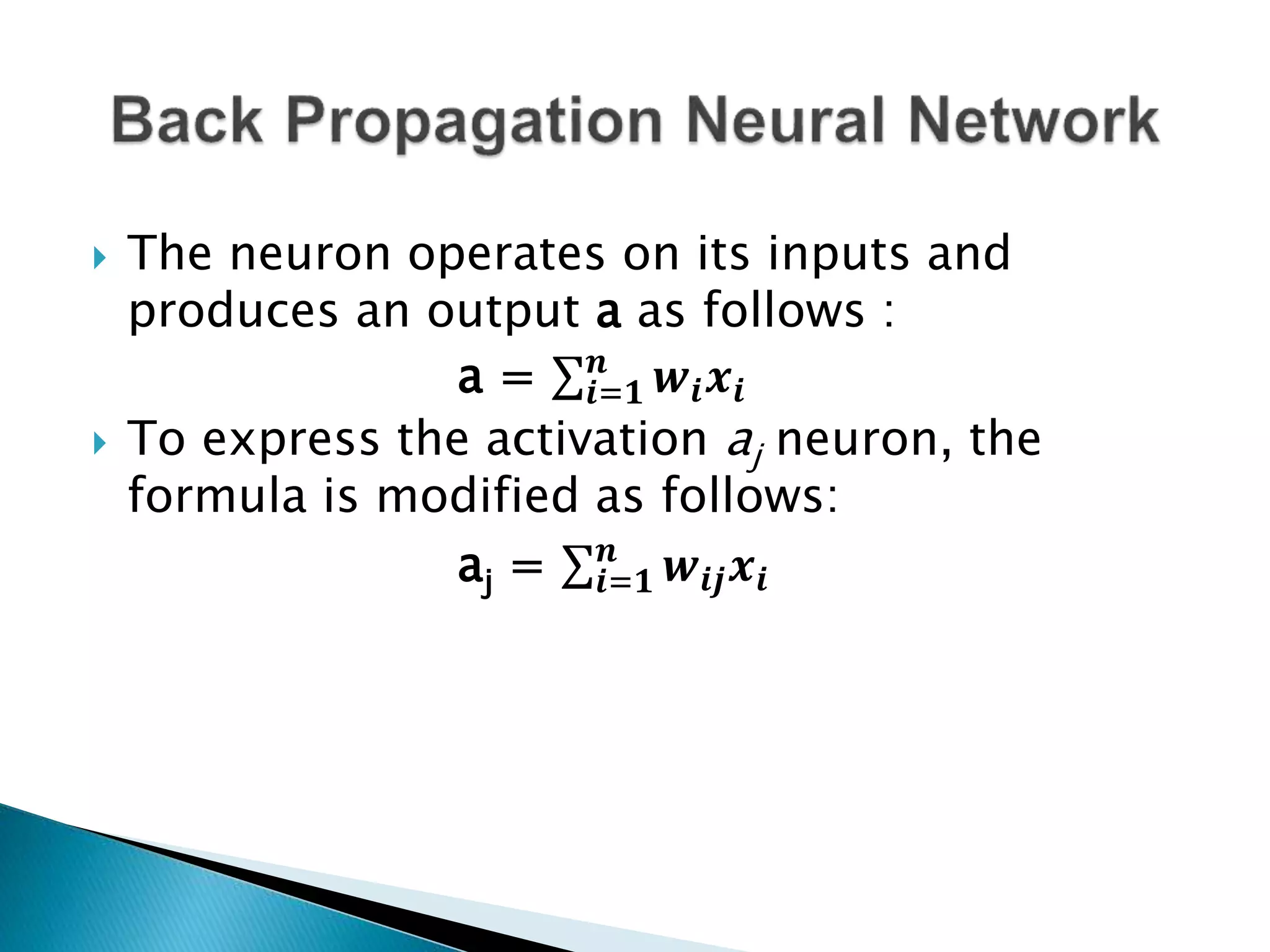
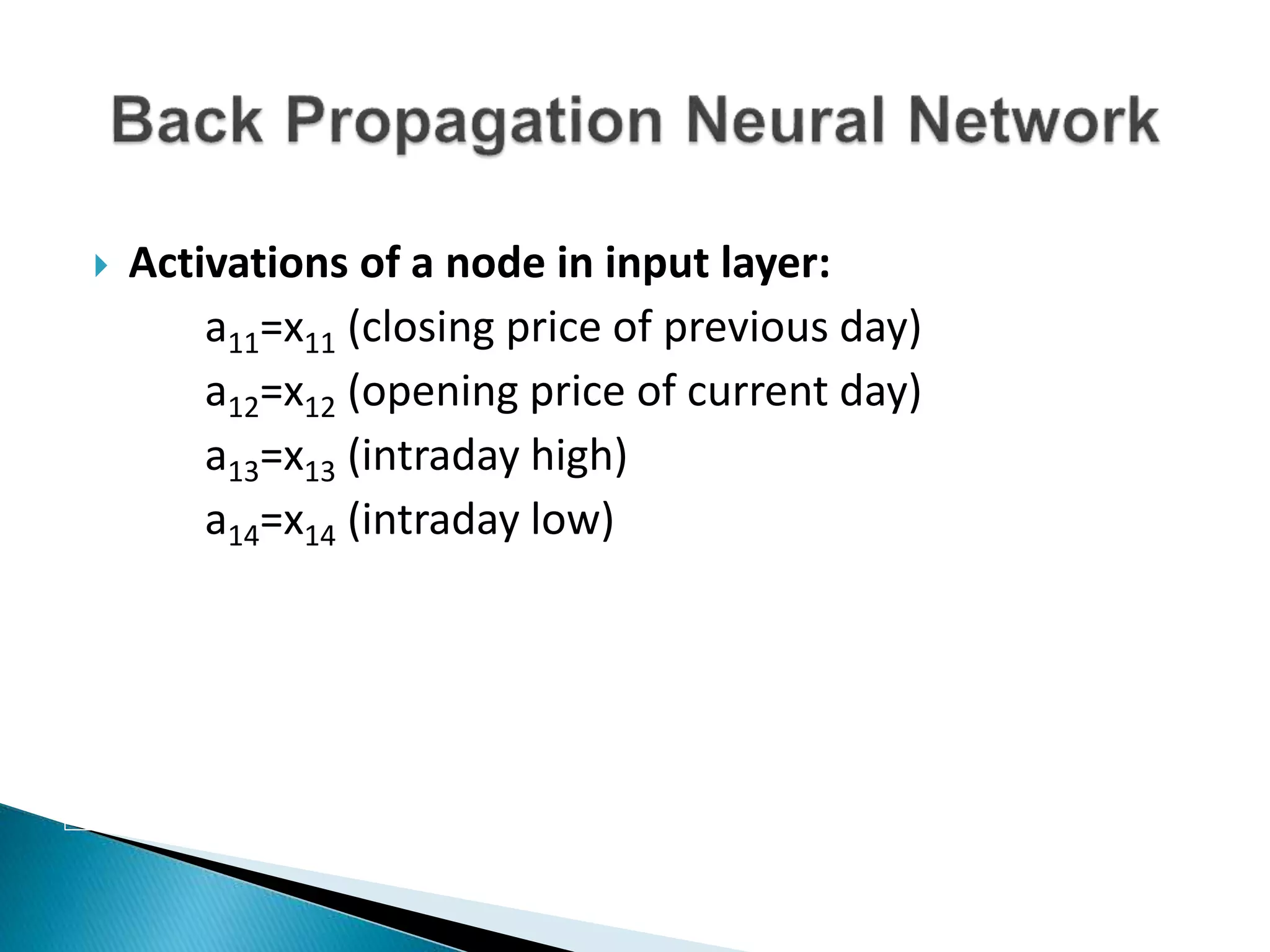
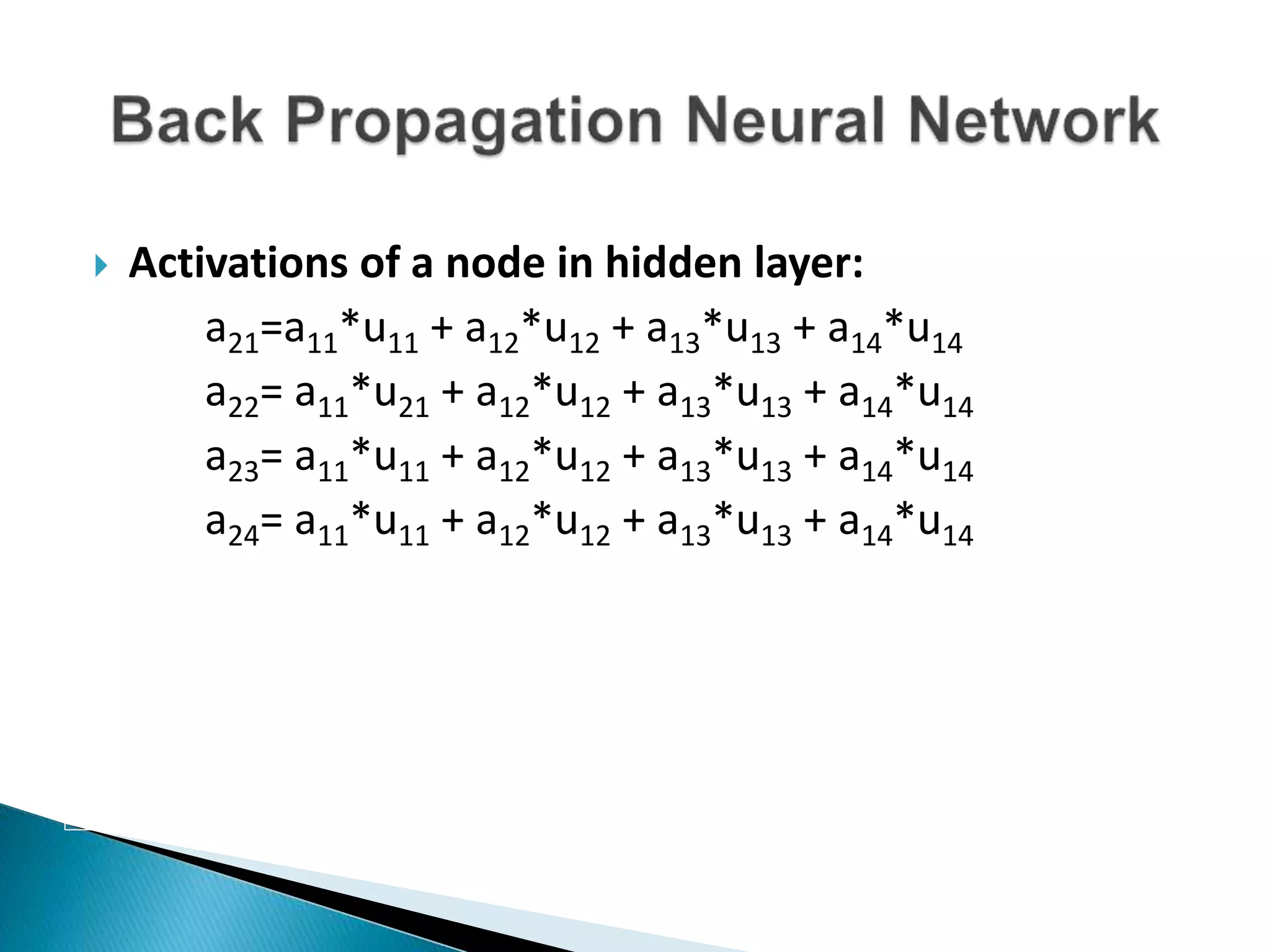
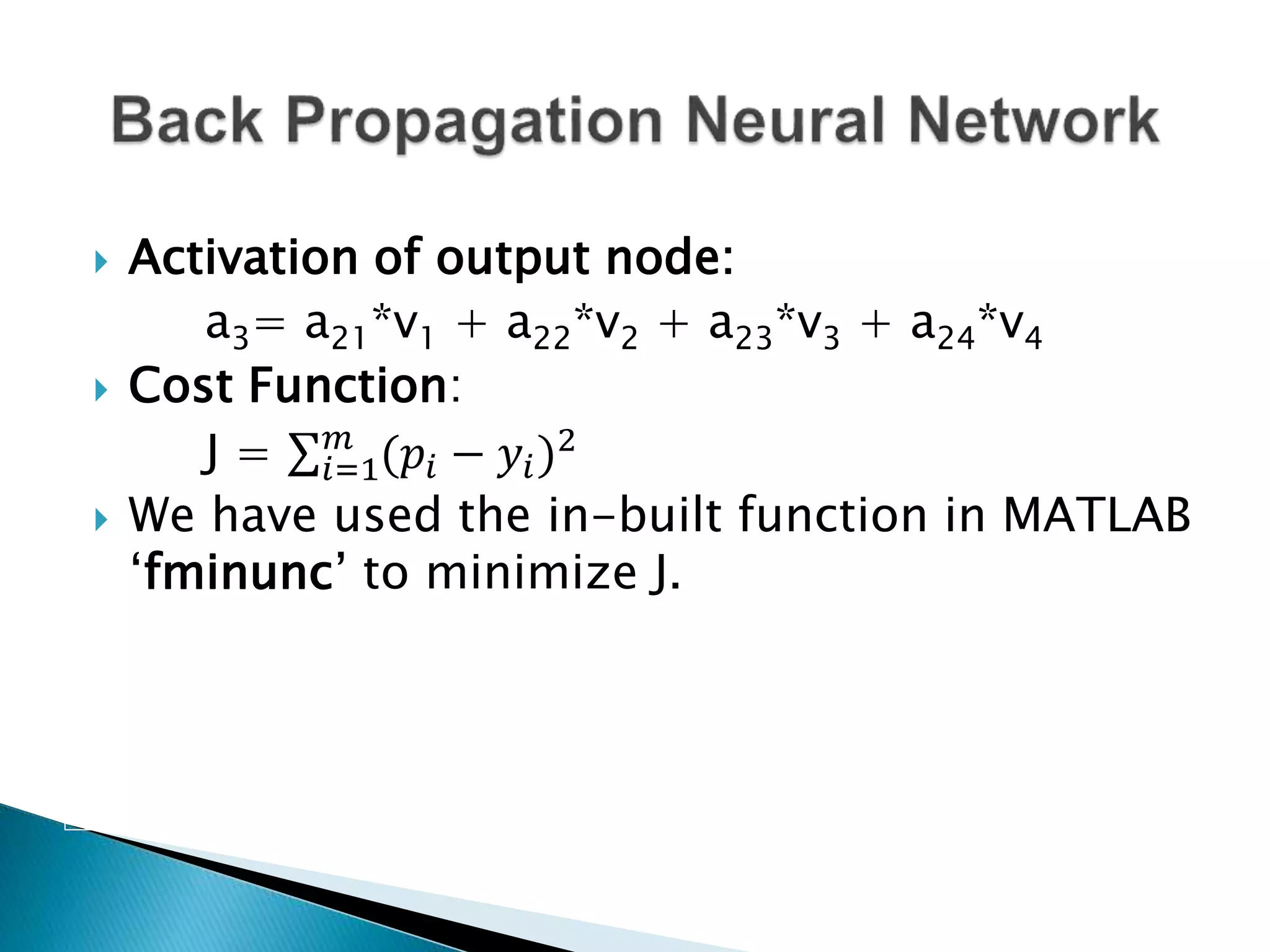
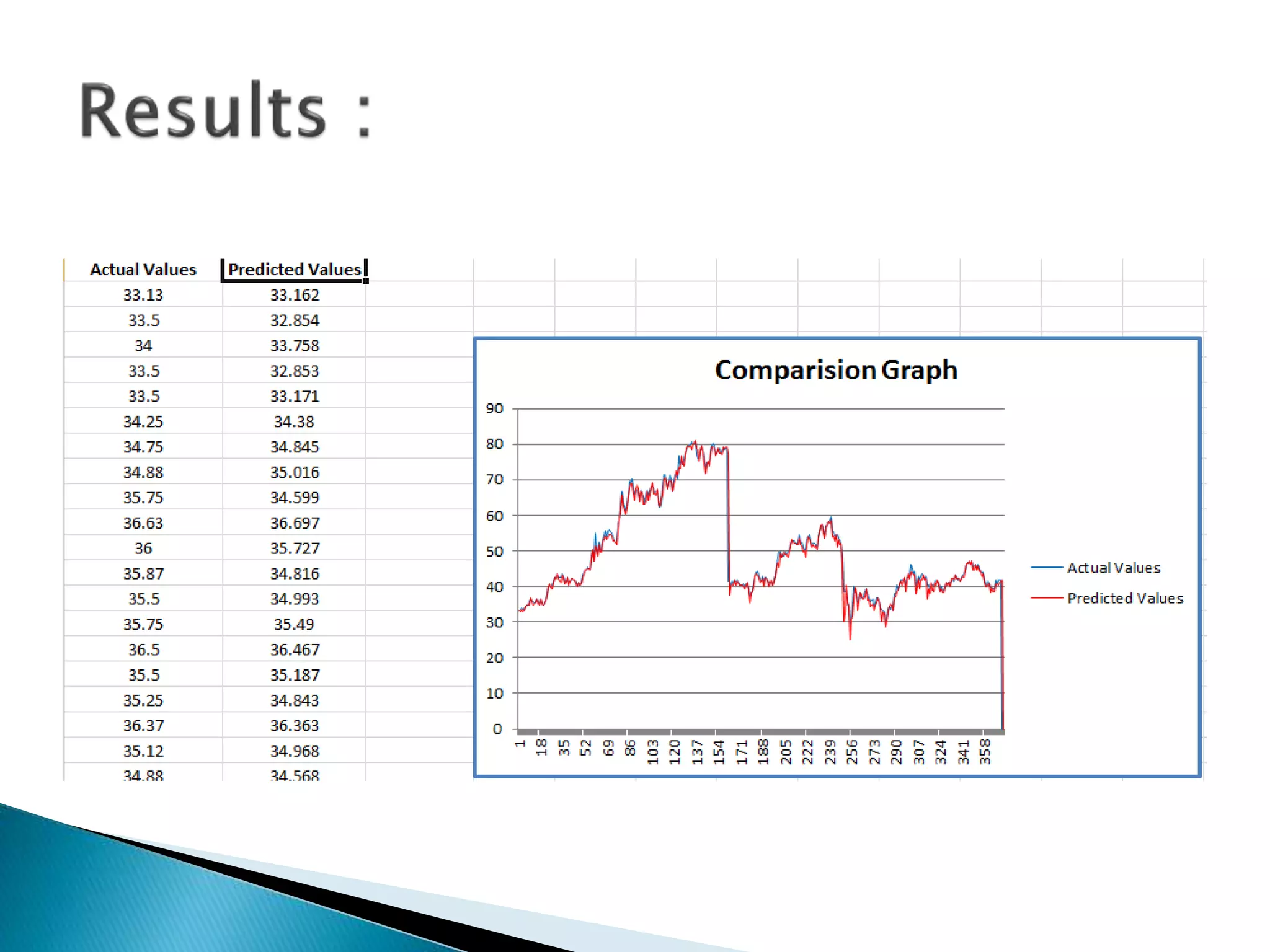
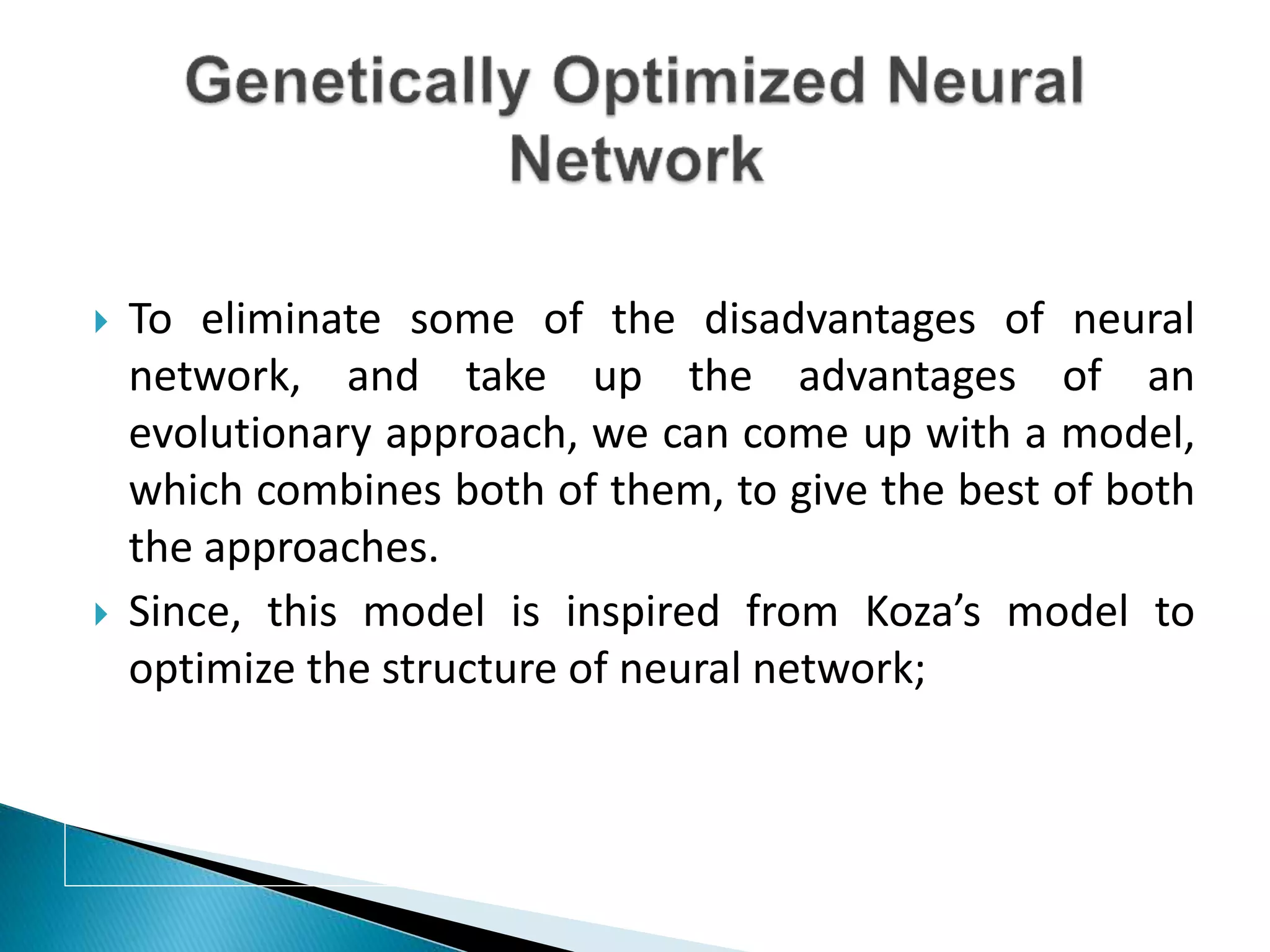
