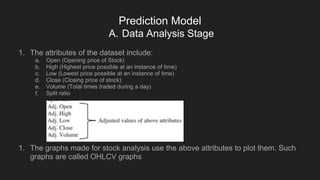
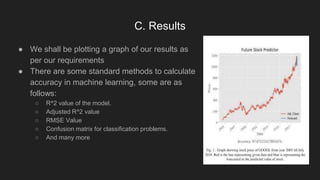
This document summarizes a paper on using machine learning algorithms to predict stock prices. It discusses using open source libraries to build prediction models from historical stock data, including attributes like open, high, low, close prices and volume. Linear regression is used to identify relationships between attributes and predict future prices. The model is trained and tested on preprocessed data, and accuracy is evaluated using metrics like R^2 and RMSE. Common mistakes like data leakage and overfitting are also discussed.