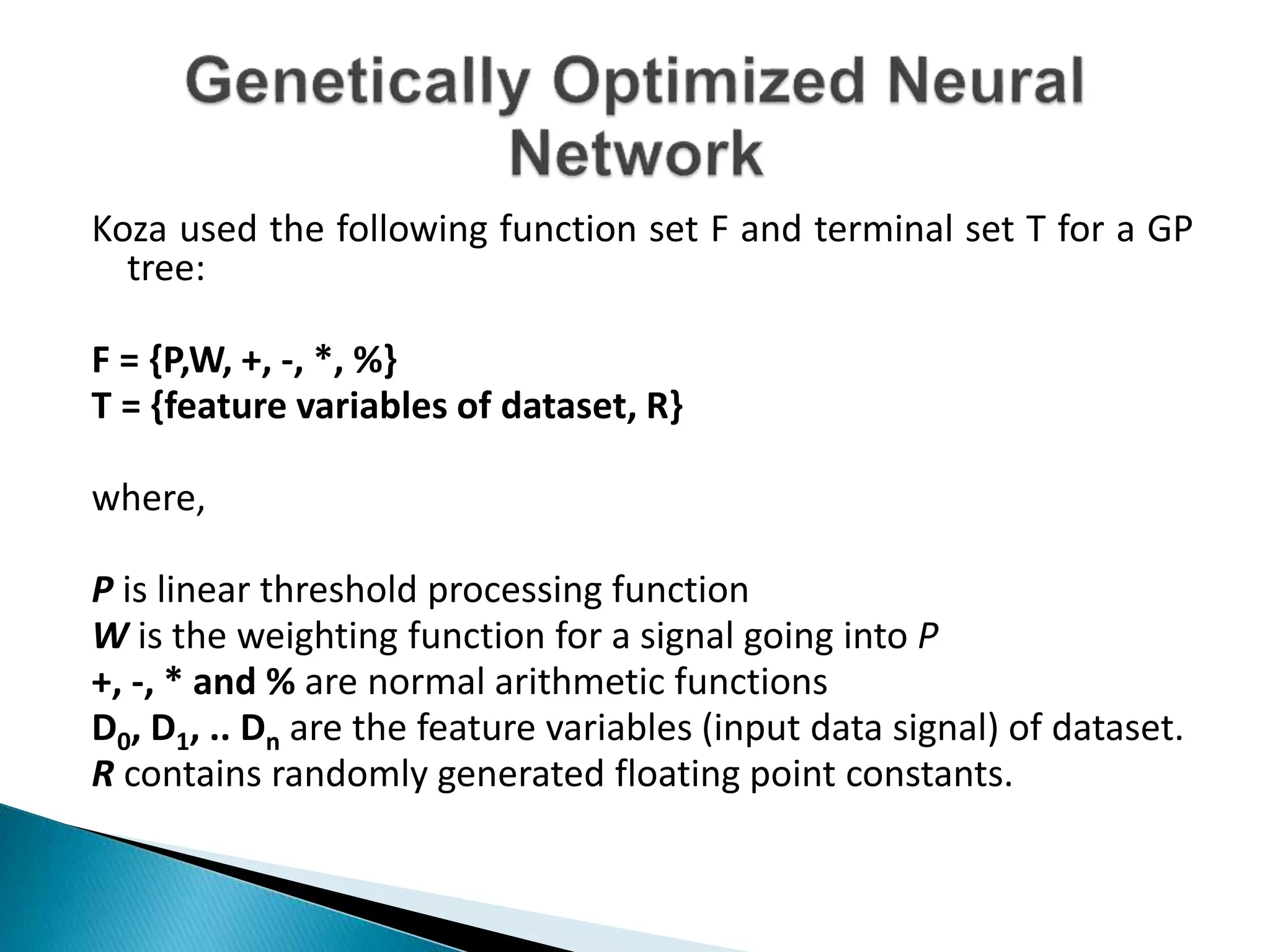
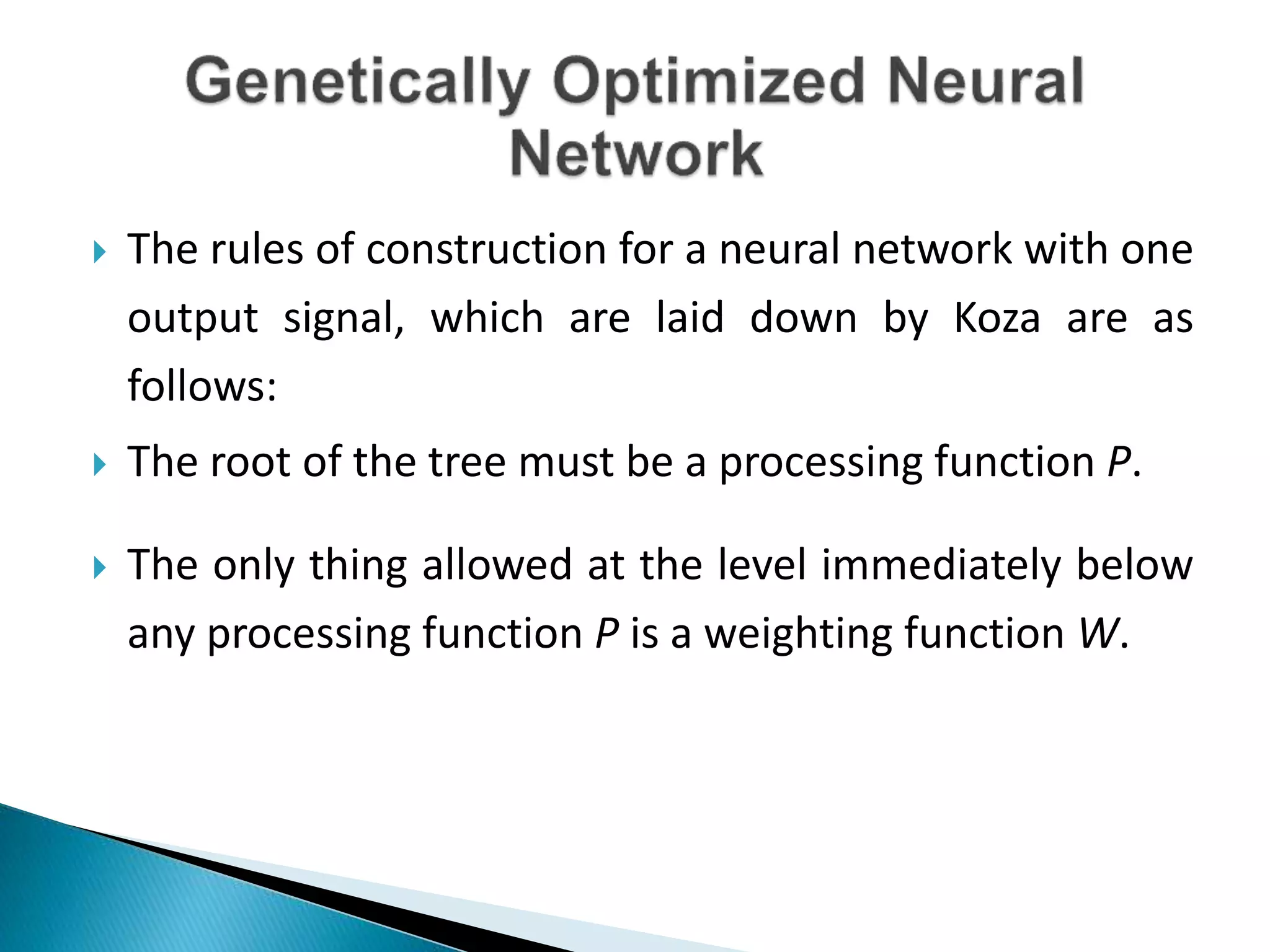
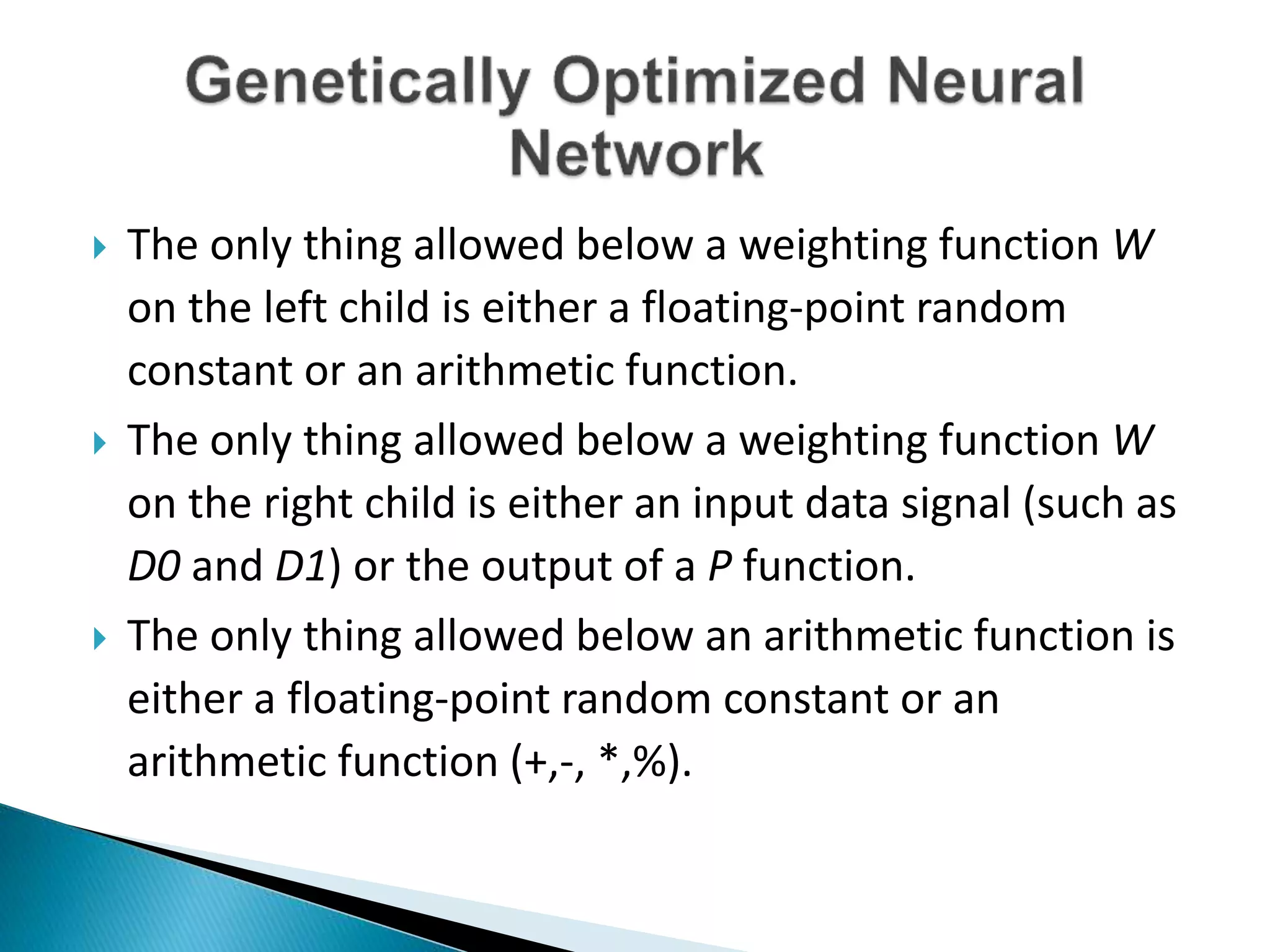
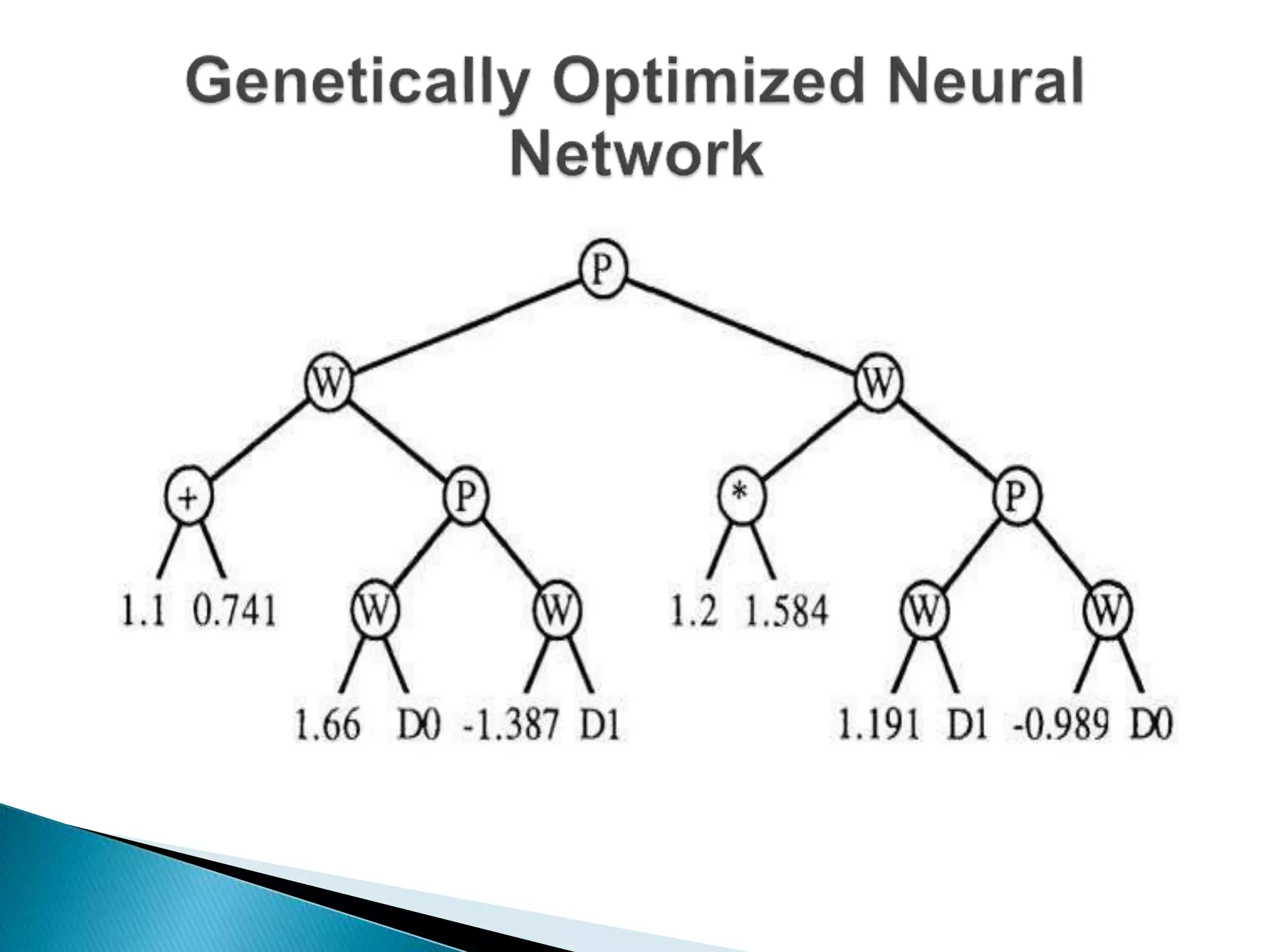
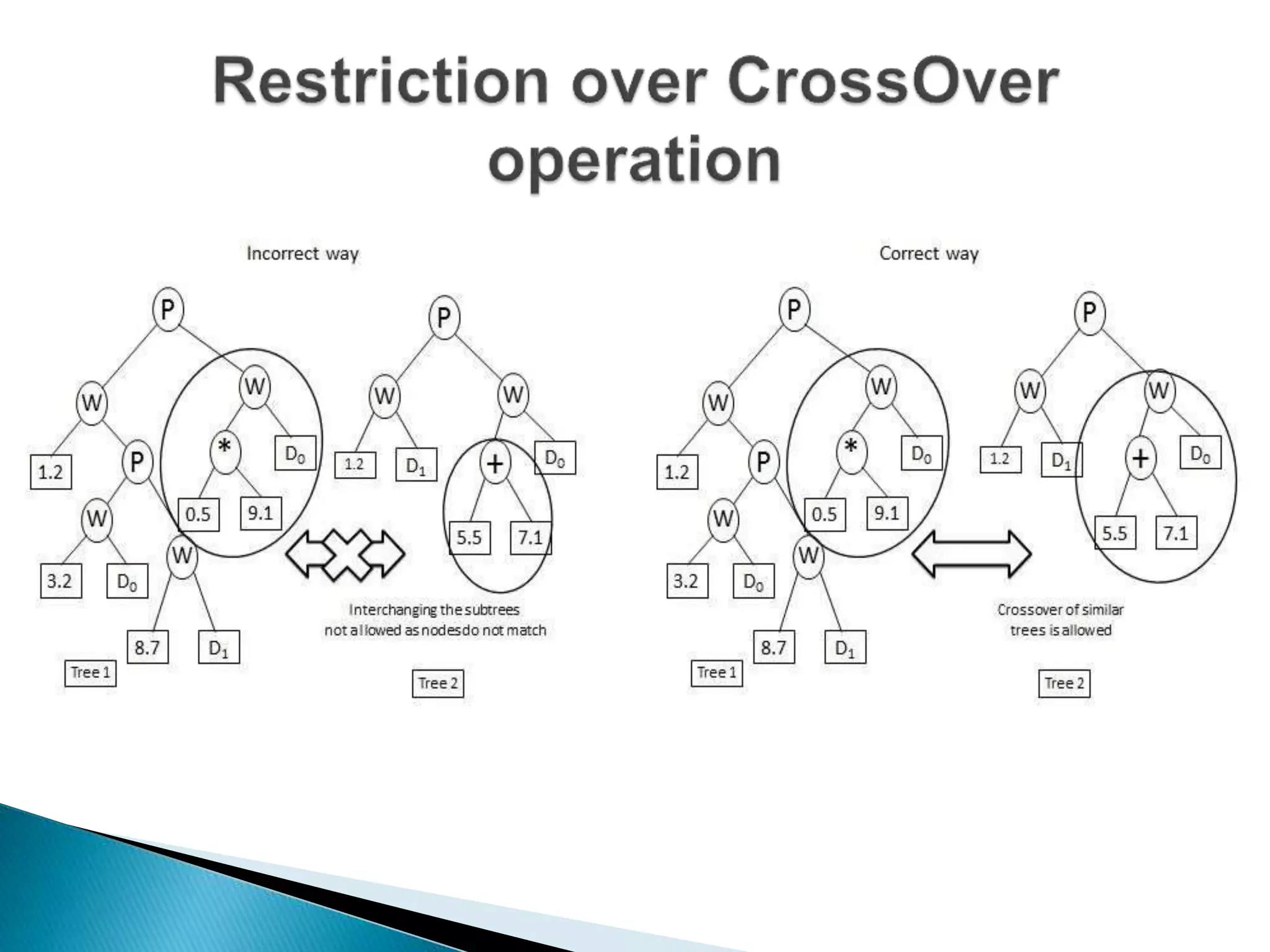
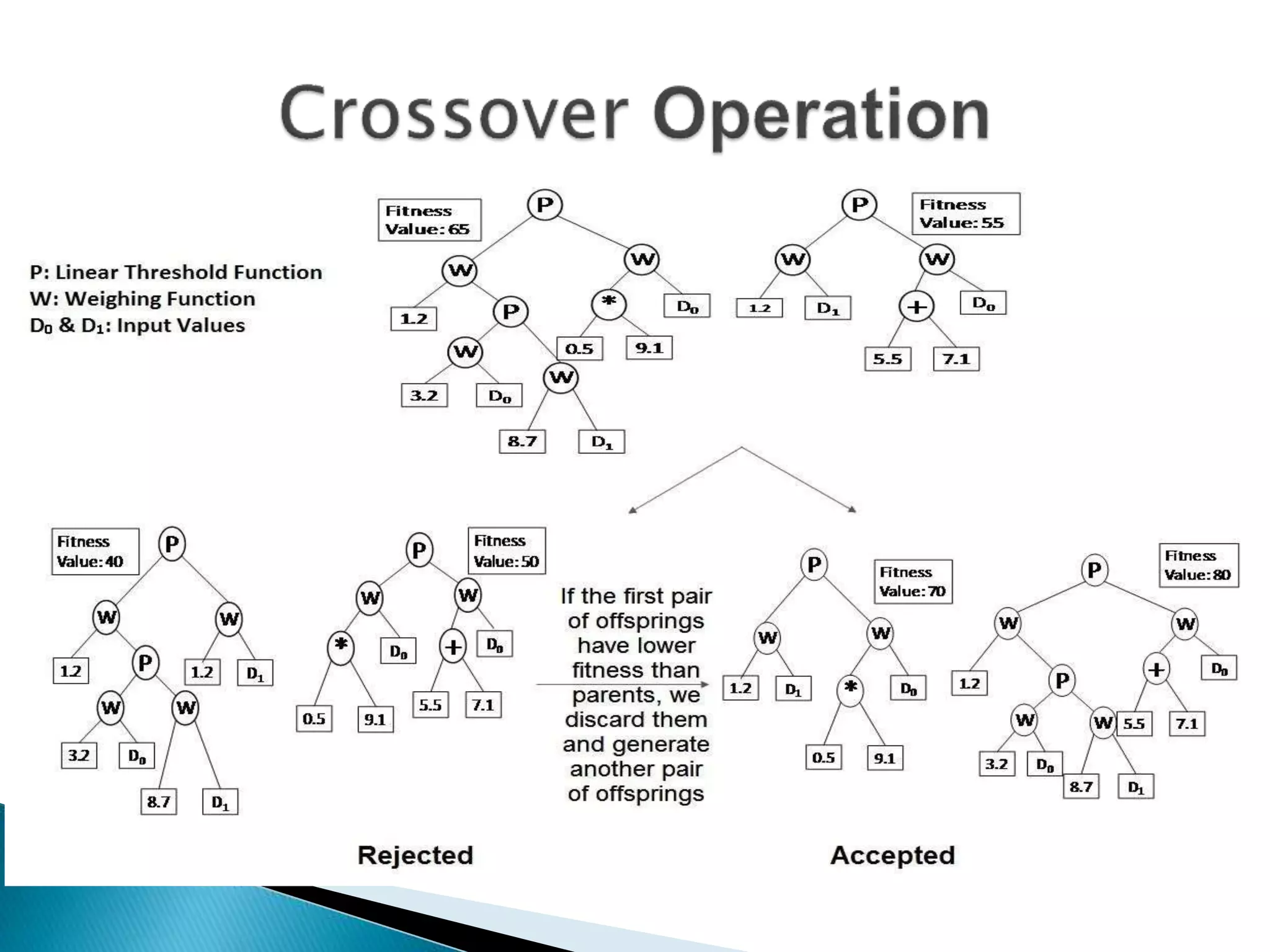
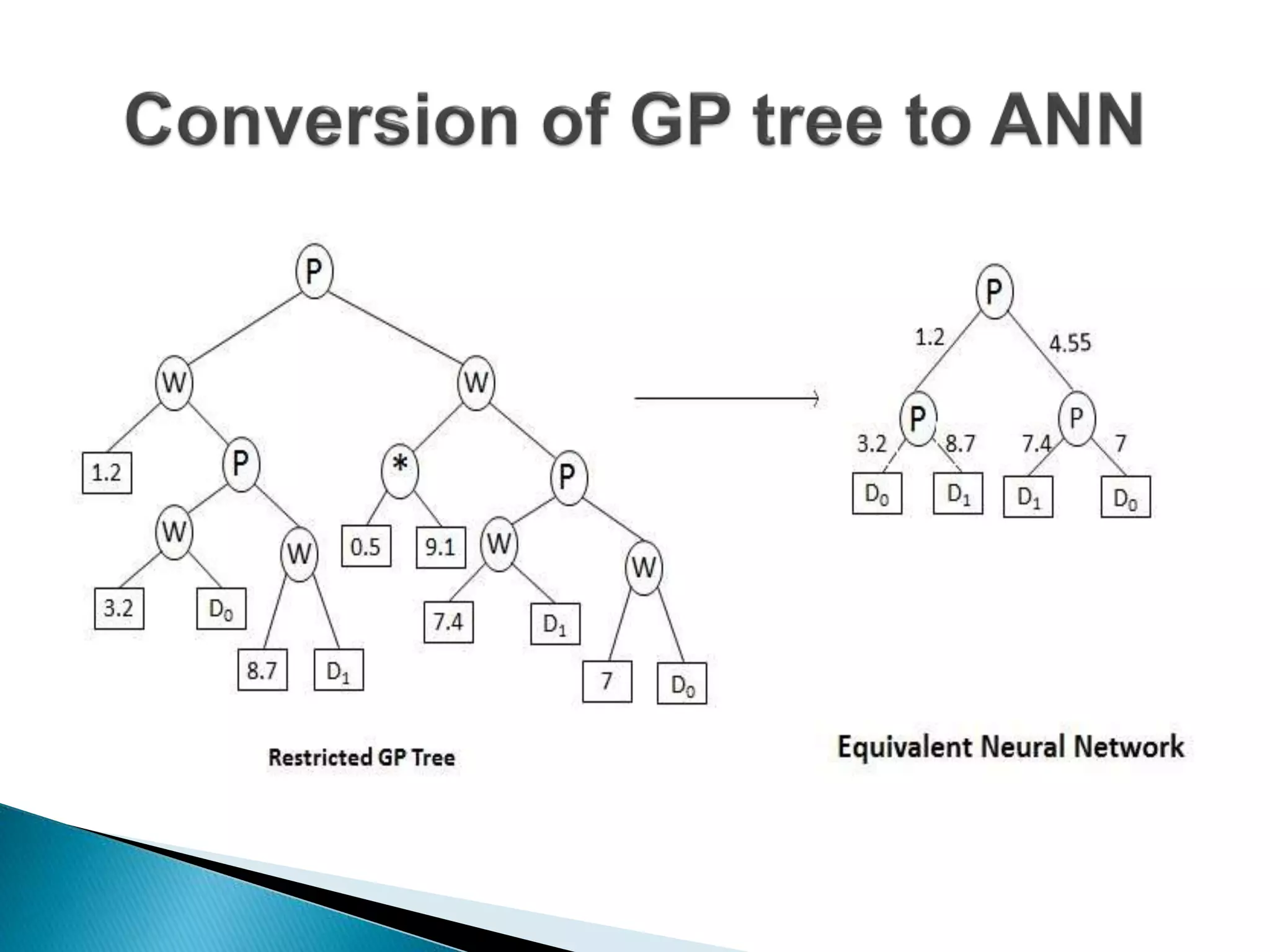
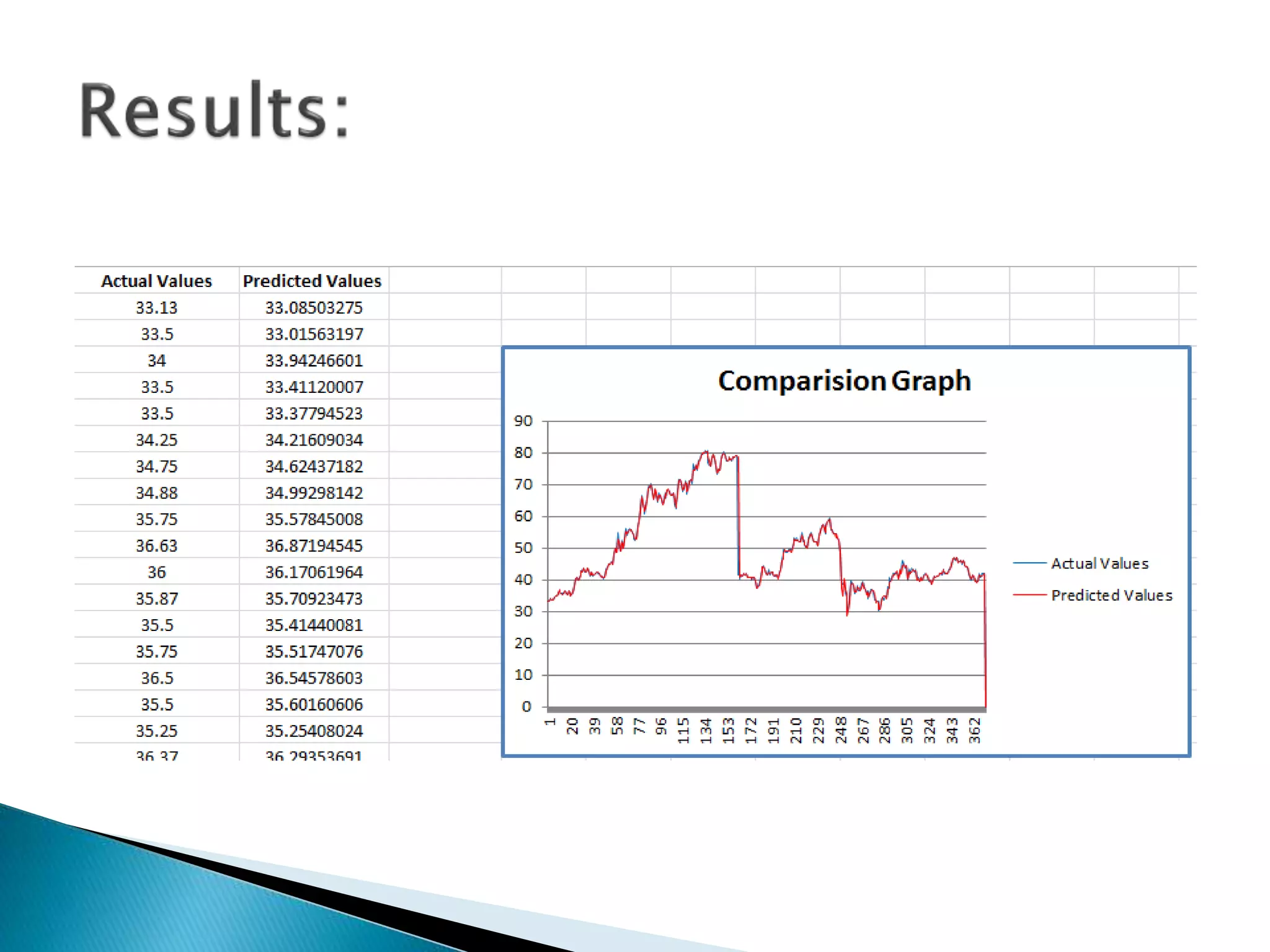
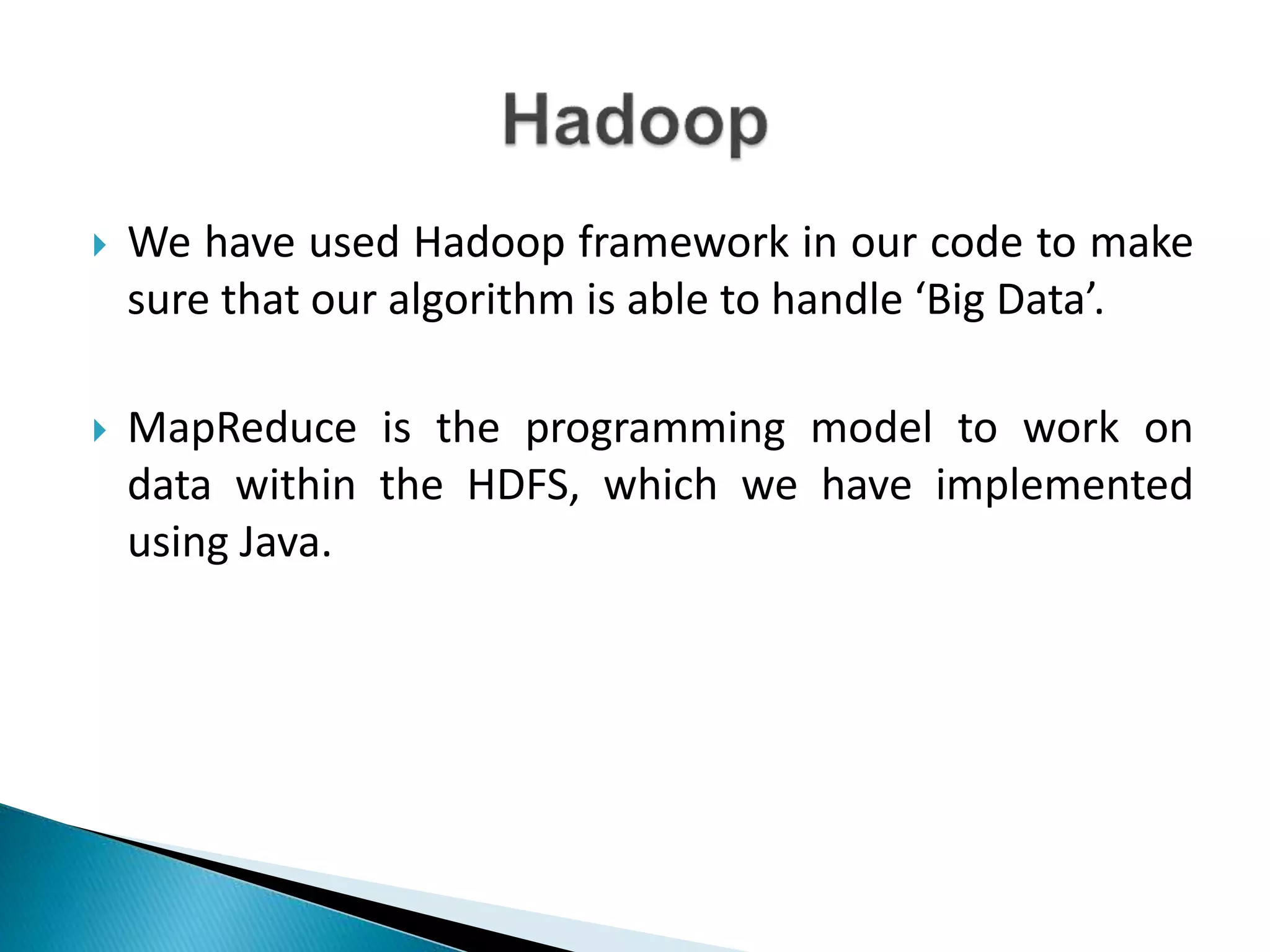
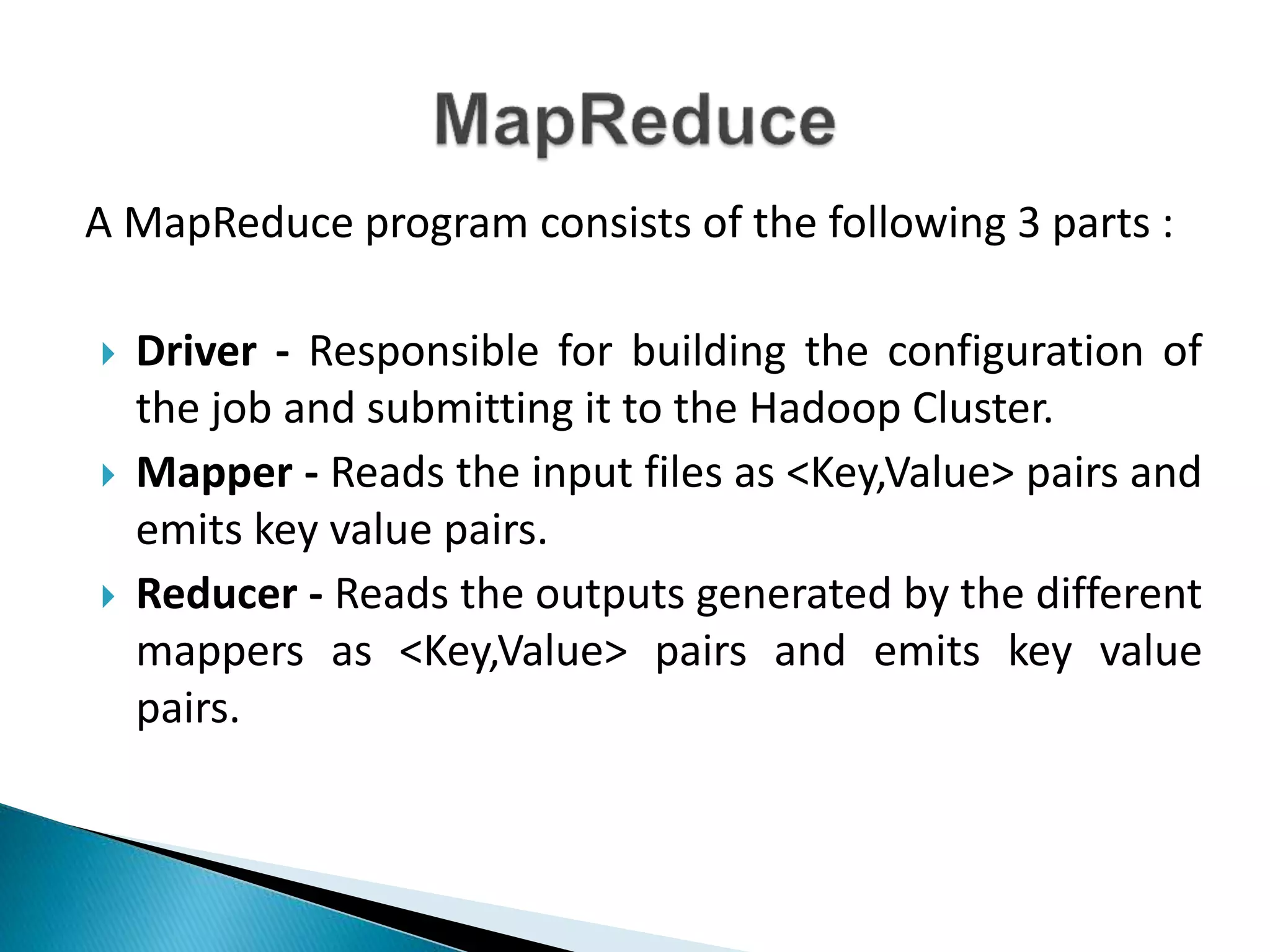
The document discusses the application of artificial intelligence and soft computing techniques in stock market prediction, using back propagation neural networks and genetically optimized neural networks. It highlights the importance of Hadoop for managing big data and the role of sentiment analysis in predicting stock prices based on news sentiment. The methodology includes systematized input/output processes, mathematical formulations, and the use of MapReduce in Hadoop, emphasizing the correlation between news sentiment and stock market behavior.








![ Uploading the jar file of our code application to the
master instance,
Uploading the input f iles (past stock market data) on
Google cloud storage bucket associate with the project
Running the jar file through driver class of
MapReduce by passing the required arguments
[input and output paths]
Saved the output files , and note down algorithm-
execution information, like time taken.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anintelligentscalablestockmarketpredictionsystem1-150510122038-lva1-app6892/75/An-intelligent-scalable-stock-market-prediction-system-32-2048.jpg)